In 2026, most businesses have already adopted AI. The real question is no longer whether to use it, but why their AI still feels limited.
Chatbots can answer questions. Automations can trigger workflows. Dashboards can surface data. Yet when it comes to real decision-making, most AI systems still fall short. Enterprises now expect AI to think through problems, take informed actions, and adjust decisions dynamically across real business workflows.
This is where ReAct agents are changing the game.
ReAct agents introduce a new paradigm in AI systems, one where reasoning and action work together in a continuous loop. Instead of following static instructions, these agents analyze a problem, take actions using tools or APIs, observe outcomes, and refine their decisions in real time. The result is AI that behaves less like a scripted assistant and more like a human operator.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
-
What a ReAct agent is
-
How ReAct agents work internally using reasoning and action loops
-
Where enterprises are already using ReAct agents today
-
How can businesses design, build, and deploy ReAct agents effectively?
What is a ReAct Agent?
A ReAct agent is an AI agent that combines reasoning and action in a continuous loop. Instead of generating a single response, the agent:
-
Thinks about the problem
-
Takes an action using tools or systems
-
Observes the result
-
Refines its next step
This process continues until the task is completed. From a business perspective, the key difference is this:
A ReAct agent doesn’t just answer questions. It works through problems.
Unlike traditional LLM-based systems that stop after generating text, ReAct agents interact with databases, APIs, internal tools, and external systems while actively reasoning about what to do next.
How Do ReAct Agents Work? Step-by-Step Process in 2026
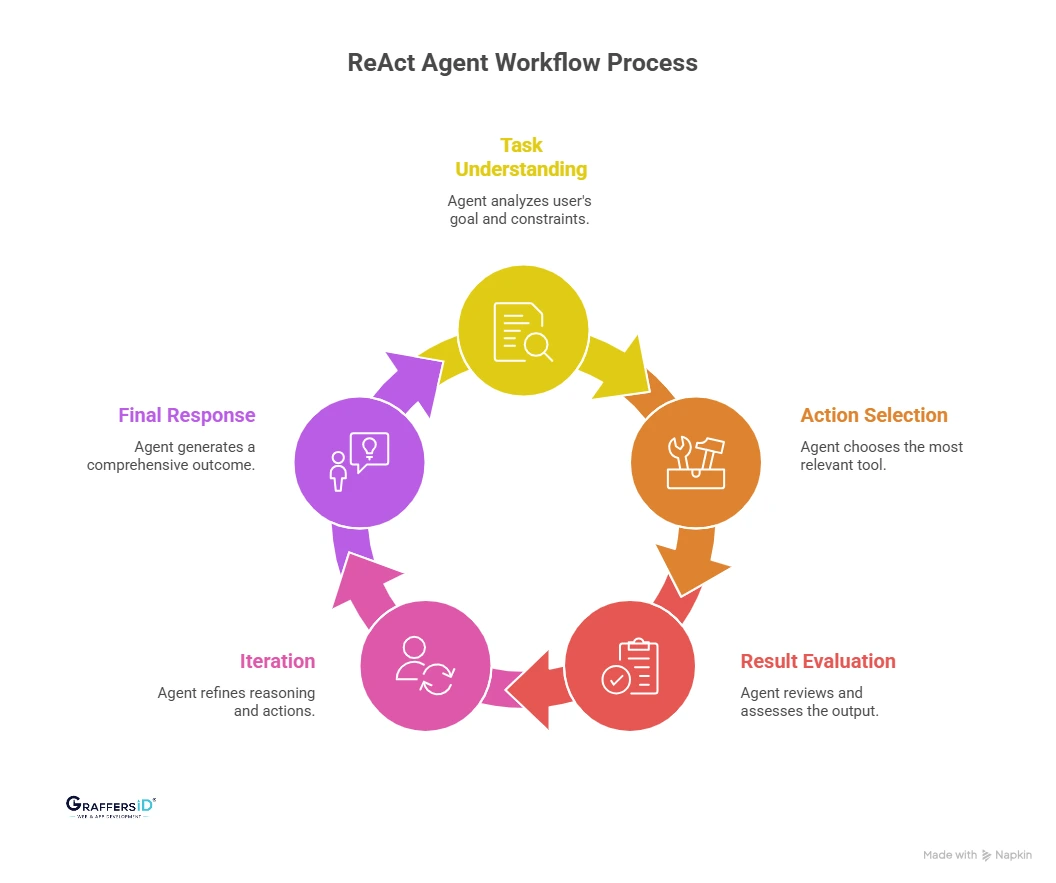
1. Task Understanding and Reasoning
The ReAct agent begins by analyzing the user’s goal, constraints, and required outcomes. It reasons through what information is needed and identifies gaps before taking any action.
Example: “I need real-time data plus historical context to answer this accurately.”
2. Selecting the Right Action or Tool
Based on its reasoning, the agent chooses the most relevant tool to use. This could be a web search, internal database, API, calculator, or enterprise system like a CRM or ERP.
The key difference is that the agent decides which tool to use, rather than being told explicitly.
3. Observing and Evaluating the Results
After executing the action, the agent reviews the output and evaluates whether it moves closer to the goal. It checks for accuracy, relevance, and completeness before proceeding further.
4. Iterating Through Reasoning and Action
If the result is incomplete or raises new questions, the agent reasons again and selects the next best action. This loop continues until the agent has enough validated information to proceed confidently.
5. Generating the Final Response or Outcome
Once the task is sufficiently resolved, the agent produces a final response or completes the workflow. The output is typically more accurate, contextual, and actionable than a single-pass LLM response.
Read More: AI Agent vs. Chatbot: Key Differences, Use Cases & Future of Intelligent CX (2026)
Why Does the ReAct Framework Matter for Enterprises?
ReAct agents solve several real-world AI limitations that businesses faced before 2025.
Key advantages include
-
Multi-step reasoning for complex decisions
-
Lower hallucination risk through validation
-
Dynamic workflows instead of rigid scripts
-
Tool-driven intelligence connected to live systems
For enterprises, this means AI that can actually execute business logic, not just describe it.
Key Components of a ReAct Agent Architecture in 2026
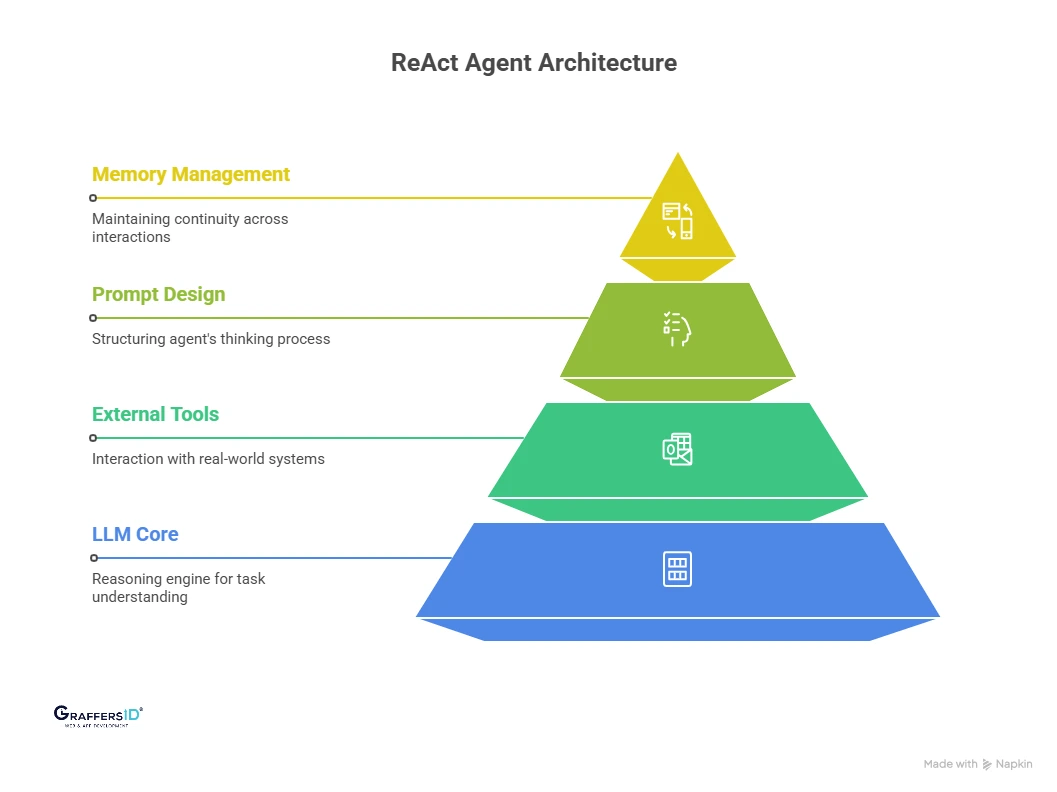
1. Large Language Model (LLM)
The large language model acts as the core reasoning engine of a ReAct agent. It is responsible for understanding the task, breaking it into steps, and deciding what action to take next. In 2026, enterprises commonly use advanced proprietary models like GPT-4–class systems, Gemini, and Claude, along with fine-tuned open-source LLMs for cost control, data privacy, and domain-specific intelligence.
2. External Tools and APIs
ReAct agents become truly useful when they can interact with real-world systems through tools and APIs. These integrations allow the agent to fetch live data, trigger workflows, and validate decisions. Typical tools include search engines, internal dashboards, payment systems, analytics platforms, and customer databases, enabling the agent to move beyond text generation into real business execution.
3. ReAct Prompt Design
ReAct prompts define how the agent reasons, acts, and learns from outcomes. Instead of simple instructions, these prompts structure the agent’s thinking into reasoning steps, action selection, and observation analysis. Well-designed ReAct prompts are critical for reducing errors, improving accuracy, and ensuring predictable behavior across complex workflows.
4. Memory and Context Management
Memory enables ReAct agents to maintain continuity across interactions and decisions. Enterprise-grade agents typically use short-term memory to track the current task and long-term memory to store user preferences, historical context, and past outcomes. This allows the agent to deliver more personalized, consistent, and context-aware responses over time.
Real-World Use Cases of ReAct Agents in Enterprise AI in 2026
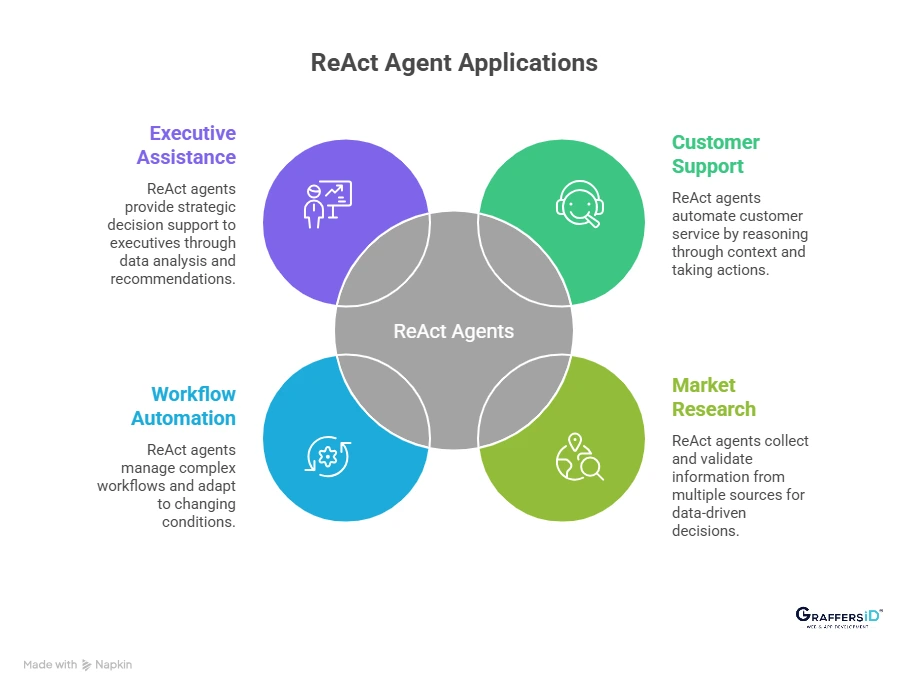
- Customer Support Automation with ReAct Agents: ReAct agents handle customer issues by reasoning through context instead of responding with predefined scripts. They analyze customer history, query internal systems, and take actions such as initiating refunds or escalating tickets.
- Market Research and Business Intelligence Automation: Product teams, market analysts, and strategy leaders use ReAct agents to collect and validate information from multiple sources. These agents reason through conflicting data, cross-check insights, and generate concise summaries that support data-driven decision-making.
- Workflow and Business Process Automation: ReAct agents manage complex workflows that involve multiple steps and systems. They handle approvals, reconcile data across platforms, and adapt decisions based on real-time inputs. Unlike rule-based automation, these agents adjust dynamically when conditions change.
- AI-Powered Executive Assistants for Decision Support: Executives use ReAct agents as intelligent assistants for planning, analysis, and strategic decision support. These agents retrieve relevant data, evaluate multiple scenarios, and provide recommendations based on real-time business context.
How to Build a ReAct Agent? Step-by-Step Process in 2026
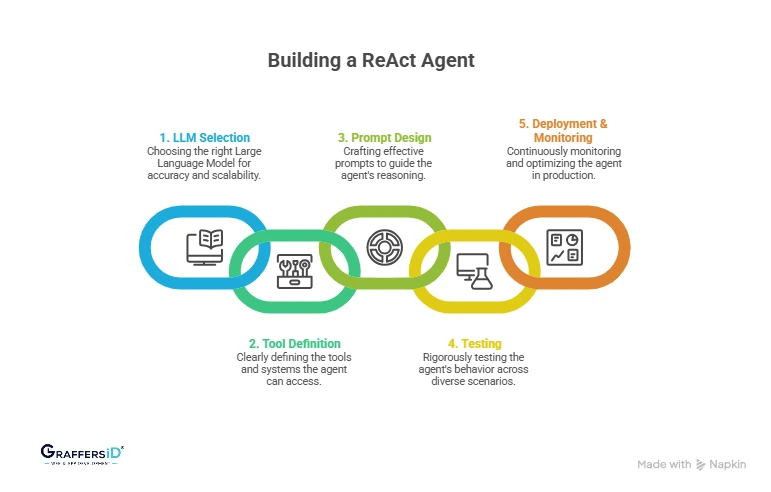
1. Choose the Right Large Language Model (LLM)
Selecting the right LLM is the foundation of a reliable ReAct agent. Businesses should evaluate models based on accuracy, reasoning depth, response latency, and overall cost at scale. Fine-tuning and instruction-following capabilities are critical for maintaining consistent reasoning across complex workflows.
Key factors to evaluate:
-
Reasoning accuracy and reliability
-
Inference cost and scalability
-
Latency for real-time use cases
-
Support for fine-tuning or prompt optimization
2. Define Agent Tools and System Access Clearly
A ReAct agent is only as powerful as the tools it can use. Clearly define which APIs, databases, internal systems, and external services the agent can access. Well-scoped tool definitions reduce errors and improve decision quality during reasoning loops.
Common tools include:
-
Internal databases and dashboards
-
Search and retrieval systems
-
Business APIs (CRM, ERP, billing, analytics)
3. Design Effective ReAct Prompts and Reasoning Structure
ReAct agents rely on structured prompts that guide how the agent reasons, selects actions, and interprets results. Prompts should explicitly separate reasoning, action selection, and observation to ensure predictable behavior and easier debugging.
Best practices for prompt design:
-
Use clear reasoning-action-observation patterns
-
Limit ambiguity in tool selection
-
Standardize output formats for enterprise use
Read More: Agentic AI vs. AI Agents: Key Differences, Real-World Examples, and Business Use Cases (2026 Guide)
4. Test Agent Behavior Across Iterations and Edge Cases
Before production deployment, ReAct agents must be tested across multiple scenarios. This includes evaluating loop termination conditions, error handling, fallback behaviors, and cost efficiency across repeated reasoning cycles.
What to test:
-
Infinite loop prevention and stop conditions
-
Error recovery when tools fail
-
Cost control during long reasoning chains
5. Deploy and Monitor ReAct Agents in Production
Production-grade ReAct agents require continuous monitoring to maintain performance and business value. Track accuracy, response times, tool usage patterns, and real-world outcomes to optimize the agent over time.
Key monitoring metrics:
-
Task success rate and accuracy
-
Latency and tool execution time
-
Business impact and ROI
Conclusion: Why ReAct Agents Are Essential for Businesses in 2026?
ReAct agents are redefining enterprise AI by combining reasoning, action, and real-time adaptation. Unlike traditional AI systems that only respond or automate tasks, ReAct agents execute complex workflows, validate outcomes, and optimize processes dynamically, delivering measurable business results.
For enterprises, this means AI that doesn’t just assist teams; it drives smarter decisions, reduces operational inefficiencies, and scales with evolving business needs.
If your organization is exploring AI-driven automation, intelligent decision support, or next-generation AI products, ReAct agents are no longer optional; they are critical to staying competitive.
At GraffersID, we help companies:
-
Hire experienced AI developers for custom solutions
-
Build custom AI agents and intelligent automation workflows
-
Develop scalable web and mobile applications
-
Integrate AI into real-world business operations
Contact GraffersID today to build future-ready AI systems that reason, act, and deliver results.