Artificial intelligence has evolved beyond making predictions. In 2026, the real competitive advantage lies in AI systems that can make decisions, learn from outcomes, and improve continuously.
As businesses move past static machine learning models, a new class of intelligent systems is taking center stage, systems that adapt in real time, respond to changing environments, and optimize results without constant human intervention. Reinforcement Learning (RL) is the foundation behind this shift.
From autonomous software agents and AI-powered recommendation engines to intelligent automation and real-time optimization platforms, reinforcement learning drives many of today’s most advanced AI applications. It enables machines not just to analyze data but to choose the best actions over time.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
-
What reinforcement learning is and how it works, explained simply
-
How RL differs from traditional machine learning approaches
-
Where reinforcement learning is being applied in real-world business scenarios
If you’re evaluating AI investments, building intelligent products, or exploring automation at scale, this article will give you a clear, practical understanding of reinforcement learning and why it matters now more than ever.
What is Reinforcement Learning in AI?
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a machine learning approach where an AI system learns how to make better decisions by interacting with its environment and learning from feedback.
Instead of being trained on pre-labeled datasets, a reinforcement learning model improves through trial and error. Each action the system takes leads to an outcome, and that outcome generates a reward or penalty. Over time, the system learns which actions lead to the best results.
Reinforcement Learning vs. Supervised and Unsupervised Learning
Understanding where reinforcement learning fits in modern AI systems and how it helps businesses choose the right AI model for the right problem. Each method is designed for a specific type of data, objective, and decision complexity.
1. Supervised Learning
Supervised learning trains models using labeled data, where the correct output is already known. The model learns by mapping inputs to predefined outputs and improving accuracy over time.
It is best suited for prediction and classification tasks where historical data clearly defines the outcome. Common examples include spam detection, demand forecasting, fraud detection, and sentiment analysis. Supervised learning works well when patterns are stable, and decisions do not change the environment.
Read More: Top 5 AI Development Companies in India in 2026: Cost, Services & Expertise
2. Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data, meaning the system looks for patterns, structures, or relationships without predefined outcomes.
It is commonly used for clustering, segmentation, and anomaly detection. Businesses use unsupervised learning for customer segmentation, behavior analysis, and data exploration. While it reveals insights, it does not actively make or optimize decisions.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is fundamentally different. Instead of learning from static datasets, it learns by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties.
This approach continuously improves by learning from outcomes, making it ideal for dynamic, real-time decision-making scenarios such as recommendation systems, autonomous agents, robotics, and process optimization.
Core Reinforcement Learning Concepts in 2026
Reinforcement learning works on a small set of foundational concepts. Understanding these basics makes it much easier to see how RL systems learn, adapt, and make decisions in real-world scenarios.
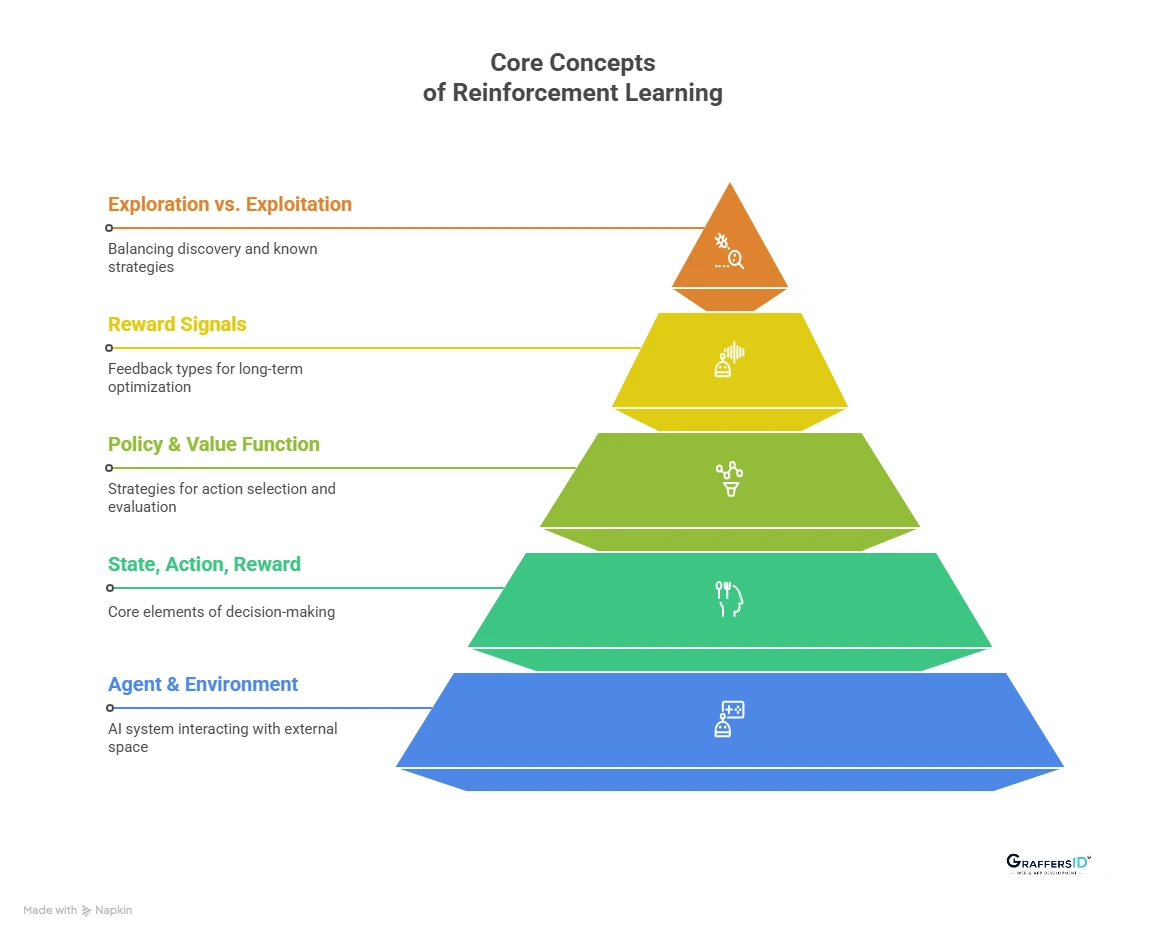
1. Agent and Environment in Reinforcement Learning
In reinforcement learning, everything starts with the agent and the environment.
-
Agent: The AI system that makes decisions and takes actions.
-
Environment: The external system or space where the agent operates and receives feedback.
The agent continuously interacts with the environment, learns from outcomes, and improves its behavior over time.
Example: A delivery robot is the agent, and the city—roads, traffic signals, pedestrians, and weather- is the environment it operates in.
2. State, Action, and Reward Explained
Reinforcement learning models decision-making using three core elements:
-
State: The current situation the agent is in.
-
Action: The possible move or decision the agent can take.
-
Reward: Feedback from the environment after an action is taken.
The reward tells the agent whether its decision was good or bad.
Example:
-
State: Current traffic conditions
-
Action: Selecting a delivery route
-
Reward: Faster delivery time or delay due to congestion
Over time, the agent learns which actions lead to better rewards in different states.
3. Policy and Value Function in Reinforcement Learning
To make intelligent decisions, reinforcement learning relies on two key ideas:
-
Policy: A strategy that defines how the agent chooses actions in different situations.
-
Value Function: A measure of how beneficial a state or action is based on expected future rewards.
Instead of focusing on immediate results, the value function helps the agent evaluate long-term outcomes, making decisions that perform well over time.
This is especially important for business systems where short-term gains may lead to long-term losses.
4. Reward Signals and Long-Term Optimization
In reinforcement learning, rewards can be:
-
Immediate: Received right after an action
-
Delayed: Received after a series of actions
RL systems are designed to maximize cumulative rewards, not just individual successes. This long-term optimization makes reinforcement learning highly effective for complex business problems such as pricing strategies, supply chain optimization, and intelligent automation.
5. Exploration vs. Exploitation Trade-Off
One of the most important challenges in reinforcement learning is balancing:
-
Exploration: Trying new actions to discover better outcomes
-
Exploitation: Using known actions that already produce good results
If an agent explores too much, it may perform poorly. If it exploits too early, it may miss better strategies. Successful RL systems continuously balance both, which is essential for stable and reliable real-world deployment.
How Reinforcement Learning Works: A Step-by-Step Process in 2026
Reinforcement learning works through a continuous learning loop, where an AI system improves its decisions by interacting with its environment and learning from feedback over time.
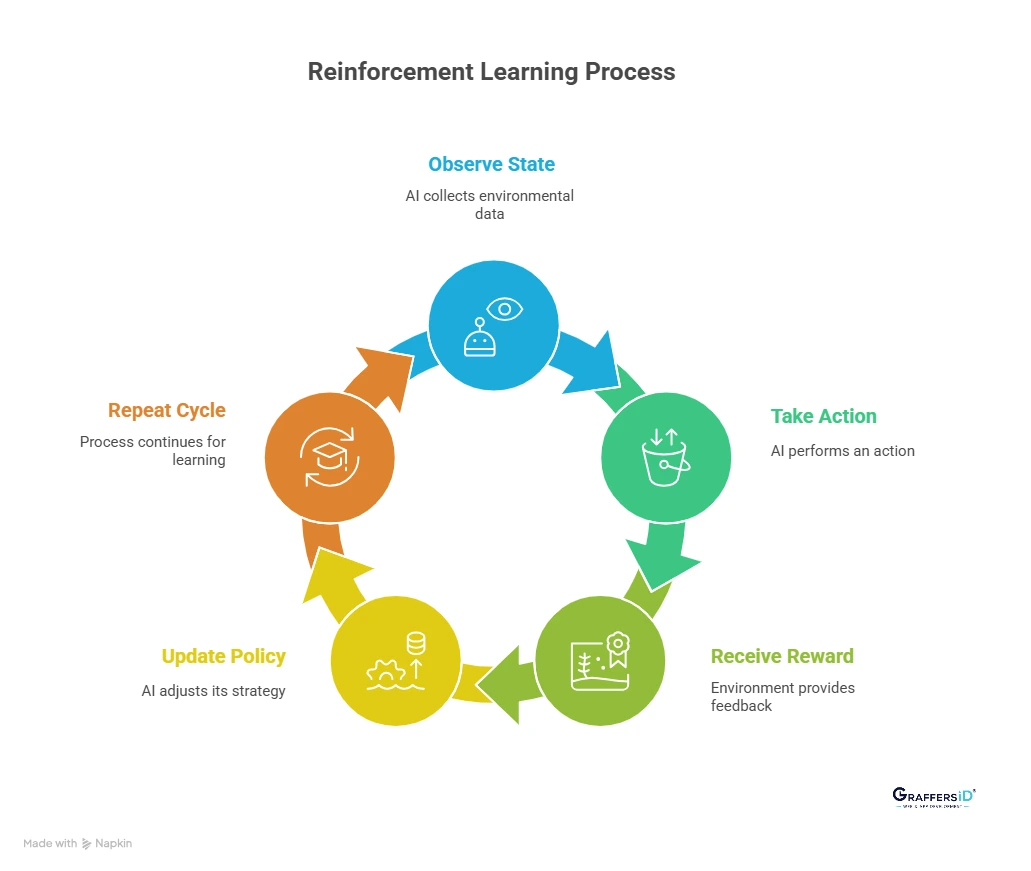
Here’s how the reinforcement learning process works step by step:
-
The agent observes the current state: The AI system (agent) collects information about its current situation or environment, such as user behavior, system conditions, or real-time data inputs.
-
The agent takes an action: Based on its current policy, the agent selects and performs an action. This could be recommending content, adjusting a process, choosing a route, or triggering an automated decision.
-
The environment provides feedback as a reward: After the action is taken, the environment responds with a reward or penalty. This feedback indicates how good or bad the action was in achieving the desired outcome.
-
The agent updates its learning strategy (policy): Using the reward signal, the agent updates its policy and value estimates to improve future decisions. Actions that lead to higher rewards are reinforced over time.
-
The process repeats continuously: This cycle repeats across many interactions, allowing the system to learn from experience, adapt to changes, and optimize results over the long term.
Most reinforcement learning systems are built on Markov Decision Processes (MDPs), a mathematical framework designed for sequential decision-making under uncertainty.
This step-by-step learning loop is what makes reinforcement learning especially powerful for modern AI applications that require real-time adaptation, automation, and long-term optimization.
Types of Reinforcement Learning in AI Systems 2026
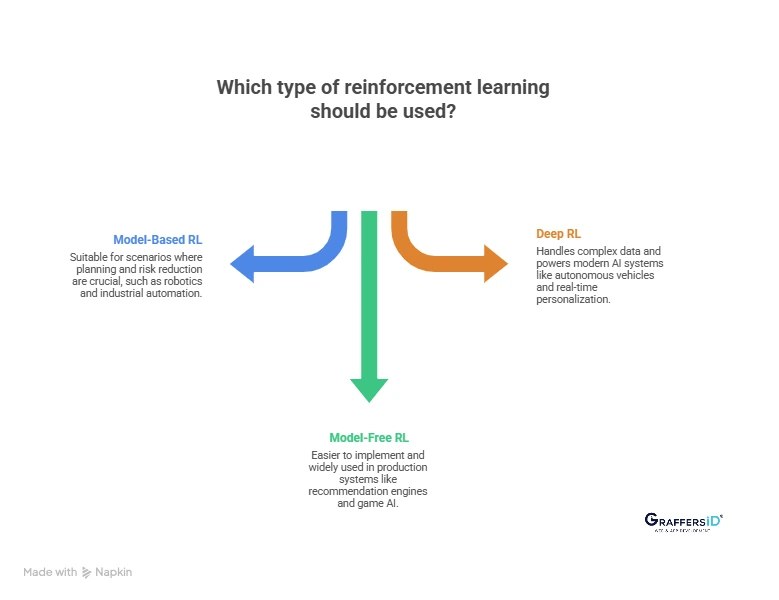
1. Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Model-based reinforcement learning works by building an internal representation of the environment before taking actions. This allows the system to plan, simulate outcomes, and reduce risk, making it suitable for scenarios where errors are expensive or unsafe, such as robotics and industrial automation.
2. Model-Free Reinforcement Learning
Model-free reinforcement learning learns directly from trial and error without creating an environment model. It is easier to implement, widely adopted in production systems, and commonly used in applications like recommendation engines and game AI, with algorithms such as Q-Learning and SARSA.
3. Deep Reinforcement Learning
Deep reinforcement learning combines reinforcement learning with deep neural networks to handle complex and high-dimensional data. It powers many modern AI systems in 2026, including autonomous systems, robotics, game intelligence, and real-time personalization platforms.
Read More: Agentic AI vs. Generative AI: Key Differences CTOs Must Know in 2026
Most Popular Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in 2026
- Q-Learning: Q-Learning is a model-free reinforcement learning algorithm that helps agents learn the best action to take in a given state by maximizing long-term rewards, commonly used in discrete environments.
- Policy Gradient Methods: Policy gradient algorithms directly learn the optimal policy by adjusting action probabilities, making them effective for complex and continuous decision-making problems.
- Actor-Critic Algorithms: Actor-Critic methods combine policy learning and value estimation to improve training stability and speed, making them well-suited for real-time and dynamic systems.
- Deep Q-Networks (DQN): Deep Q-Networks use neural networks to approximate Q-values, enabling reinforcement learning in high-dimensional environments such as games, simulations, and visual systems.
- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) and A3C: PPO and A3C are scalable, production-ready algorithms designed for faster training and stable performance, widely used in modern enterprise and autonomous AI systems.
Choosing the right reinforcement learning algorithm depends on the problem being solved.
Read More: 5 Best AI Frameworks and Libraries in 2026 Trusted by Leading Tech Companies
Real-World Applications of Reinforcement Learning in 2026
- Robotics and Autonomous Systems: Reinforcement learning enables robots and autonomous machines to navigate environments, plan paths, and perform precise actions by learning from real-time feedback and outcomes.
- Game AI and Simulation-Based Training: RL is used to train AI agents in simulated environments, helping them develop strategic decision-making skills that can later be transferred to real-world systems.
- Recommendation Systems and Personalization: Reinforcement learning continuously optimizes content and product recommendations by learning from user interactions and adjusting decisions to maximize long-term engagement.
- Finance and Business Optimization: In finance and operations, RL powers dynamic pricing, algorithmic trading, and supply chain optimization by adapting decisions based on changing market conditions.
- Enterprise Automation and AI Agents: Reinforcement learning drives intelligent automation by enabling AI agents to optimize workflows, make context-aware decisions, and improve business processes over time.
Key Benefits of Reinforcement Learning for Businesses in 2026
Reinforcement learning enables:
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: Reinforcement learning systems improve over time by learning from real-world outcomes, eliminating the need for frequent full retraining and enabling long-term performance gains.
- Optimized Decision-Making in Complex Environments: RL helps businesses make better decisions in dynamic, multi-variable environments where traditional rules or static models fail to deliver consistent results.
- Reduced Need for Labeled Training Data: Unlike supervised learning, reinforcement learning does not rely heavily on labeled datasets, making it cost-effective for use cases where data labeling is expensive or impractical.
- Smarter Automation Focused on Long-Term Goals: Reinforcement learning enables automation systems to optimize for long-term objectives rather than short-term wins, improving operational efficiency and strategic outcomes.
- Adaptive Systems That Evolve With User Behavior: RL-powered systems continuously adapt to changing user behavior, market conditions, and operational inputs, helping businesses stay competitive in fast-moving environments.
Implementing Reinforcement Learning in Real-World Systems
Modern RL development typically uses:
-
Frameworks: PyTorch, TensorFlow, RLlib
-
Simulation tools: OpenAI Gym-style environments
-
Infrastructure: Scalable cloud or edge systems
Best practices include:
-
Careful reward design
-
Simulated training before real-world deployment
-
Ongoing monitoring and tuning
RL is most effective when integrated with broader AI and software systems, not used in isolation.
Conclusion: Why Reinforcement Learning Is a Strategic AI Investment?
Reinforcement learning represents the shift from traditional predictive AI to decision-driven intelligence, systems that learn, adapt, and optimize on their own.
In 2026, businesses leveraging RL can:
-
Build adaptive and intelligent systems that respond to changing conditions in real time
-
Continuously optimize operations to maximize efficiency and reduce costs
-
Deliver personalized, automated experiences at scale, improving customer satisfaction and engagement
As AI becomes more autonomous, reinforcement learning is no longer optional; it’s a strategic investment that determines how organizations compete, innovate, and lead in their industries.
At GraffersID, we help businesses hire experienced AI developers and build custom AI-powered solutions. Contact us today to start building your next-generation AI system.