In 2026, cloud computing isn’t just a backend utility; it’s the core driver of enterprise AI, automation, and innovation. From deploying large language models (LLMs) and managing real-time analytics pipelines to scaling global web and mobile applications, every digital strategy today runs on the cloud.
But here’s the catch: the cloud you choose defines your speed, security, and scalability.
The market leaders: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are no longer competing just on storage or cost. They’re redefining the cloud race with AI-native infrastructure, sustainable data centers, and developer-focused automation tools.
So in 2026, which platform truly leads the way for innovation and growth?
Let’s dive deep into the real-world strengths, weaknesses, and future outlook of AWS, Azure, and GCP, and help you decide which cloud aligns best with your business goals.
What is Cloud Computing? (2026 Definition)
Cloud computing in 2026 refers to the on-demand delivery of computing services, such as storage, processing power, networking, and software, over the internet rather than relying on local servers or physical hardware.
Unlike traditional infrastructure, today’s cloud environments are intelligent, AI-driven ecosystems. They integrate machine learning (ML), edge computing, and automation to help enterprises:
-
Scale operations faster without a heavy upfront investment
-
Reduce infrastructure and maintenance costs
-
Leverage emerging technologies like large language models (LLMs), predictive analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT)
In simple terms, cloud computing in 2026 is no longer just about hosting; it’s about innovation, agility, and intelligence at scale.
What is AWS (Amazon Web Services)?
Founded in 2006, AWS dominates the global cloud market (~30% share) with over 200 enterprise-grade services spanning compute, storage, databases, AI, and machine learning. It’s the preferred choice for businesses seeking unmatched scalability, reliability, and global reach.
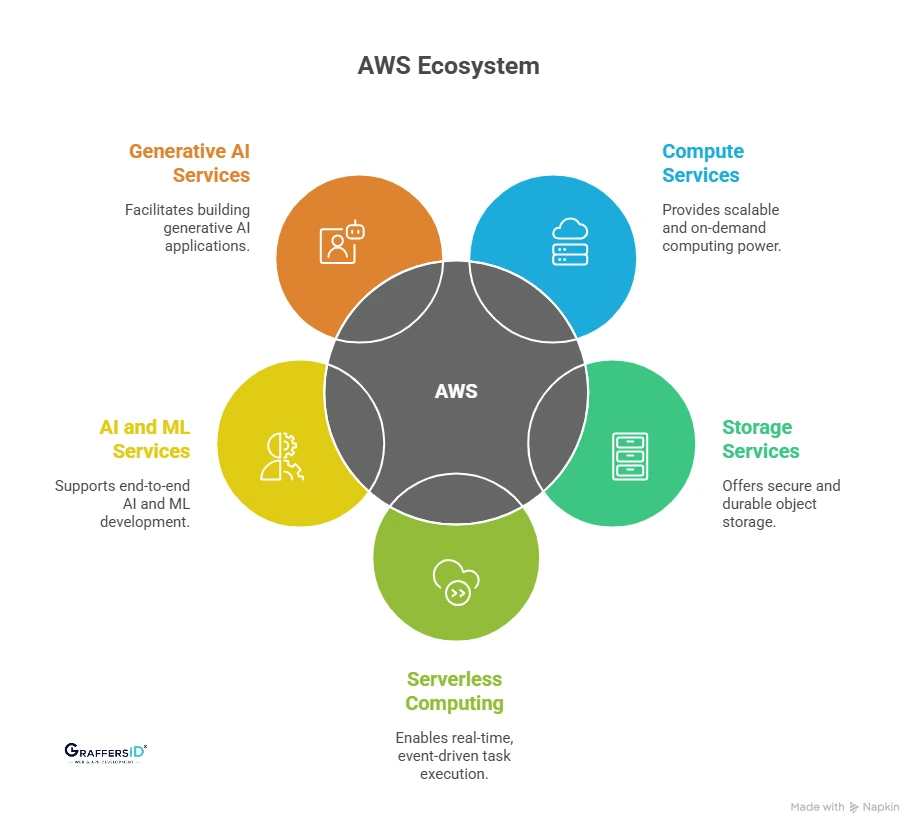
Key Features of AWS (Amazon Web Services)
Here are some notable features of AWS:
-
Amazon EC2: Elastic compute power for dynamic workloads and on-demand scaling.
-
Amazon S3: Secure object storage with 99.999999999% data durability.
-
AWS Lambda: Serverless computing for real-time, event-driven tasks.
-
Amazon SageMaker: End-to-end AI and ML development platform for enterprises.
-
Amazon Bedrock (2026): New managed service for building generative AI applications with foundation models.
Pros of AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- Market-leading scalability and uptime across 25+ regions.
- Vast integration ecosystem supporting third-party and open-source tools.
- Robust AI and ML suite (SageMaker, Bedrock) for innovation at scale.
- Proven enterprise-grade reliability and compliance certifications.
Cons of AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- Complex pricing and billing structure for growing workloads.
- Steep learning curve for small teams or startups.
- Vendor lock-in risks with proprietary AWS tools and services.
Best For
Enterprises, AI-driven SaaS platforms, and global applications that demand consistent performance, scalability, and reliability.
What is Microsoft Azure?
Launched in 2010, Microsoft Azure has grown into the second-largest cloud platform, holding nearly 22% of the global market share. Its biggest strength lies in smooth integration with Microsoft products, a natural fit for businesses using Windows, Office 365, or Dynamics 365.

Key Features of Microsoft Azure
Azure offers a wide range of services, particularly strong in hybrid cloud and enterprise solutions. Key features include:
-
Azure Virtual Machines: Flexible and scalable compute resources for cloud workloads.
-
Azure Blob Storage: Secure, cost-efficient, and infinitely scalable object storage.
-
Azure Synapse Analytics: Unified analytics engine for data integration and business insights.
-
Azure OpenAI Service: Direct access to GPT-4, DALL·E, and advanced AI APIs for enterprise AI adoption.
-
Azure Arc: Simplified management for multi-cloud and on-premise environments.
Pros of Azure
- Strong hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities.
- Native integration with the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Excellent enterprise security and compliance.
- Expanding AI infrastructure (OpenAI & Copilot integrations).
Cons of Azure
- Complex configuration for new users
- Higher costs for unmanaged resources
- Periodic service outages and slower support responses
Best For
Large enterprises and hybrid setups built around Microsoft technologies seeking a secure, AI-ready cloud environment.
What is Google Cloud (Google Cloud Platform)?
Launched in 2011, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) has evolved into the go-to choice for AI, data analytics, and cloud-native startups. With innovations like TensorFlow, Vertex AI, and the new Gemini AI suite (2026), GCP leads in intelligent automation and developer-first tools.
Key Features of Google Cloud
Google Cloud stands out in data analytics and machine learning. Its notable features include:
-
Compute Engine: Delivers ultra-fast, scalable virtual machines for modern workloads.
-
BigQuery: A serverless data warehouse built for real-time analytics at petabyte scale.
-
Vertex AI: Unified machine learning platform to train, deploy, and manage models smoothly.
-
Cloud Functions: Event-driven, serverless compute for cost-efficient automation.
-
Gemini AI (2026): Google’s latest enterprise-grade foundation model suite for AI-driven applications.
Pros of Google Cloud
- Industry-leading AI and ML ecosystem.
- Transparent, cost-efficient pricing structure.
- Deep integration with Google products (Analytics, Workspace, Ads).
- 100% carbon-free energy target by 2030.
Cons of Google Cloud
- Smaller enterprise market share than AWS or Azure.
- Limited data center coverage in certain regions.
- Enterprise support ecosystem is still maturing.
Best For
Startups, AI-first companies, and data-driven enterprises seeking cutting-edge AI and analytics performance.
AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud Pricing (2026 Overview)
In 2026, cloud pricing remains one of the biggest deciding factors for CTOs and enterprises. While each provider offers flexible pay-as-you-go models, the real savings come from optimization programs and workload patterns.
Here’s a quick snapshot of how AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud compare on core services in 2026:
| Service Type | AWS | Microsoft Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compute (Small Instance) | EC2 t3.micro – $0.010/hr | VM B1s – $0.008/hr | e2-micro – $0.007/hr |
| Storage (Standard) | S3 – $0.023/GB | Blob Storage – $0.018/GB | Cloud Storage – $0.020/GB |
| Managed SQL Database | RDS MySQL – $0.017/hr | SQL Database Basic – $0.021/hr | Cloud SQL – $0.015/hr |
2026 Pricing Insights:
-
AWS offers Savings Plans and Reserved Instances, ideal for predictable, long-term workloads.
-
Azure provides extra discounts for Microsoft 365 and Windows Server users, along with commitment-based savings.
-
Google Cloud automatically applies Sustained Use Discounts, reducing costs the longer your resources stay active.
In short: If cost optimization is your top priority, Google Cloud often leads in base pricing, while AWS and Azure excel in enterprise-grade integrations and flexibility.
AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud: Complete Comparison 2026
| Aspect | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Strength | Broadest global infrastructure and service diversity | Deep enterprise and hybrid cloud integration | AI-first infrastructure and superior data analytics |
| AI & ML Offerings | SageMaker, Bedrock, and CodeWhisperer for AI model training and deployment | Azure OpenAI Service, ML Studio, and Copilot integrations | Vertex AI, Gemini, and AutoML for end-to-end AI lifecycle |
| Developer Tools & Integration | Cloud9, CodeBuild, DevOps pipelines | GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps Center | Cloud Build, Cloud Deploy, and Artifact Registry |
| Security & Compliance | 300+ global compliance programs, IAM, GuardDuty | Azure Defender, Sentinel, and Active Directory integration | BeyondCorp Zero Trust, IAM, and Security Command Center |
| Standout Feature | Amazon Bedrock for generative AI and foundation models | Azure Copilot for enterprise automation and AI productivity | Gemini + Vertex AI integration powering real-time AI apps |
AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud: Which Cloud is Best in 2026?
Choosing the right cloud provider in 2026 depends on your business priorities, scalability goals, and AI readiness. Each platform leads in different areas:
- AWS is ideal for businesses that need global scalability, enterprise-grade reliability, and a mature developer ecosystem. Its vast service portfolio and proven infrastructure make it the go-to platform for long-term growth.
- Microsoft Azure stands out for enterprises built around Microsoft tools and hybrid environments. Its deep integration with Office 365, Windows Server, and enterprise AI features like Copilot make it perfect for corporate digital transformation.
- Google Cloud leads when it comes to AI, machine learning, and analytics-driven innovation. With Gemini and Vertex AI, it empowers companies to build smarter, faster, and more cost-efficient AI applications.
Conclusion: AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud
In 2026, the best cloud platform isn’t about who leads the market; it’s about who aligns best with your business strategy.
-
Choose AWS for unmatched scalability, global coverage, and an ecosystem built for enterprise reliability.
-
Choose Microsoft Azure if your operations depend on Microsoft products, hybrid environments, or enterprise-grade integrations.
-
Choose Google Cloud to lead in AI, data analytics, and innovation speed, especially if you’re building automation-driven products.
The cloud is no longer just a storage layer; it’s the foundation of AI transformation and digital innovation. The right platform can help your business deploy intelligent solutions faster, optimize performance, and reduce operational overhead.
At GraffersID, we empower businesses to leverage the full potential of cloud and AI. Our expert AI developers specialize in creating scalable, automation-driven applications that accelerate innovation and drive measurable ROI.
Hire AI developers from GraffersID to future-proof your tech stack, integrate smarter workflows, and stay ahead in the AI-powered era of 2026.