Machine Learning (ML) is no longer a “future technology”; it’s the engine behind nearly every intelligent system businesses rely on today. From hyper-personalized recommendations and automated risk scoring to fraud detection, predictive operations, and enterprise AI agents, ML is now at the core of how modern companies build, scale, and innovate in 2026.
Yet for most CTOs, CEOs, and product leaders, one critical question remains:
What exactly is Machine Learning, how does it work, and how can it create real business value today, not just in theory, but in practice?
This guide breaks ML down in a clear, practical, and decision-maker-friendly way. You’ll learn how ML works, where it fits in modern digital products, the technologies reshaping the field in 2026, and how leading enterprises are using it to automate processes, improve customer experience, and accelerate product development.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a core part of artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn patterns from data and make decisions without being manually programmed. Instead of following fixed rules, ML models analyze large volumes of information, identify trends, and continuously improve their accuracy over time.
In simple terms:
Machine Learning = data + algorithms that learn patterns + predictions or decisions made automatically.
Machine Learning vs. AI vs. Deep Learning
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): The umbrella concept of machines imitating human intelligence.
-
Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI focused on learning from data.
-
Deep Learning (DL): A type of ML using neural networks for complex patterns (vision, speech, NLP).
-
Generative AI (GenAI): AI systems that generate new content, text, images, code, audio, or agents.
Read More: What Is Artificial Intelligence in 2026? Definition, Types, Benefits & Real-World Use Cases
How Machine Learning Works?
Machine learning follows a predictable development lifecycle used by engineering teams worldwide. Understanding this helps decision-makers evaluate feasibility, timelines, and required resources.
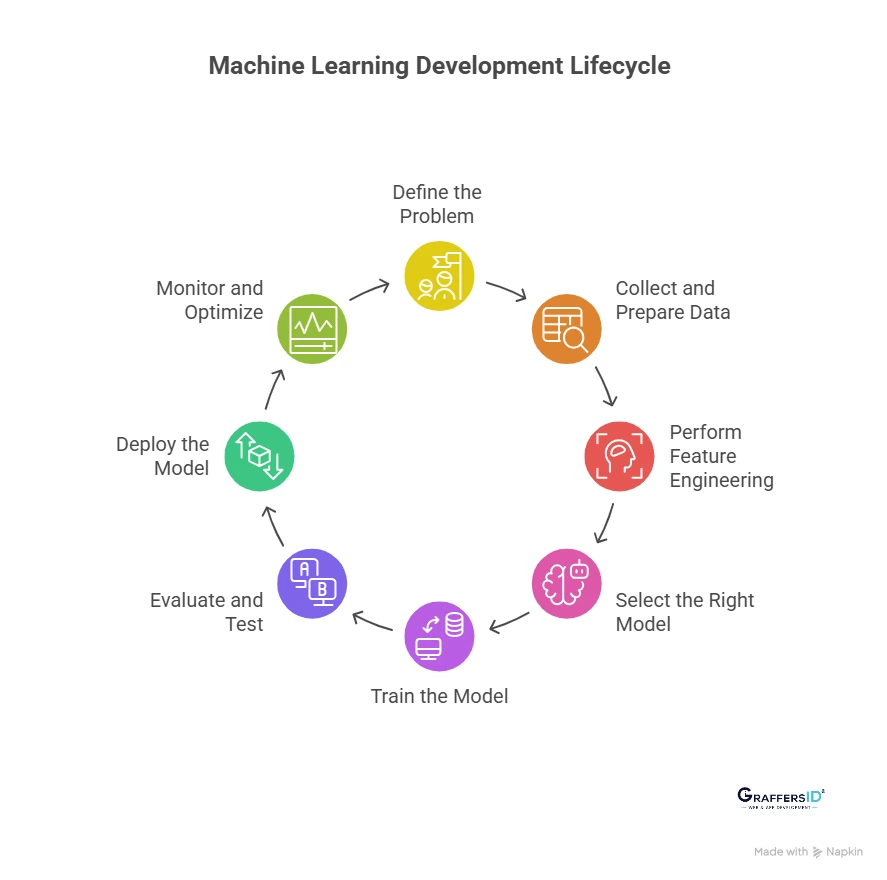
1. Define the Problem
Every ML project starts with a clear objective. This means identifying a business challenge that can be improved through prediction, classification, automation, or pattern discovery.
Common ML problem types in 2026:
-
Predicting customer demand or churn
-
Detecting anomalies or fraud
-
Recommending products or content
-
Classifying documents, emails, or support tickets
-
Automating repetitive decisions with AI agents
A clear problem definition determines the model, data needs, and expected ROI.
2. Collect and Prepare Data
Data quality determines model quality. This step typically takes 60–70% of the total ML effort.
Tasks involved:
-
Extracting data from internal systems, APIs, logs, IoT devices, CRMs, or databases
-
Cleaning, removing duplicates, fixing missing values
-
Labeling data (for supervised learning)
-
Structuring training datasets and versioning them for reproducibility
In 2026, teams often use automated data-cleaning tools and AI-assisted labeling to speed up this process.
3. Perform Feature Engineering
Feature engineering converts raw data into meaningful signals that the model can learn from.
Typical feature engineering methods:
-
Scaling and normalizing numerical values
-
Encoding categorical variables
-
Creating time-series signals
-
Building domain-specific features (e.g., customer lifetime value)
-
Removing irrelevant or noisy inputs
In 2026, many ML teams use AutoML and AI-assisted feature generation to automate this step for faster iterations.
Read More: OpenAI’s GPT vs. Google Gemini: Which AI Model is Better for Workflow Automation in 2026?
4. Select the Right Machine Learning Model
Based on the problem, developers choose the best-suited model family.
Popular model types in 2026:
-
Decision Trees & Random Forests: great for structured data
-
Gradient Boosting Models: high accuracy for tabular data
-
Neural Networks: powerful for images, text, and speech
-
Transformer Models: the 2026 standard for NLP, vision, and multi-modal tasks
-
Generative Models + RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation): used for chatbots, agents, and search
-
Hybrid ML + LLM models: powering enterprise AI systems
Model selection impacts training speed, accuracy, and infrastructure cost.
5. Train the Model
The model “learns” patterns by analyzing data multiple times.
During training:
-
The model adjusts parameters
-
Errors are reduced
-
Performance metrics steadily improve
In 2026, GPU clusters, edge accelerators, and serverless training workflows are commonly used to speed up training cycles.
6. Evaluate and Test the Model
Before deployment, the model is validated using industry-standard metrics.
Key metrics:
-
Accuracy
-
Precision
-
Recall
-
F1 score
-
ROC-AUC
-
Cross-validation results
Engineering teams also perform fairness checks, stress tests, and bias evaluations, crucial for 2026 compliance standards.
7. Deploy the Model Into Production
Once approved, the ML model is integrated into real products and workflows.
Deployment environments:
-
Web platforms
-
Cloud microservices
-
Internal enterprise dashboards
-
AI agents and automation workflows
In 2026, companies rely heavily on APIs, containerized ML models, and LLM inference servers for fast and scalable deployment.
8. Monitor, Optimize, and Retrain Continuously
ML is not a “deploy once and forget” system. Data, customer behavior, and market conditions evolve, so the model must evolve too.
Ongoing tasks include:
-
Monitoring model accuracy and data drift
-
Automating retraining pipelines
-
Updating ML/LLM versions
-
Ensuring cost-efficient inference
-
Maintaining observability and performance dashboards
This continuous improvement loop ensures long-term reliability and ROI.
Types of Machine Learning in 2026
Machine Learning systems can be grouped into four major types. Each type solves different business problems and uses different training methods. Here’s a simple, decision-maker-friendly breakdown.
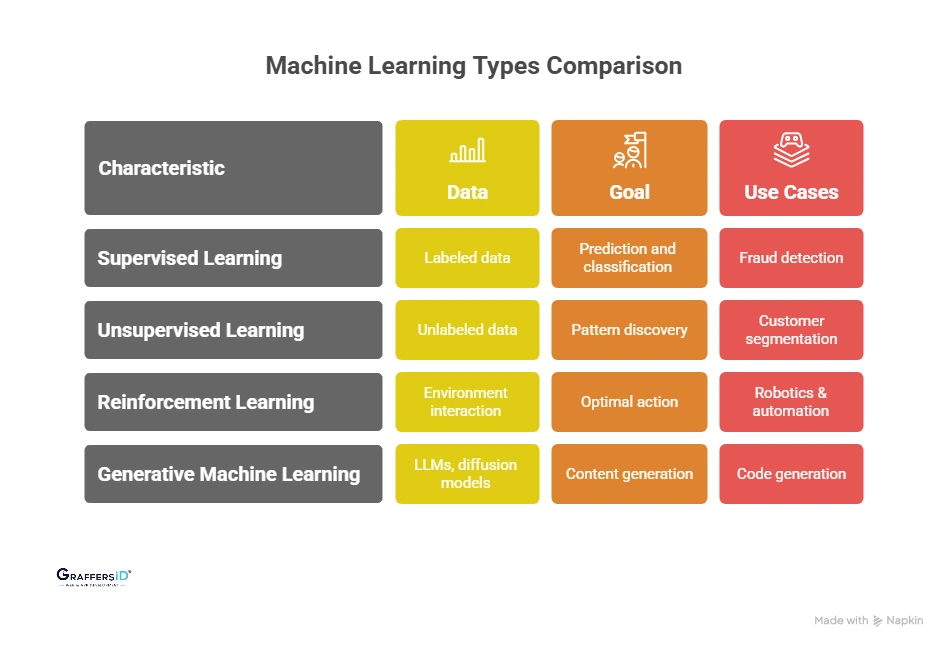
1. Supervised Learning (Best for Predictions and Classification)
In supervised learning, the model is trained using labeled data, meaning the correct answer is already known. The model learns by mapping input → output, making it highly effective for predicting outcomes.
Common Use Cases in 2026:
-
Fraud Detection: Identify fraudulent transactions in real time.
-
Spam Filtering: Automatically classify emails or messages.
-
Customer Churn Prediction: Predict users likely to leave a service.
-
Medical Diagnosis: Analyze scans or records for disease probability.
-
Price Forecasting: Predict stock prices, product demand, or inventory needs.
2. Unsupervised Learning (Finding Patterns Without Labels)
Unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data, allowing the model to discover hidden patterns or groups on its own. It’s ideal when businesses have large datasets but no predefined outcomes.
Common Use Cases in 2026:
-
Customer Segmentation: Identify buyer personas for personalization.
-
Anomaly Detection: Spot unusual patterns in transactions or logs.
-
Market Basket Analysis: Understand which products are bought together.
-
Behavior Clustering: Group users based on browsing and usage behavior.
3. Reinforcement Learning (Learning Through Rewards)
Reinforcement Learning (RL) allows models to learn by interacting with an environment, taking actions, and receiving rewards or penalties. Over time, the system learns the optimal action to achieve the best outcome.
Common Use Cases in 2026:
-
Robotics & Automation: Robots learning movement or task execution.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Real-time decision-making for navigation.
-
Dynamic Pricing: Automated price adjustments based on demand.
-
Inventory Optimization: RL agents managing stock levels.
4. Generative Machine Learning (A Key Trend Shaping 2026 AI)
Generative ML, powered by LLMs, diffusion models, vision transformers, and multi-modal models, creates new content, code, and insights. As of 2026, it’s the fastest-growing ML category.
Popular Use Cases in 2026:
-
Code Generation & AI Pair Programming.
-
Content Automation (blogs, ads, design variations, UX assets).
-
Chatbots & Virtual AI Agents for customer service and workflows.
-
Voice & Video Generation for training, marketing, or localization.
-
Synthetic Data Generation for model training and compliance.
Top Machine Learning Use Cases in 2026
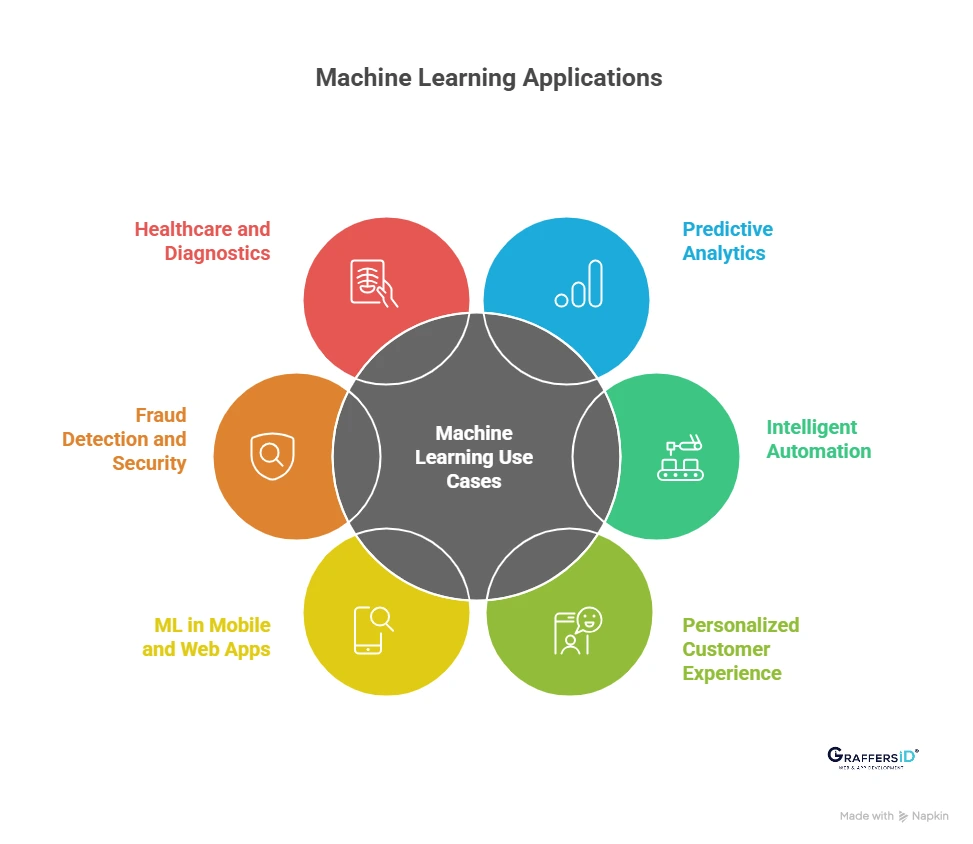
1. Predictive Analytics: ML models help businesses forecast demand, assess financial risk, predict equipment failures, and identify future revenue trends with higher accuracy than traditional analytics.
2. Intelligent Automation: Companies use ML to automate manual processes like document processing, ticket routing, claims verification, and compliance monitoring, reducing operational load and improving speed.
3. Personalized Customer Experience: Machine learning enables hyper-personalized recommendations, dynamic user journeys, and real-time customer scoring that improve engagement and conversions across digital products.
4. ML in Modern Mobile and Web Apps: Most apps now use machine learning for smarter search, voice-enabled interactions, chat-driven interfaces, and behavioral insights that adapt to user patterns in real time.
5. Fraud Detection and Security: ML systems identify suspicious transactions, detect unusual user activity, prevent identity theft, and block automated bot attacks with advanced anomaly detection techniques.
6. Healthcare and Diagnostics: Healthcare platforms rely on ML to analyze medical images, monitor patient vitals, and predict disease risks early, improving diagnosis accuracy and treatment outcomes.
Top Machine Learning Tools and Technologies Every Business Should Know in 2026
In 2026, building effective Machine Learning (ML) systems requires a combination of programming languages, frameworks, cloud platforms, and MLOps tools. Modern ML developers leverage advanced tools not only for traditional ML tasks but also for generative AI, large language models (LLMs), and AI-powered enterprise applications. Here’s a breakdown of the most important technologies and how they are used today:
1. Programming Languages and Frameworks
These are the core building blocks for ML model development:
-
Python: The most popular programming language for ML due to its simplicity, extensive libraries, and community support.
-
TensorFlow: Google’s open-source library for building scalable ML and deep learning models.
-
PyTorch: Widely used for deep learning, research, and production-ready AI solutions.
-
scikit-learn: Ideal for classical ML tasks like regression, classification, and clustering.
-
Keras: High-level neural network API for fast prototyping and simplified deep learning development.
2. LLM and Generative AI Ecosystem Tools
With the rise of generative AI in 2026, ML developers also use specialized tools to build, fine-tune, and deploy large language models:
-
LangChain: A framework for building AI applications with language models and integrating them with external data sources.
-
LlamaIndex: Helps structure, manage, and retrieve data efficiently for LLM-powered applications.
-
HuggingFace Transformers: Provides pre-trained models for NLP, vision, and multi-modal AI applications.
-
Vector Databases (Weaviate, Pinecone): Store and search embeddings for AI search, recommendation, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
-
RAG Pipelines: Combine retrieval systems with LLMs for accurate and context-aware AI outputs.
Read More: Advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) in 2026: Tools, Trends, and AI Applications
3. Cloud Machine Learning Platforms
Cloud platforms accelerate ML development, simplify deployment, and enable scalable AI solutions:
-
AWS SageMaker: Fully managed platform for building, training, and deploying ML models.
-
Google Vertex AI: Offers end-to-end tools for ML lifecycle, from data preparation to production.
-
Azure ML Studio: Simplifies model building, experimentation, and deployment for enterprise applications.
4. MLOps and Deployment Tools
MLOps ensures that ML models are production-ready, maintainable, and scalable:
-
MLflow: Tracks experiments, manages models, and streamlines ML lifecycle management.
-
Airflow: Orchestrates complex data pipelines for training and deploying ML workflows.
-
Docker: Containerizes ML applications for consistent deployment across environments.
-
Kubernetes: Automates deployment, scaling, and management of containerized ML models.
-
Ray: Distributed computing framework to speed up training and deployment of large models.
By combining these tools, modern ML developers can build robust, scalable, and intelligent systems, from classical predictive models to generative AI applications, helping businesses leverage the full potential of machine learning in 2026.
Conclusion: Why Machine Learning is Essential for Businesses in 2026
Machine Learning has evolved from a specialized technology to a core driver of innovation and competitiveness in 2026. From powering predictive analytics and intelligent automation to delivering hyper-personalized experiences and optimizing operational efficiency, ML is now at the heart of every data-driven enterprise.
For CTOs, CEOs, and product leaders, understanding and implementing ML is no longer optional; it’s critical for building smart digital products, scaling business operations, and making informed strategic decisions. Companies that leverage ML effectively gain a clear edge in speed, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Whether you’re exploring AI-powered solutions, integrating ML into existing systems, or developing next-generation intelligent apps, having the right technical expertise is crucial.
Ready to bring ML into your business?
GraffersID provides expert ML and AI developers to help you build scalable, intelligent applications efficiently. Hire remote AI developers with GraffersID to accelerate innovation and stay ahead in 2026.