As AI adoption increases across industries, the subject matter has shifted from “What can AI generate?” to “What can AI do?” Generative AI provided organizations with unparalleled speed in content creation and the automation of repetitive cognitive processes. However, a new concept is emerging in 2026: agentic AI, or AI that acts autonomously not just to do tasks but to accomplish business objectives.
Agentic AI is making its way from research labs to enterprise production environments, where it can be used to do everything from write code and schedule meetings to carry out entire sales operations. Thus, CTOs and tech leaders must understand the differences between generative and agentic AI to determine the proper AI adoption strategy.
In this blog, we will discuss the key differences that every CTO, CIO, or digital transformation executive must understand in order to make informed, strategic decisions regarding their AI investments in 2026 and beyond.
Generative AI vs. Agentic AI: Overview (2026)
Generative AI
Generative AI refers to models (often diffusion or large language models) that generate new content based on prompts. These systems can generate text, graphics, audio, video, or code of excellent quality after being trained on large datasets.
Related: What is Generative AI and How Does It Affect Software Development?
- How it works: Based on statistical patterns, it generates an output when you give it an input (for example, “Write an email to a client”).
- Memory: These systems are usually stateless or maintain short-term context within the session.
- Example tools:
- ChatGPT (OpenAI): Conversational agent.
- Midjourney: AI-generated visuals.
- GitHub Copilot: Code autocompletion.
Agentic AI
Agentic AI systems are designed to act autonomously in a goal-directed way. These systems perform complex multi-step tasks without the need for constant human guidance using their reasoning, planning, memory, and tool execution skills.
- How it works: When you give it a task (for example, “Fix bugs in this repository”), the AI divides it up into smaller tasks, decides what to do, uses tools, and does it on its own.
- Memory: Long-term persistent memory to track tasks, tools, and context.
- Example tools:
- AutoGPT: Multi-agent task execution.
- Devin AI: Full-stack developer agent.
- Meta CICERO: Negotiation and reasoning agent.
- ReAct-based agents: Plan-act-feedback loop implementations.
Generative AI vs. Agentic AI: What’s the Difference in 2026?
Understanding the basic differences between these systems helps CTOs in aligning the appropriate AI tech stack to their business use cases.
| Feature | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
| Input-Output Model | Prompt-based generation | Goal/objective-driven autonomy |
| Memory | Stateless or short-term | Persistent long-term memory (vector DBs) |
| Tool Use | Limited plugin/API access | Deep API integrations, browser, CLI, tools |
| Reasoning & Planning | One-shot or chain-of-thought (basic logic) | Multi-step reasoning, recursive planning |
| Feedback Loop | Human-in-the-loop | Self-feedback or environment-feedback capable |
| Integration Use Cases | Content creation, code assist, chatbot | Complex workflow automation, task orchestration |
- Input-Output Model: Generative AI functions like a very smart assistant; ask and receive. Agentic AI behaves more like an autonomous employee; assign a job, and it will plan and act.
- Memory: Generative AI has a limited memory capacity for previous decisions or conversations. For context-aware decision-making, agentic AI uses persistent memory.
- Reasoning & Planning: Generative AI answers based on patterns. Agentic AI reasons through sequences, backtracks if needed, and optimizes plans on the go.
- Feedback Loop: Human validation is necessary for generative AI. Agentic AI can detect success or failure conditions and adapt actions accordingly.
- Tool Use: Agentic AI can write code, execute it, scrape web pages, send emails, and access databases, like a developer with a toolbox.
Generative AI vs. Agentic AI: Real-World Business Use Cases in 2026
Use Cases of Generative AI
By 2026, generative AI will be used in many sectors by the majority of businesses.
- Marketing: Auto-generating blog content, product descriptions, and email campaigns.
- Product: Creating documentation, user manuals, and onboarding flows.
- Development: Suggesting code snippets, writing test cases, and commenting code.
Example: A SaaS company uses ChatGPT to auto-generate customer onboarding emails and Copilot to assist in backend logic.
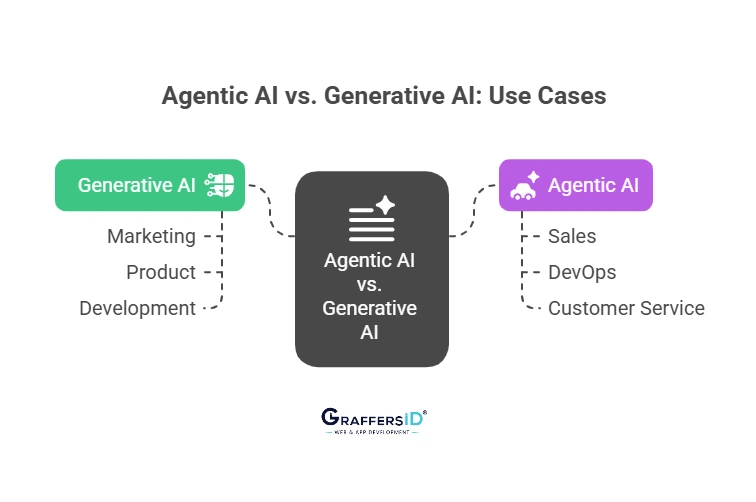
Use Cases of Agentic AI
Agentic AI moves beyond augmentation to autonomous task execution.
- Sales: Agents that research leads, enrich profiles, send emails, follow up, and book demos.
- DevOps: Automatically identifying server problems, executing commands, launching instances, and notifying stakeholders.
- Customer Service: Addressing grievances, giving reimbursements, and elevating only complicated problems.
Example: A logistics company deploys an agent that automatically checks shipping delays, updates internal systems, and notifies clients, all without the need for human intervention.
Insight: Generative AI boosts individuals. Agentic AI transforms systems.
Generative AI vs. Agentic AI: Which One Should Your Tech Team Invest in? (2026)
Choosing between generative and agentic AI depends on your company’s maturity, business goals, and operational pain points.
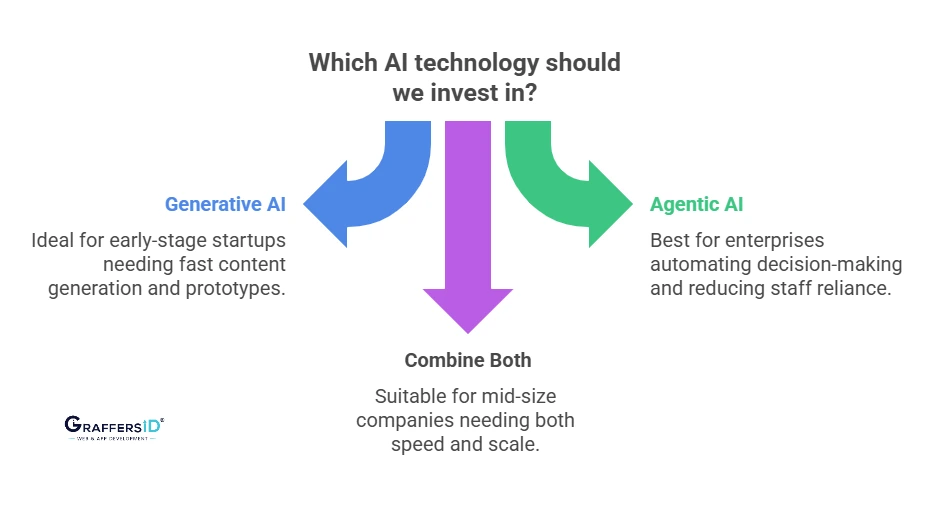
Early-Stage Startups
- Generative AI can help you speed up the go-to-market process for website text, investor decks, and prototypes.
- Agentic AI is unnecessary unless automation is essential to the product.
Mid-Size Companies
- Combine both: Use generative AI for internal productivity and agentic AI for targeted automation (e.g., support workflows, sales operations).
Enterprises
- Automates repeated decision-making, operates around the clock, and reduces reliance on staff members.
- For a secure deployment, combine with governance and observability tools.
Decision Flow Example:
- Need fast content generation: Generative AI
- Need process automation: Agentic AI
- Need both speed and scale: Combine both in hybrid architectures
Read More: Top 10 Generative AI Trends in 2026: How Enterprises Are Transforming With AI?
Cost, Risk & Compliance Comparison for 2026: Generative AI vs. Agentic AI
Generative AI
- Low implementation costs; only requires an API key (e.g., OpenAI, Claude, or Cohere).
- Excellent for internal tools, customer support augmentation, and MVPs.
- Risks:
- Hallucinations: Factual inaccuracies.
- Data security: Prompted data may leak sensitive info.
- Compliance: GDPR and HIPAA must be configured manually.
Agentic AI
- Higher cost of setup:
- Requires vector databases, orchestration tools (LangChain, AutoGen), APIs, observability tools, and test environments.
- Risks:
- Autonomy errors: Unauthorized behavior (such as data deletion).
- Role limitations and sandboxing are required.
- Extended testing and QA cycle to ensure secure automation.
Tip for CTOs: Use role-based execution boundaries, agent approval queues, and observability dashboards before giving agents real-world access.
Comparing ROI: Agentic AI vs. Generative AI 2026
| Metric | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
| Time to Deploy | Fast (1–3 weeks) | Moderate to Long (6–12 weeks) |
| Initial Investment | Low | Medium to High |
| Time to ROI | Immediate (1–2 months) | Medium-Term (3–6+ months) |
| ROI Growth Curve | Quick rise, then plateaus | Slow start, exponential after 6–12 months |
| Strategic Impact | Productivity boost | Operational transformation |
Conclusion: Choose the Right AI
Generative AI is a creative assistant that enables teams to think faster and execute more effectively. It excels in settings that require augmentation, communication, and idea generation.
Agentic AI is your autonomous employee, performing tasks from start to finish, freeing up bandwidth, scaling operations, and driving true digital transformation.
In 2026, the smartest AI strategies will combine both. But which one to lead with depends on your company’s goals, infrastructure readiness, and willingness to manage AI autonomy.
Ready to move beyond just generating ideas and start getting real work done with AI?
At GraffersID, we help startups and enterprises design, build, and deploy custom AI systems from GenAI-powered assistants to fully agentic autonomous task engines.