Artificial Intelligence (AI) in 2026 is no longer a futuristic concept; it is the driving force behind digital transformation across industries. From agentic AI agents and generative AI models to AI voice assistants, autonomous vehicles, and enterprise-scale automation, AI has moved beyond experimentation and is now a strategic necessity for businesses.
Whether in healthcare diagnostics, fraud detection, customer experience, or software development, AI systems are reshaping how enterprises operate, scale, and make decisions. As we move closer to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), understanding AI’s foundations, evolution, and practical applications is crucial for every decision-maker.
In this blog, we will explore:
- The latest definition of AI in 2026
- The evolution of AI from early research to generative and agentic AI
- The three major types of AI are Narrow, General, and Super AI
- Core AI technologies, including Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Generative AI, and Agentic AI
- Key benefits of AI in 2026
- Use cases and real-world applications across industries
What is Artificial Intelligence in 2026?
Artificial Intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to learn, reason, adapt, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. Unlike traditional software that follows fixed rules, AI systems leverage large datasets, neural networks, and real-time processing to improve performance autonomously.
In 2026, AI has advanced to include:
- Generative AI: Creating content, images, and simulations.
- Agentic AI: Autonomous AI agents capable of planning, reasoning, and executing tasks at scale.
- Industry-specific AI solutions: Powering finance, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and logistics with intelligent automation.
Read More: 7 Emerging AI Tools Every Tech Leader Should Know in 2026
Evolution of AI: 1950s to 2026
AI has evolved greatly since its launch. Let’s discuss how:
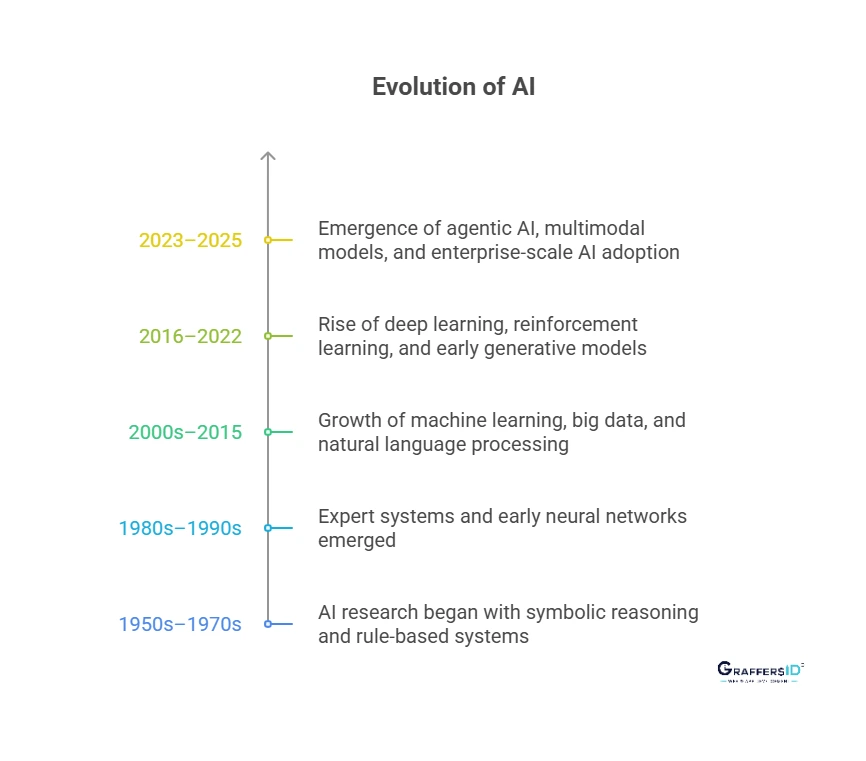
- 1950s–1970s: AI research began with symbolic reasoning and rule-based systems.
- 1980s–1990s: Expert systems and early neural networks emerged.
- 2000s–2015: Growth of machine learning, big data, and natural language processing.
- 2016–2022: Rise of deep learning, reinforcement learning, and early generative models.
- 2023–2026: Emergence of agentic AI, multimodal models (like GPT-4o, Gemini, and DeepSeek), and enterprise-scale AI adoption across industries.
- Future: Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), AI that can perform all human cognitive tasks.
Types of AI in 2026
Artificial Intelligence has three types. We will discuss each type of AI in detail, how it works, and its functions.
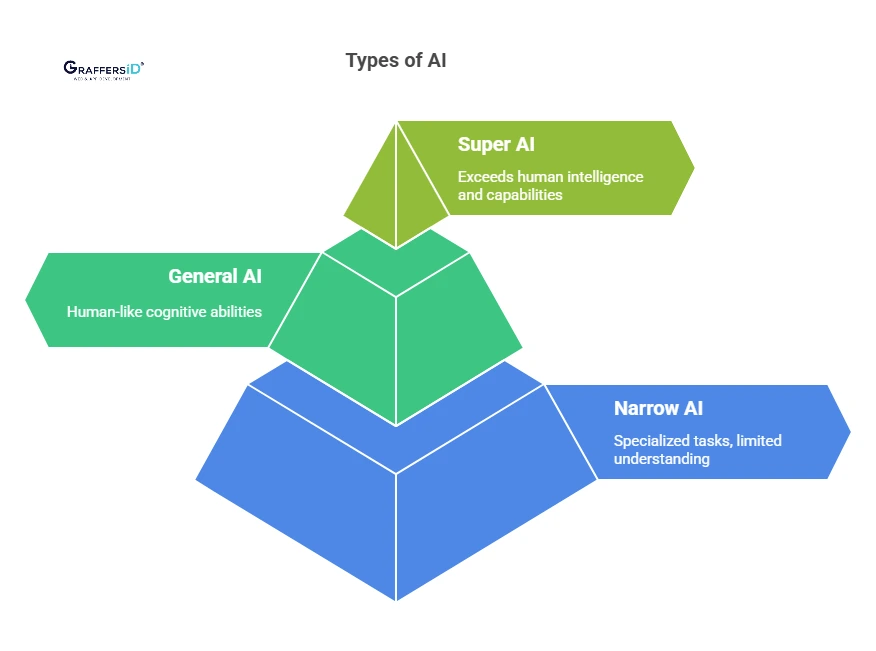
1. Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, refers to AI systems that are designed and trained for a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. These systems excel in performing predefined functions with a high level of accuracy. Examples of narrow AI are virtual personal assistants like Siri and Alexa, which can understand and respond to specific voice commands, and recommendation systems that suggest products or content based on user preferences.
Narrow AI is designed for specific tasks and cannot generalize beyond them. Examples include:
- Voice assistants: AI-driven tools like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant that respond to commands and perform tasks.
- Recommendation systems: AI that suggests products, movies, or music based on user preferences (e.g., Netflix, Amazon, Spotify).
- Chatbots and customer support AI: Automated customer service assistants that handle queries and provide support in real-time.
Limitations of Narrow AI:
-
Lacks true intelligence: It cannot think, reason, or understand emotions like humans.
-
Confined to specific domains: Cannot generalize knowledge to different tasks or areas.
-
Requires extensive training data: Performance depends on the quality and quantity of data used in training.
2. General AI (Strong AI)
General AI is a more advanced form of artificial intelligence with cognitive capacities similar to humans. Unlike narrow AI, which is confined to specific tasks, general AI is capable of understanding, learning, and applying knowledge across a wide range of tasks.
This type of AI has the potential to reason, solve problems, and engage in open-ended conversations. Although it is still theoretical, developments in deep learning and cognitive computing are making progress in that direction. General AI is capable of:
- Understanding and learning any task without being explicitly programmed.
- Exhibiting human-like reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
- Adapting to new challenges across multiple domains.
Limitations of General AI:
-
Complexity of Human Intelligence: Replicating the human brain’s learning process and adaptability is highly challenging.
-
Massive Computational Power: General AI requires immense processing capabilities and data storage.
-
Ethical and Security Concerns: If AI achieves human-like intelligence, ensuring its ethical use and control will be crucial.
3. Super AI (Artificial Superintelligence)
Super AI, also known as Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), will outperform human intelligence in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making. The concept of ASI raises important ethical questions and considerations about control, safety, and the impact on society. Some of the major issues are:
- Loss of human control over artificial intelligence systems.
- AI-powered decision-making exceeds human intelligence.
- AI autonomy raises ethical concerns.
Core AI Technologies in 2026
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is powered by some core technologies that allow machines to learn, process data, and provide insights. Three major AI technologies are:
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data and improve their performance without requiring additional programming. ML is classified into the following types:
- Supervised Learning: Trains models using labeled data (for example, spam detection and image recognition). The AI learns patterns from input-output pairs.
- Unsupervised Learning: Detects patterns in unlabeled data (for example, customer segmentation, anomaly detection). The AI identifies hidden structures in data.
- Reinforcement Learning: AI learns by interacting with its surroundings and getting input (for example, self-driving cars and AlphaGo). The AI optimizes activities based on benefits and penalties.
2. Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that processes complex patterns using artificial neural networks. These neural networks simulate the human brain’s structure, allowing AI models to learn from large amounts of unstructured data, such as images, audio, and text.
Applications of Deep Learning:
- Image and Speech Recognition: AI models used in security systems and social media platforms (e.g., Apple’s Face ID, Facebook’s photo tagging). AI-powered assistants like Siri and Google Assistant convert speech into text.
- 2. Autonomous Vehicles: AI-driven self-driving cars process visual data from cameras, detect objects, and make real-time driving decisions.
- 3. Healthcare Diagnostics: AI models analyze X-rays and MRI scans to detect diseases like cancer and pneumonia.
3. Generative AI
Generative AI models create new content, including text, images, music, and videos, by learning from existing data. These models use advanced deep learning techniques such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformers to generate realistic content.
Applications of Generative AI:
- Text Generation: Assists in content creation, article writing, and summarization.
- Image and Video Generation: Creates realistic images and videos from text descriptions.
- Music and Voice Generation: Generates human-like synthetic voices like famous artists.
4. Agentic AI
Agentic AI is the latest advancement in artificial intelligence, enabling systems to autonomously reason, plan, and execute end-to-end tasks without constant human input. Unlike traditional AI that depends on prompts, Agentic AI functions as a self-directed agent, capable of breaking down goals, making contextual decisions, and integrating with tools or applications to complete workflows.
Applications of Agentic AI:
- Autonomous Business Workflows: AI agents that handle customer queries, process transactions, and manage tasks across CRMs, ERPs, and enterprise platforms without human supervision.
- Personal AI Assistants: Advanced assistants that don’t just respond to commands but proactively manage calendars, book travel, negotiate contracts, or coordinate across apps.
- AI in Software Development: Agents that can plan, generate, debug, and deploy code with minimal input from developers, accelerating the SDLC.
- Enterprise Decision-Making: AI agents that analyze financial data, market trends, or supply chain conditions and independently recommend or execute strategies.
Read More: Agentic AI vs. Generative AI: Key Differences CTOs Must Know in 2026
Benefits of AI in 2026
1. Enterprise-Scale Automation
AI in 2026 enables businesses to automate millions of transactions, workflows, and customer interactions simultaneously. From BFSI enterprises processing 10,000+ calls a day to global e-commerce giants managing supply chains, AI ensures operations run seamlessly with minimal human intervention. This not only reduces costs but also accelerates efficiency at scale.
2. Smarter Data-Driven Decision-Making
With advanced predictive analytics and real-time intelligence, AI helps leaders reduce risks and maximize ROI. Enterprises can now process multi-source, multimodal data (text, voice, image, and sensor data) for strategic decisions, whether predicting stock market trends, optimizing logistics, or personalizing customer journeys.
3. Hyper-Personalization at Scale
AI in 2026 goes beyond generic recommendations to deliver deeply personalized experiences. From e-commerce platforms suggesting tailored products to healthcare providers creating patient-specific treatment plans, hyper-personalization powered by AI enhances customer engagement, trust, and outcomes.
4. 24/7 Intelligent Operations
AI systems don’t require breaks, making them indispensable for round-the-clock enterprise operations. Whether managing cybersecurity monitoring, financial transactions, or global customer support, AI ensures businesses remain competitive and responsive across time zones without downtime.
5. Error Reduction & Enhanced Compliance
AI reduces human errors by performing tasks with consistent accuracy and also supports regulatory compliance in industries like finance, BFSI, and healthcare. In 2026, enterprises rely on AI to detect anomalies, prevent fraud, and maintain compliance with evolving data security laws, ensuring both accuracy and trust.
AI Use Cases Across Industries in 2026
The following is a detailed explanation of how AI is used across different industries:
1. AI in Healthcare
AI is reshaping the healthcare industry by enhancing diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care.
a. AI-Powered Diagnostics
AI programs analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to detect cancer, fractures, and infections. AI models trained on large datasets can identify abnormalities with great accuracy, sometimes outperforming human radiologists.
For example, Google’s DeepMind created an AI model that can identify more than 50 eye conditions based on retinal scans.
b. Drug Discovery and Personalized Treatment
AI speeds up drug research by analyzing complex biological data to find possible drug candidates. It also helps in personalizing treatments depending on an individual’s genetic composition, hence improving therapy effectiveness.
For example, IBM Watson uses AI to provide personalized cancer treatments based on a patient’s medical history and genetic profile.
c. AI Chatbots for Mental Health Support
AI-powered chatbots and virtual therapists help people with mental health issues by engaging them in conversations, providing coping skills, and identifying signs of mental illness. These AI-powered solutions make therapy easier and more affordable.
Woebot and Wysa, for example, are AI chatbots that promote mental health through cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
2. AI in Finance
Financial organizations use AI for various banking offerings, such as:
a. Fraud Detection and Risk Assessment
AI monitors financial transactions in real time to detect unusual activities like identity theft and money laundering. Machine learning models analyze spending patterns and identify unusual events that may indicate fraud.
For instance, PayPal and Mastercard use AI to detect fraudulent transactions and prevent illegal access.
b. AI-Powered Investment Strategies and Trading
AI-powered trading systems analyze market trends, historical data, and real-time financial information to make investment decisions. These systems can execute high-frequency trades much more quickly than human dealers.
c. Personalized Financial Planning
AI-powered financial advisors evaluate users’ income, expenses, and financial goals to make personalized investment and savings advice.
For example, robo-advisors such as Betterment and Wealthfront provide automated portfolio management based on AI analysis.
Read More: What Is Open Source AI in 2026? Benefits, Top Open-Source AI Models, Challenges, and Future Trends
3. AI in E-Commerce
AI in e-commerce improves the online shopping experience by offering customized suggestions, automating customer service, and managing inventory. These can be studied in detail below:
a. Personalized Shopping Suggestion Engines
AI analyzes customer behavior, purchase history, and preferences to suggest items that are tailored to each unique user, increasing sales and engagement.
For example, Amazon and Flipkart use AI to recommend products based on browsing history and previous purchases.
b. AI Chatbots for Customer Engagement
AI-powered chatbots respond to consumer inquiries, process orders, and resolve issues in real time, ensuring a smooth shopping experience.
Chatbots, such as Shopify’s Kit and Drift, help clients by answering questions and offering product recommendations.
c. Automated Inventory Management
AI analyzes sales patterns, seasonal trends, and supply chain data to forecast demand changes and optimize inventory levels.
For example, Walmart uses AI to forecast demand promptly and restock products, removing overstocking and stockout issues.
4. AI in Manufacturing
AI-driven automation boosts efficiency, reduces downtime, and maintains product quality in manufacturing.
a. Predictive Maintenance for Machinery
AI analyzes machinery performance through sensors and predicts when machinery is likely to break down, allowing for timely maintenance and decreasing unexpected downtime.
For example, General Electric uses AI-powered predictive maintenance to increase operational efficiency at factories.
b. AI-Driven Quality Control
Computer vision and machine learning algorithms scan products on assembly lines to identify defects and ensure high-quality standards.
For example, Tesla uses AI-powered cameras to identify any issues in car parts during the production process.
c. Robotics in Assembly Lines
Complex assembly tasks are accurately completed by AI-powered robots, speeding up production and reducing the cost of human labor.
For example, BMW and Ford use AI-powered robots for their assembly tasks.
5. AI in Software/Web Development
AI is transforming the web and software development industry by automating coding, enhancing cybersecurity, and optimizing user experience.
a. AI-Assisted Software Development
AI-powered tools assist developers by generating code, suggesting optimizations, and automating debugging. AI can analyze existing codebases and predict the best ways to optimize performance and reduce bugs.
Example: GitHub Copilot and Tabnine use AI to suggest code snippets and autocomplete functions for developers.
b. AI for Cybersecurity and Threat Detection
AI-powered security systems analyze network traffic and detect potential cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, and DDoS attacks, in real-time. AI-driven anomaly detection helps identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Example: Darktrace and CrowdStrike use AI to detect and neutralize cyber threats before they cause damage.
c. Automated Testing and Bug Fixing
AI-powered testing tools automate software testing, reducing manual efforts and speeding up the development cycle. AI can identify errors, predict potential bugs, and suggest fixes, improving software reliability.
Example: AI-driven testing platforms like Testim and Applitools automate UI and functional testing in software development.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence in 2026 has become a core enabler of innovation, transforming industries at scale. Businesses must now focus on responsible adoption, ethical AI, and compliance-driven deployment to leverage their full potential.
At GraffersID, we help enterprises build AI-powered applications, automation workflows, and custom AI solutions to drive growth and efficiency. If you’re looking to develop an AI-powered solution, partner with GraffersID to hire expert AI developers and speed up your innovation.