In 2026, data is the new currency, from online shopping patterns to health records and biometric identifiers, our digital footprints are constantly collected, analyzed, and monetized. While this powers personalization and innovation, it also exposes individuals and organizations to privacy breaches, AI-driven cyberattacks, and surveillance risks.
With AI now at the heart of data collection, security, and compliance, protecting personal data is no longer optional; it’s a fundamental digital right. This blog will break down:
- What does data privacy mean in 2026?
- Key differences between data privacy and data protection.
- AI-driven risks and challenges.
- Best practices for individuals, startups, and enterprises.
- The latest privacy laws and compliance requirements.
- How you can use AI and advanced security tools to stay safe.
What is Data Privacy in 2026?
Data privacy refers to the responsible handling, storage, and use of personal information, from basic identifiers (name, email, location) to highly sensitive data (financial records, genetic information, biometric scans).
In 2026, data privacy is no longer just about “who has your data”; it’s also about how AI systems process, analyze, and repurpose it. With the rise of generative AI and agentic AI, companies now collect and train models on user data, making privacy more complex than ever before.
Why is Data Privacy Critical in 2026?
Data privacy is of much importance for several reasons:
- AI-Powered Data Exploitation: Advanced AI can infer private details (location, health conditions, habits) from minimal digital traces.
- Identity Theft & Deepfake Fraud: Cybercriminals now use AI-generated deepfakes and voice cloning for scams.
- Regulatory Pressures: Global frameworks like GDPR, CCPA, and India’s DPDP Act (2023) enforce strict compliance.
- Consumer Trust & Reputation: Users expect a privacy-first design; violations result in reputational and financial loss.
- Ethical Responsibility: Beyond laws, businesses must commit to responsible AI and ethical data use.
Who Collects Your Data and Why?
Data is collected by a wide range of organizations for different purposes, which include:
- AI-powered Companies & Platforms: Gather data for personalized recommendations, predictive analytics, and training AI models.
- Marketers & Advertisers: Use AI-driven targeting for hyper-personalized ads.
- Social Media & Entertainment Apps: Collect behavioral data to train recommender algorithms and boost engagement.
- Governments & Institutions: Rely on data for national security, AI-driven surveillance, and policy-making.
- Service Providers (Telecom, ISPs, Cloud): Monitor activity for billing, optimization, and fraud detection.
Given how much personal data is collected, it’s vital to know how to protect our information.
Read More: Biggest Cybersecurity Threats And How to Protect Yourself
Data Privacy vs. Data Protection in 2026
Data Privacy is about rights and control. It controls who has access to your data and under what conditions. It focuses on policies and user expectations regarding the use of their personal information.
Data Protection is the organizational and technical steps taken to protect data from theft, corruption, and unauthorized access. This includes firewalls, access controls, encryption, and frequent security assessments.
| Aspect | Data Privacy | Data Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | User rights, choices & control over data use | Safeguards preventing breaches & misuse |
| Focus Area | Who can access data, under what terms | How data is secured (AI & tech-driven) |
| Objective | Give individuals autonomy & transparency | Defend data from threats (AI & cyberattacks) |
| Concerned With | Consent, ethical AI use, legal frameworks | Encryption, AI threat detection, zero-trust models |
| Example | Gaining consent before AI training on user data | Using AI-based intrusion detection to block hackers |
| Legal Frameworks | GDPR, CCPA, DPDP Act (India), AI Act (EU 2026) | ISO/IEC 27001, NIST, AI security standards |
| Enforced By | Privacy officers, compliance teams | Cybersecurity & AI security experts |
Together, privacy and protection form a comprehensive approach: privacy defines the ‘why’ and ‘who’ of data usage, while protection ensures the ‘how’ is secure and compliant.
Key Principles of Data Privacy in 2026
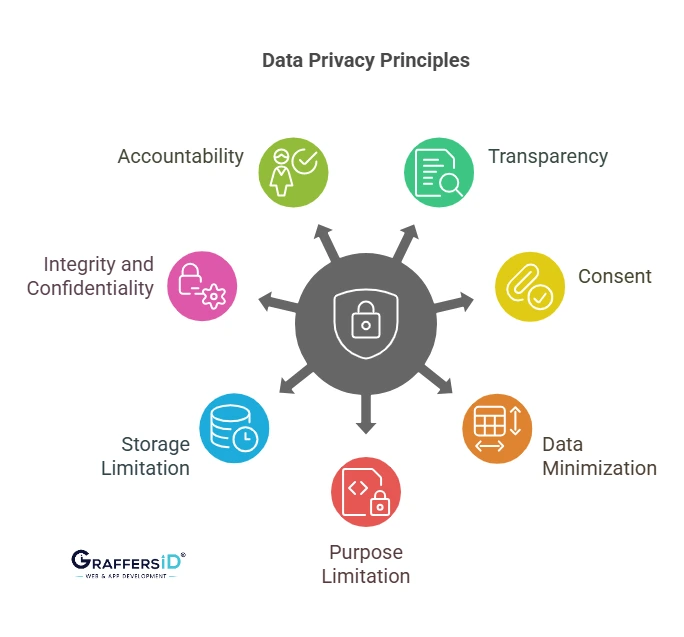
- Transparency: Users must know when AI models use their data.
- Consent: AI platforms must obtain clear opt-in before training on personal data.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the minimum data needed, not entire digital identities.
- Purpose Limitation: Data collected for one purpose (e.g., healthcare) shouldn’t be reused for another (e.g., advertising).
- Storage Limitation: Use ephemeral storage and auto-delete policies.
- Integrity & Confidentiality: Employ AI-driven anomaly detection, end-to-end encryption, and zero-trust security models.
- Accountability: Businesses must prove AI model transparency, explainability, and ethical compliance.
AI-Driven Data Privacy Challenges in 2026
In the modern era, data privacy is increasingly at risk due to various challenges that arise from the widespread collection, sharing, and storage of personal information. Below are some common cyber challenges:
-
AI-Powered Surveillance: Governments and companies use AI to track online behavior.
-
AI-Enhanced Data Breaches: Hackers leverage AI to crack passwords, automate phishing, and bypass security.
-
Third-Party AI Sharing: Many businesses share data with external AI vendors and cloud providers, often without user awareness.
-
Dark Patterns with AI UX: AI-powered apps trick users into oversharing data via nudges and manipulative consent flows.
-
Lack of Digital Literacy: Many users don’t fully understand AI privacy policies or how their data trains algorithms.
Read More: AI and Cybersecurity in 2026: Emerging Threats, Global Trends & Cybersecurity Best Practices
Startups & Data Privacy in 2026
Startups are more at risk of cyberattacks and data breaches than larger organizations because they lack a strong cybersecurity infrastructure and depend heavily on new technology. According to reports, 43% of cyberattacks are targeted at small and medium-sized organizations, including startups.
Startups face heightened risks due to:
- Limited budgets for AI-driven cybersecurity.
- Heavy reliance on third-party SaaS and cloud providers.
- Handling sensitive customer data (payments, biometrics, health info).
Common AI-Era Risks for Startups:
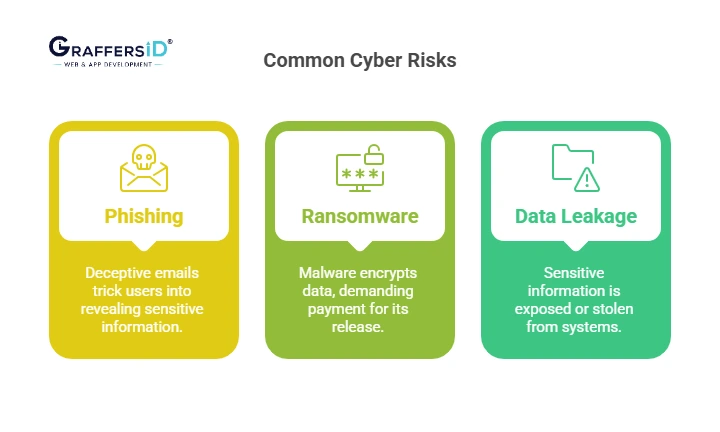
1. AI Phishing
Phishing attacks, which account for more than 90% of all cyberattacks, trick victims into disclosing personal information such as usernames and passwords, frequently via fake messages and URLs.
2. Ransomware 2.0
Ransomware is a type of virus that encrypts or locks down a company’s important data until the victim pays a fee. Hackers prefer payments in the form of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin because they are more difficult to trace than cash or online transactions.
3. Data Leakage in AI APIs
A data leak happens when sensitive information, such as user credentials or payment card information, is accidentally or purposely disclosed to the public.
As a start-up owner, knowing these threats is the first step toward securing your business and protecting your data.
Risks of Oversharing on Social Media (2026)
In today’s digital age, we freely publish personal information on social media and other online platforms without fully understanding the impacts. While these platforms are convenient, they also pose serious hazards to our privacy, security, and financial well-being. Here are some risks of excess sharing:

-
AI Identity Theft: Deepfake fraud using your public posts.
-
Reputation Damage: Old posts resurfacing via AI search tools.
-
Targeted Manipulation: AI-driven propaganda influencing decisions.
-
Legal Risks: Violations of data privacy laws due to accidental sharing.
Tip: Use privacy-first AI tools (VPNs with AI threat detection, encrypted messaging apps, decentralized ID solutions).
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Privacy
To ensure the security and privacy of your data, it’s essential to implement robust practices that mitigate the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. By following these practices, you can significantly enhance your data protection measures. Here are some best practices:
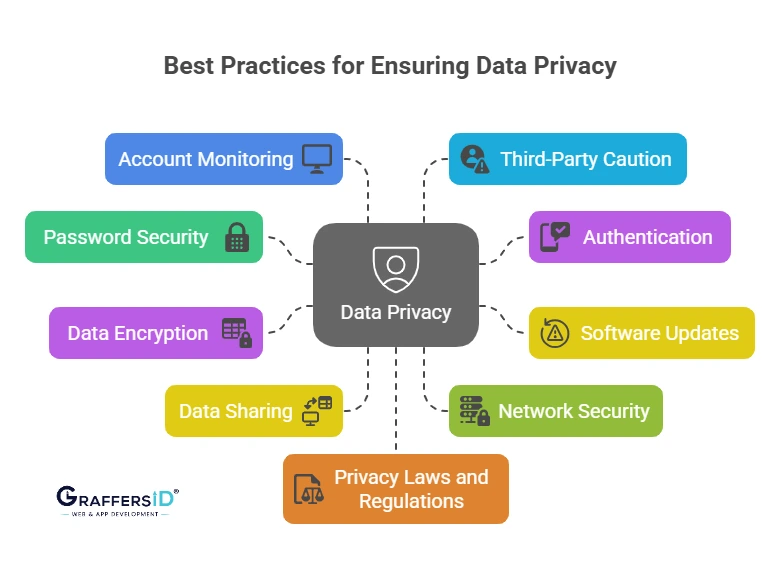
1. Use AI-Generated Strong Passwords
- Strong passwords are your first line of defense against unauthorized access. Use a combination of letters (upper and lowercase), numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easy-to-guess passwords like “12345678” or “password.”
- Consider using a password manager to store complex passwords securely, so you don’t have to remember them all.
2. Enable MFA & Biometric Authentication
- Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to verify your identity using a second method (e.g., a code sent to your phone) in addition to your password.
- Enable 2FA on all your accounts where possible, especially for critical services like email, banking, and social media.
3. Keep AI Systems Updated
- Regularly update your software, applications, and operating systems. Developers frequently provide updates to address issues and enhance security features.
- Enable automatic updates wherever possible to ensure you’re constantly protected from the latest threats. If you still have downloaded malware that endangers your data, click here to see how to remove it.
4. Encrypt Data End-to-End
- Data encryption ensures that even if your data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it cannot be read without the encryption key.
- Encrypt files, emails, and backups to safeguard your sensitive information, especially for businesses dealing with customer or financial data.
5. Limit Data Sharing
- Pay close attention to the information you post online, especially on public forums and social media. Avoid posting sensitive personal information like your full name, address, phone number, or financial details.
- For businesses, only collect the data that’s necessary for your operations and ensure that it’s stored securely.
6. Use AI-Enhanced Security Tools
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks to access sensitive data. Public networks are more vulnerable to attacks, making it easier for cybercriminals to intercept your data.
- Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to encrypt your internet traffic when accessing sensitive data over any network, including public Wi-Fi.
7. Secure Networks with AI Firewalls & VPNs
- Check your social media accounts, credit reports, and bank accounts frequently for any unusual activity. Early detection can help you mitigate potential damage from identity theft or fraud.
- Install anti-malware software to protect your devices from malicious attacks.
8. Audit Third-Party AI Apps
- Be selective about the third-party apps and services you use. Before granting access to your data, carefully read their privacy policies and permissions.
- Revoke access to apps and services that you no longer use or trust.
9. Continuous Education
- Stay informed about the latest web development trends, shaping data privacy regulations and security threats. Cybersecurity best practices evolve quickly, so continuous learning is key to protecting yourself.
- If you run a business, regularly educate your employees on data privacy and security best practices. Ensure that they understand the importance of safeguarding sensitive information.
10. Follow Global Compliance
- Familiarize yourself with data privacy laws like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). Ensure that your data practices comply with applicable regulations, especially for businesses that handle customer data.
- Implement privacy policies that respect the rights of individuals and ensure transparency about how data is collected, used, and stored.
Read More: Boost Your Startup Cybersecurity with These Powerful Tips
Key Data Privacy Regulations in 2026
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, data privacy and protection have become top priorities for businesses and individuals alike. Governments worldwide have enacted various regulations to safeguard personal information and ensure that businesses respect users’ privacy rights. Some important key regulations to keep in mind are:
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR, introduced by the European Union in 2018, is one of the most comprehensive data protection regulations globally. It applies to businesses that collect or process personal data of individuals located in the EU, regardless of where the company is based.
Key Features
- Consent: Organizations must obtain clear, explicit consent from individuals before processing their personal data.
- Rights of Individuals: Individuals have the right to access, rectify, delete, and restrict the processing of their data. They also have the right to object to certain types of data processing and to data portability.
- Data Breach Notification: Businesses must notify authorities and affected individuals of a data breach within 72 hours.
- Penalties: Non-compliance with the GDPR can result in hefty fines of up to 4% of global annual turnover or €20 million (whichever is greater).
2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA, enacted in 2020, applies to businesses operating in California or those that collect personal data of California residents. The law is designed to provide more control over personal data to California residents.
Key Features
- Right to Know: Consumers can request businesses to disclose the personal data they collect, the purpose of its collection, and how it is used or shared.
- Right to Delete: Consumers have the right to request the deletion of their personal data, subject to certain exceptions.
- Right to Opt-Out: Consumers can opt out of the sale of their personal information to third parties.
- Non-Discrimination: Businesses cannot discriminate against consumers for exercising their rights under the CCPA.
- Penalties: The CCPA allows for fines of up to $2,500 per violation and $7,500 per intentional violation.
Conclusion
In 2026, data privacy is inseparable from AI security. With cybercriminals and organizations both leveraging AI, individuals and businesses must adopt privacy-first strategies, AI-enhanced defenses, and global compliance practices.
At GraffersID, we help enterprises and startups build secure, AI-ready websites and applications with privacy by design, robust encryption, and compliance with global regulations.
Partner with GraffersID to build future-ready, privacy-first solutions.