In 2026, AI voice assistants have moved far beyond simple command-and-response tools like Siri or Alexa. By 2030, the AI voice assistant market is expected to surpass USD 15.87 billion, doubling from 2024. Today, they power the majority of the business operations, reshaping customer engagement, workforce automation, and business intelligence. With natural, human-like conversations, multilingual fluency, and emotion-aware responses, voice assistants are no longer just futuristic add-ons; they’ve become essential business tools.
For startups and enterprises alike, building an AI voice assistant in 2026 means blending the latest speech recognition models, large language models (LLMs), and text-to-speech (TTS) technologies with smart integrations into CRMs, ERPs, and cloud platforms. But where do you start? What technology stack should you choose?
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the complete process of building an AI voice assistant in 2026, from defining its core purpose to training, testing, deploying, and continuously optimizing it.
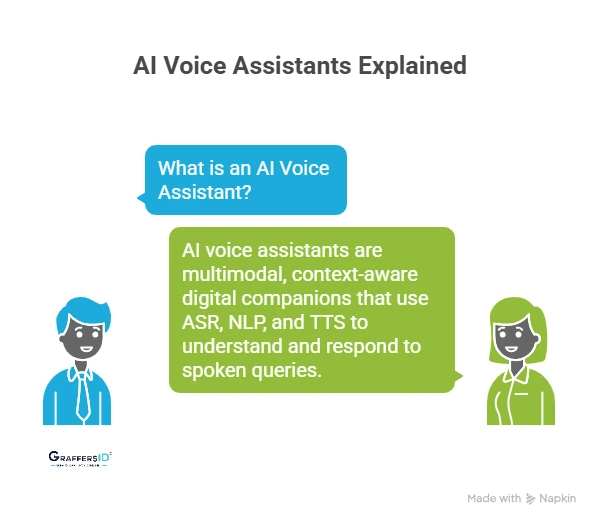
What is an AI Voice Assistant in 2026?
AI voice assistants have evolved into multimodal, context-aware digital companions. Unlike earlier rule-based systems, 2026 assistants leverage:
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Converts spoken words into text using models like OpenAI WhisperX, Google Chirp, or NVIDIA Riva.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Large Language Models (LLMs): Understands context, intent, and complex queries via GPT-5, LLaMA 3.1, or Anthropic Claude 3.5.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) with Emotional AI: Generates natural, human-like responses using Amazon Polly Neural, ElevenLabs, or OpenAI Voice Engine.
Unlike chatbots, voice assistants maintain multi-turn context and support real-time, conversational engagement. They’re increasingly deployed in enterprise settings where voice-driven workflows reduce friction and speed up operations.
Read More: What is an AI Voicebot? How Voicebots Work, Benefits & Use Cases for Businesses in 2026
Voice Assistants vs. Chatbots in 2026
- Chatbots: Primarily text-based, ideal for structured workflows like FAQs.
- Voice Assistants: Contextual, hands-free, multimodal (voice + visual), and capable of complex tasks.
Example: A chatbot may confirm your order, while a voice assistant can check stock levels, process payment, and update CRM records in real time.
Use Cases of AI Voice Assistants in 2026
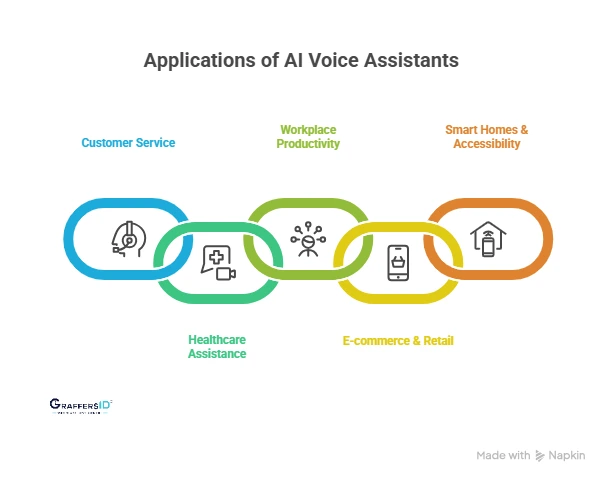
1. Customer Service & Virtual Agents:
Companies use AI voice assistants to manage customer queries, automate FAQs, and provide 24/7 multilingual support, reducing wait times and improving satisfaction.
2. Healthcare Assistance:
Patients use voice AI to book appointments, track health data, and get medication reminders, while doctors rely on it for quick record access and AI-powered documentation.
3. Workplace Productivity:
Enterprises integrate voice assistants into tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams for meeting scheduling, note-taking, and instant data retrieval, boosting efficiency.
4. E-commerce & Retail:
Voice shopping is on the rise; users can search, compare, and purchase products hands-free, while businesses leverage assistants for personalized recommendations.
5. Smart Homes & Accessibility:
From controlling smart appliances to helping people with disabilities navigate devices, AI voice assistants make homes smarter and technology more inclusive.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building an AI Voice Assistant in 2026
Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to building an AI voice assistant in 2026:
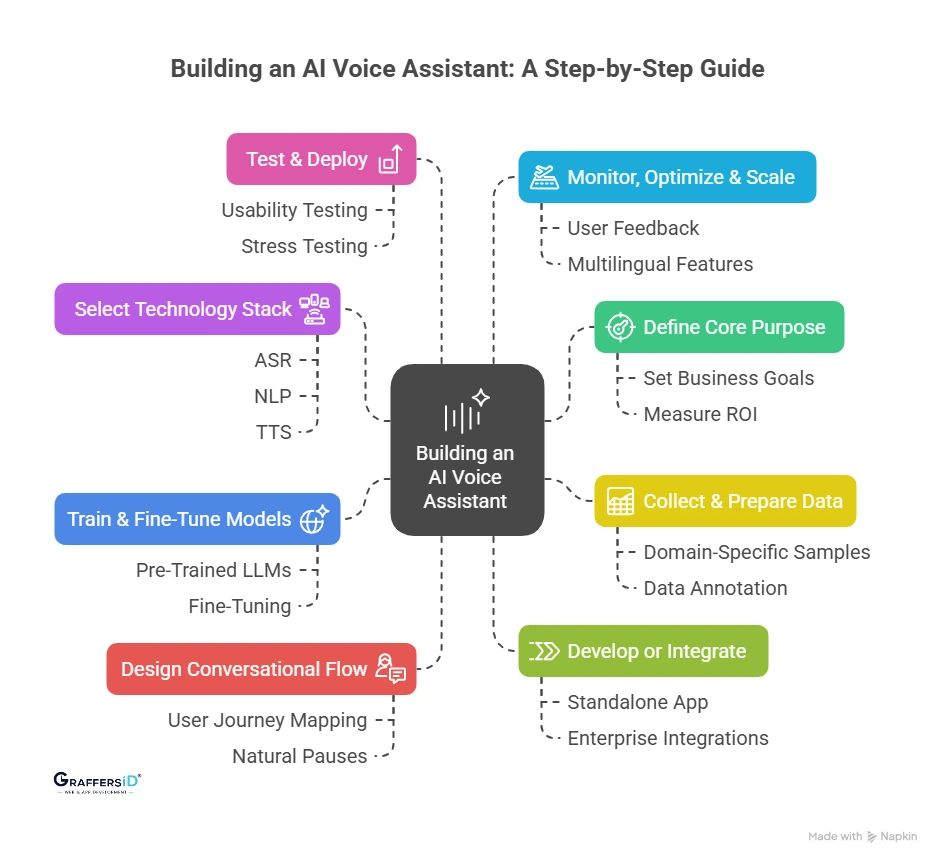
Step 1: Define the Core Purpose of Your AI Voice Assistant
Before touching technology, clarify the business problem your voice assistant will solve.
- Set business goals: Is it for customer support (24/7 FAQs), sales enablement (lead qualification, product demos), or internal automation (HR queries, IT helpdesk)?
- Start small, scale later: Instead of building a general-purpose AI, begin with one high-value use case. Example: Automating tier-1 customer queries before expanding to voice-driven CRM integration.
- Measure ROI: Define KPIs like average handling time reduction, customer satisfaction (CSAT), or cost per resolved query.
Read More: How to Build an AI Voice Agent in 2026: Step-by-Step Guide, Tools, and Future Trends
Step 2: Select the Right Technology Stack (2026 Edition)
Choosing the right tech stack ensures your AI voice assistant delivers accuracy, speed, and natural human-like interactions.
- ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition): WhisperX, Google Speech-to-Text, NVIDIA Riva.
- NLP / LLMs (Natural Language Processing): GPT-5, Claude 3.5, LLaMA 3.1, or open-source Rasa.
- TTS (Text-to-Speech): ElevenLabs, OpenAI Voice Engine (emotional & multilingual).
- Cloud AI Platforms: AWS AI, Azure Cognitive Services, and Google Cloud Vertex AI.
- Frameworks for Voice-First Development: LiveKit Agents, Jovo, and BotPress for voice-first applications.
Step 3: Collect & Prepare Training Data
Data quality directly impacts accuracy and user satisfaction.
- Use domain-specific speech samples (finance, healthcare, retail).
- Ensure diversity in accents, languages, and noise environments.
- Annotate data with metadata (timestamps, emotional tone, and interruptions).
💡 Tip: If you don’t have proprietary data, leverage synthetic voice datasets generated via advanced TTS models.
Step 4: Train & Fine-Tune AI Models
Training from scratch is expensive; fine-tune pre-trained LLMs and ASR models for cost efficiency.
- Leverage pre-trained LLMs (saves cost & time).
- Fine-tune with industry-specific vocabulary & workflows.
- Evaluate with Word Error Rate (WER) & conversation success rates.
Step 5: Design Conversational Flow
Great AI voice assistants feel human-like, empathetic, and frictionless.
- Map user journeys with tools like UXpressia or Miro.
- Build for interruptions, clarifications, and natural pauses.
- Keep responses concise, contextual, and empathetic.
- Always provide clarification prompts or human handoff options when AI is unsure.
Step 6: Develop or Integrate Your Voice Assistant
Decide whether to build a standalone AI assistant or integrate with existing systems.
- Standalone App Development: Build with Rasa, Python, or Node.js.
- Enterprise Integrations: Connect to CRM (Salesforce, HubSpot), ERP (SAP, Oracle), or IT helpdesks (ServiceNow).
- Use APIs like Twilio or Microsoft Voice API for telephony integration.
Step 7: Test & Deploy the Voice Assistant
A voice AI that fails in accuracy or usability won’t scale.
- Usability Testing: Ensure natural, frustration-free conversations.
- Stress Testing: Simulate peak query loads (thousands of concurrent calls).
- ASR Accuracy Checks: Aim for <5% Word Error Rate for enterprise adoption.
- A/B Testing: Compare conversational variations for better engagement.
Read More: AI Voice Generators in 2026: How Enterprises Are Using Text-to-Speech to Scale Communication
Step 8: Monitor, Optimize & Scale
Building is only step one; continuous optimization keeps your AI competitive.
- Collect voice feedback directly from users (“Did this answer your question?”).
- Expand to multilingual, multimodal, and emotion-aware features.
- Implement end-to-end encryption, compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA), and regular audits.
Future Trends of AI Voice Assistants (2026 & Beyond)
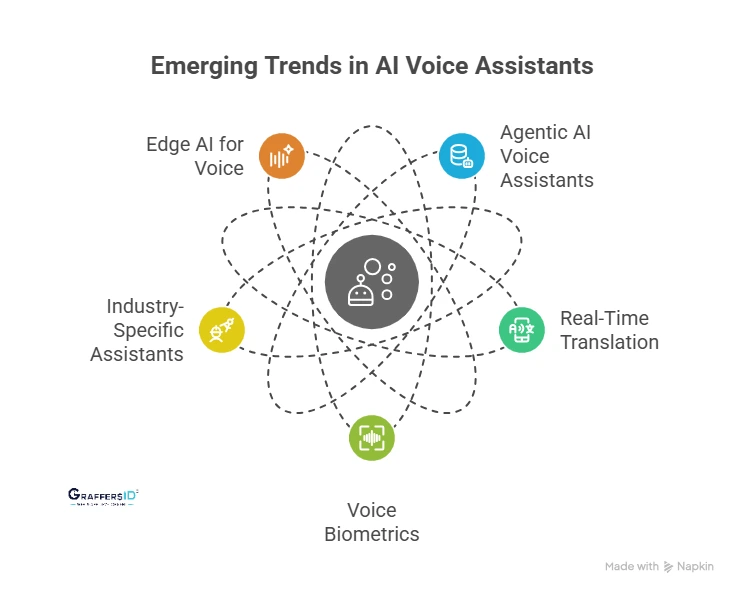
- Agentic AI Voice Assistants: Autonomous assistants that act on behalf of users (e.g., booking, reporting, and approvals).
- Real-Time Translation: Voice-to-voice AI translates conversations across languages instantly.
- Voice Biometrics: Secure, voice-based authentication replacing passwords.
- Industry-Specific Assistants: Verticalized solutions in healthcare, legal, finance, and education.
- Edge AI for Voice: Running assistants directly on devices for low-latency, privacy-first experiences.
Conclusion
AI voice assistants in 2026 are no longer experimental; they’re a business necessity for companies aiming to enhance customer experience and reduce operational costs. From advanced speech recognition to emotion-aware responses and multilingual capabilities, today’s assistants can bridge the gap between humans and machines.
If you’re considering developing a future-ready AI voice assistant but are unsure where to start, GraffersID can help. With our expertise in AI development, custom software, and remote teams, we’ve helped startups and enterprises build scalable, secure, and intelligent solutions.