Artificial intelligence is no longer about building smarter standalone models; it’s about enabling collaborative ecosystems of AI agents. This shift has given rise to Multi-Agent Systems (MAS), where multiple autonomous agents work together, share knowledge, and solve complex problems that single agents or monolithic systems struggle to manage.
In 2026, MAS has become central to agentic AI, AI copilots, and LLM-driven collaboration, powering industries from autonomous transportation to intelligent supply chains. Imagine fleets of AI-driven vehicles coordinating in real time, or AI agents negotiating supply chain contracts within seconds; this is the promise of multi-agent systems.
This guide explains the core concepts, architectures, benefits, and industry applications of MAS, highlighting why they are shaping the future of AI in 2026.
What is a Multi-Agent System (MAS)?
A multi-agent system is a distributed network of autonomous agents, software programs, AI bots, physical robots, or sensors that interact with each other and their environment to achieve individual or collective goals. Unlike traditional AI setups that rely on centralized control, MAS leverages distributed decision-making, making it more scalable, adaptive, and resilient.
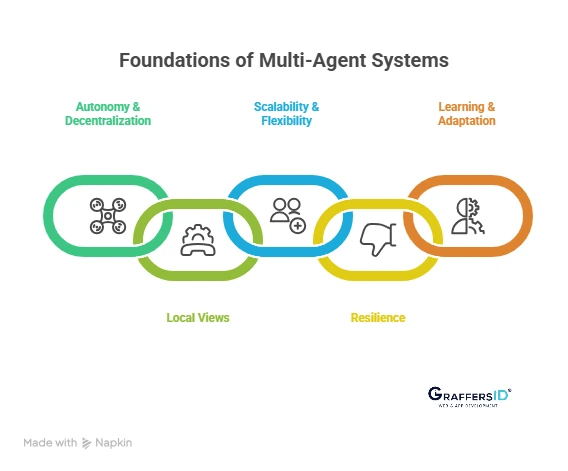
Key Features of Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) in 2026
- Autonomy & Decentralization: Each agent makes independent decisions without a central authority.
- Local Views: No single agent sees the entire system, forcing collaboration for efficiency.
- Scalability & Flexibility: New agents can join or leave without disrupting the system.
- Resilience: If one agent fails, others continue functioning, ensuring robustness.
- Learning & Adaptation: With advancements in LLMs and reinforcement learning, agents now learn from interactions, share insights, and continuously optimize performance.
This distributed intelligence approach mirrors human teamwork, where different specialists contribute unique skills toward solving complex challenges.
Read More: What Are Multi-Modal AI Agents? Features, Enterprise Benefits & Use Cases (2026 Guide)
Architectures and Structures of Multi-Agent AI Systems
The performance of MAS depends on how agents are structured and connected. In 2026, organizations use hybrid architectures powered by workflow orchestrators and LLM-enabled agent frameworks.
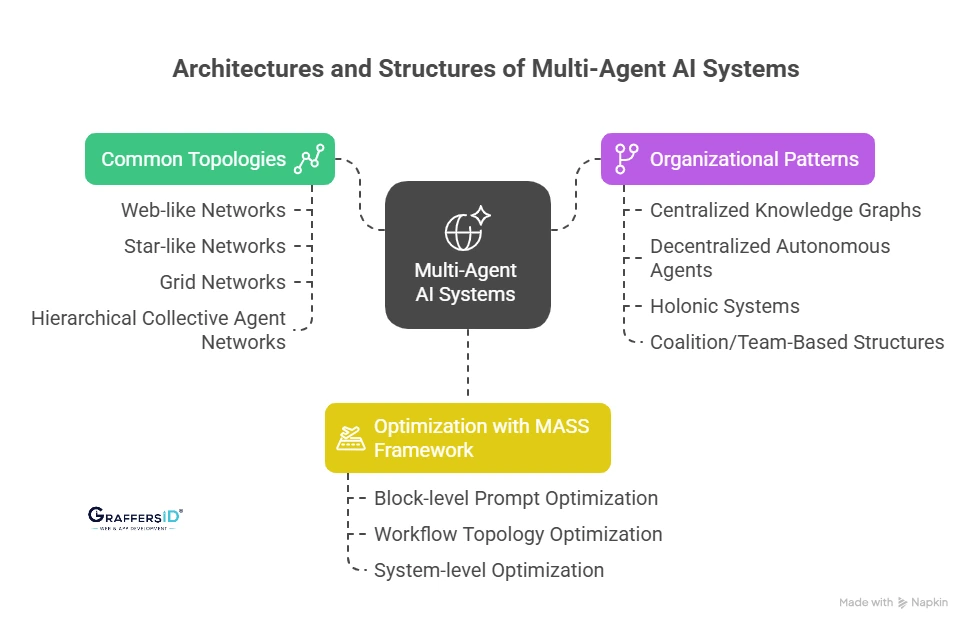
Types of Network Topologies in Multi-Agent Systems
- Web-like Networks: Every agent connects with all others for high collaboration.
- Star-like Networks: A central hub mediates communication (often seen in enterprise AI copilots).
- Grid Networks: Agents only interact with neighbors, useful in logistics and swarm robotics.
- Hierarchical Collective Agent Networks (HCAN): Combine layered hierarchies with autonomy for large-scale coordination.
Organizational Structures of Multi-Agent Systems in 2026
- Centralized Knowledge Graphs: All agents reference a shared LLM-powered knowledge base.
- Decentralized Autonomous Agents (DAA): Agents operate independently, relying on peer-to-peer negotiation (popular in blockchain + AI integrations).
- Holonic Systems: Nested hierarchies where sub-agents self-organize and collaborate.
- Coalition/Team-Based Structures: Agents dynamically form temporary groups to solve domain-specific tasks.
How Multi-Agent Systems Use the MASS Framework for Optimization?
The Multi-Agent System Search (MASS) framework now integrates AI workflow optimization with three layers:
- Block-level prompt optimization (agent task instructions)
- Workflow topology optimization (how agents connect)
- System-level optimization (orchestration for efficiency at scale)
This modular design ensures MAS can handle everything from AI copilots for enterprises to autonomous IoT ecosystems.
Benefits of Multi-Agent Systems in 2026
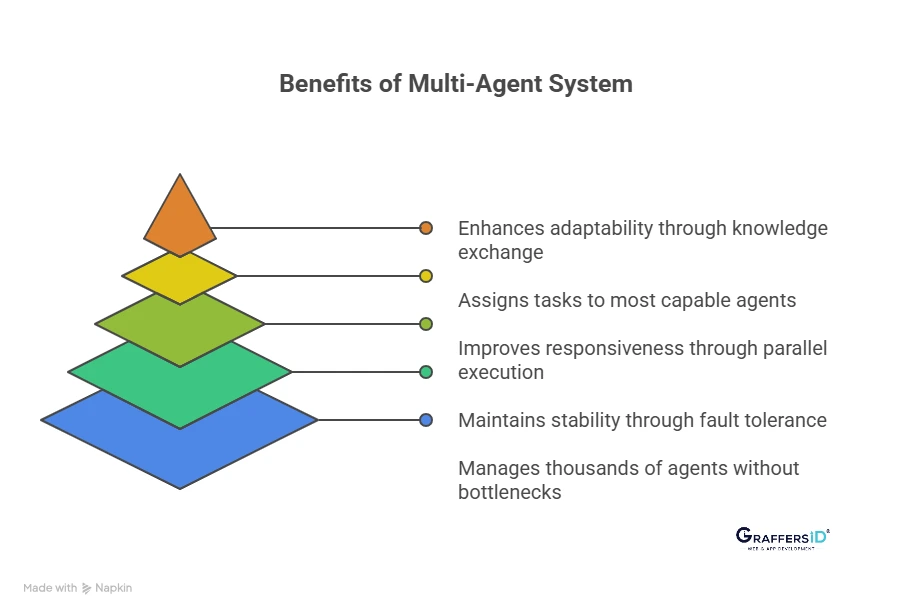
1. Scalability
Multi-agent systems can scale horizontally to manage thousands of concurrent agents without central bottlenecks. By leveraging distributed processing, asynchronous messaging, and decentralized orchestration, multi-agent systems support large-scale deployments in domains like smart grids, IoT, and autonomous mobility.
2. Robustness
MAS exhibits fault tolerance through distributed redundancy. If one or several agents fail, the system’s adaptive fault recovery protocols and redundant communication pathways ensure continuity, maintaining overall system stability and minimizing downtime in mission-critical environments.
3. Efficiency
Through parallelized task execution and workload partitioning, multi-agent systems reduce computational overhead and improve real-time responsiveness. By distributing processes across specialized agents, the system minimizes latency and achieves higher throughput compared to monolithic AI architectures.
Read More: What is Generative AI and How Does It Affect Software Development?
4. Specialization
Agents are designed as domain-specific, modular entities with specialized skill sets, such as optimization, negotiation, or real-time perception. This allows MAS to assign tasks to the most capable agent, ensuring domain-optimized problem-solving without overloading generic AI models.
5. Shared Learning
Multi-agent systems enable cross-agent knowledge distillation by allowing agents to exchange insights from different problem domains. This shared intelligence fosters emergent behaviors, creative cross-domain solutions, and reinforcement learning feedback loops, which enhance system adaptability over time.
In 2026, MAS is increasingly being paired with AI copilots, LLM agents, and agent orchestration frameworks (like LangChain, AutoGen, and CrewAI) to scale enterprise automation.
Real-World Applications of Multi-Agent Systems in 2026
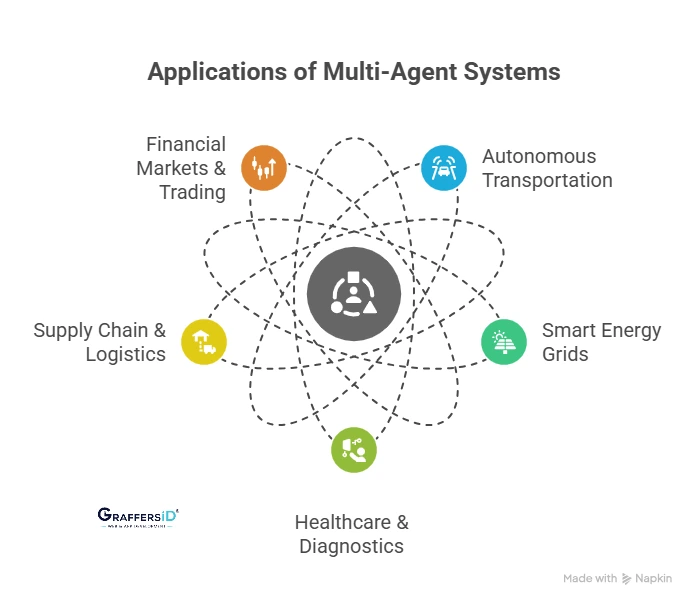
1. Autonomous Transportation & Mobility
Multi-agent systems power fleets of autonomous cars, drones, and delivery robots. Agents collaborate to reduce congestion, optimize routes, and avoid collisions. Companies like Waymo and Tesla now use MAS-driven simulation environments for traffic-scale coordination.
2. Smart Energy Grids
Decentralized MAS enables real-time balancing of renewable energy sources, improving efficiency and reducing blackouts. Agents negotiate energy trades across smart cities using blockchain-based verification.
3. Healthcare & Diagnostics
MAS supports multi-doctor AI copilots for patient monitoring, diagnosis, and treatment planning. For example, agents representing radiology, cardiology, and pharmacy collaborate for holistic decision-making.
4. Supply Chain & Logistics
Agents represent suppliers, warehouses, and distributors, enabling real-time negotiation and automated decision-making. MAS reduces delays, predicts shortages, and adapts instantly to market changes.
5. Financial Markets & Trading
MAS-based trading bots simulate thousands of market scenarios, cooperate, or compete to optimize investment strategies, creating more robust portfolio management.
Conclusion: Why are Multi-Agent Systems the Future of AI in 2026?
Multi-agent systems represent the next frontier in artificial intelligence. Instead of relying on a single all-powerful model, multi-agent systems distribute intelligence across a network of specialized agents, just like human teams.
As industries adopt AI at scale, MAS ensures that systems remain adaptive, resilient, and scalable, capable of handling complexity that no single agent can.
At GraffersID, we help enterprises harness Multi-Agent AI systems to build scalable, resilient, and intelligent solutions.
Ready to future-proof your business? Contact our AI experts today!