So, you’re contemplating diving into the world of work, but you’re torn between freelancing and committing to a full-time developer to hire for your next project. It’s a tough decision, and rightly so. Both options offer their own set of advantages and challenges, not the least of which is the financial aspect. In this article, we’ll dissect the costs associated with both freelance vs full-time costs to help you make an informed decision about which path might lead to greener pastures, financially speaking for your project.
Understanding Freelance Work
At its core, freelancing involves offering your skills and services to clients on a project-by-project basis, rather than being employed by a single company. Freelancers are essentially independent contractors who have the freedom to choose the projects they work on, set their rates, and determine their schedules. This level of autonomy is one of the key attractions of freelancing, allowing individuals to pursue their passions while maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
Origins of Freelance Work:
The concept of freelancing traces back centuries, with roots in the medieval era when skilled craftsmen and artisans operated independently, taking on various projects for different patrons. These freelancers, often referred to as “freelancers,” were not bound by the constraints of traditional employment but instead offered their services on a project-by-project basis.
The Industrial Revolution marked a shift towards more structured employment models, but freelance work persisted, particularly among writers, artists, and other creative professionals. However, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that freelance work began to gain widespread traction, spurred by technological advancements and changing attitudes toward work.
Rise of Freelancing:
The advent of the internet and digital platforms revolutionized the way freelance work was conducted. Online marketplaces such as Upwork, Freelancer, and Fiverr provide a platform for freelancers to connect with clients from around the world, transcending geographical barriers and opening up a wealth of opportunities.
The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, further propelled the growth of freelancing. Companies embraced the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of hiring freelancers for specific projects, leading to a surge in demand for freelance services across industries.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work practices, prompting many traditional employees to explore freelancing as a viable alternative. As businesses adapted to remote operations, they increasingly turned to freelancers to fill skill gaps and meet project deadlines.
Growing Trends in 2024:
In 2024, the landscape of freelance work continues to evolve, driven by several key trends:
-
Specialization:
Freelancers are increasingly specializing in niche areas to stand out in a competitive market. Whether it’s blockchain development, content marketing, or graphic design, clients are seeking experts with specific skills to deliver high-quality results.
-
Remote Collaboration:
Collaboration tools and communication platforms have made it easier for freelancers to collaborate with clients and fellow freelancers regardless of location. Virtual meetings, project management software, and cloud-based storage facilitate seamless communication and workflow management.
-
Gig Platforms and Blockchain:
The emergence of blockchain technology is revolutionizing freelancing platforms, offering enhanced security, transparency, and payment processing. Decentralized platforms powered by blockchain ensure fair compensation for freelancers and eliminate intermediaries, resulting in lower fees and faster transactions.
-
Work-Life Balance:
Freelancing offers greater autonomy and flexibility, allowing individuals to design their work schedules around personal priorities. As more people prioritize work-life balance, freelancing becomes an attractive option for achieving greater control over one’s time and workload.
-
Upskilling and Continuous Learning:
To remain competitive in the freelance market, professionals must continuously upskill and adapt to evolving industry trends. Online learning platforms and certification programs provide opportunities for freelancers to expand their skill sets and stay ahead of the curve.
What is Full-Time Work?
Full-time work is a concept familiar to many, yet its nuances and implications may not be fully understood. In this article, we’ll delve into the definition, advantages, disadvantages, and practicalities of full-time employment. Whether you’re contemplating entering the workforce, considering a job change, or simply curious, understanding what full-time work entails is essential. So, let’s break it down.

Origins of Full-Time Work
The roots of full-time in-house work can be traced back centuries, to a time when agrarian societies formed the basis of human civilization. In these early societies, individuals worked directly for landowners or lords, performing various tasks and labor in exchange for shelter, protection, and sustenance.
As societies evolved and economies developed, the concept of full-time in-house work expanded beyond agriculture to encompass various industries and professions. With the rise of industrialization in the 18th and 19th centuries, factories and manufacturing plants became hubs of full-time employment, where workers were employed permanently to operate machinery and produce goods.
Evolution in the 20th Century
The 20th century witnessed significant advancements in full-time in-house work, driven by industrialization, urbanization, and technological innovation. As economies transitioned from agrarian to industrial and later to service-based, the nature of full-time in-house work evolved to meet the changing demands of society.
With the emergence of office-based work in the early 20th century, companies began hiring employees to work in dedicated office spaces, performing administrative tasks, sales, and other functions essential to business operations. This marked the beginning of the modern era of full-time in-house work, characterized by long-term employment contracts, fixed working hours, and on-site supervision.
Full-Time Work in the Digital Age
In the 21st century, full-time in-house work continues to be a prevalent employment model, albeit with notable adaptations to accommodate changing workforce dynamics and technological advancements. Here’s how full-time in-house work has evolved in the digital age:
-
Technology Integration:
Integrating technology into the workplace has transformed how full-time in-house work is performed. From email communication to enterprise software solutions, employees now rely on digital tools to streamline workflows, collaborate with colleagues, and access information in real time.
-
Flexible Work Arrangements:
In response to shifting employee preferences and demands for work-life balance, many companies have begun offering flexible work arrangements within the framework of full-time in-house employment. This may include options such as remote work, flexible hours, and compressed workweeks.
-
Emphasis on Company Culture:
With the rise of remote work and distributed teams, companies are placing greater emphasis on fostering a strong company culture to engage and retain employees. This may involve initiatives such as team-building activities, wellness programs, and diversity and inclusion efforts.
-
Investment in Employee Development:
Recognizing the importance of talent retention and skill development, companies are investing in employee training and development programs to upskill and reskill their workforce. This not only benefits employees in their professional growth but also enhances the company’s overall competitiveness.
Growth of Full-Time Cost Work in 2024
As we navigate the year 2024, full-time in-house work remains a foundational pillar of the global economy, with several key trends shaping its growth:
- Focus on Employee Well-Being: Employers are prioritizing employee well-being and mental health, offering support services and resources to help employees maintain a healthy work-life balance and thrive in their roles.
- Digital Transformation: The ongoing digital transformation is revolutionizing the workplace, with companies embracing automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics to streamline operations and drive innovation within their full-time in-house workforce.
- Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives: Companies are increasingly prioritizing diversity, equity, and inclusion within their full-time in-house workforce, recognizing the value of a diverse talent pool in driving creativity, innovation, and business success.
- Hybrid Work Models: While full-time in-house work remains the norm for many organizations, the adoption of hybrid work models combining in-house and remote work is becoming more prevalent, offering employees greater flexibility and autonomy in how they work.
Differences Between Freelance & Full-Time Costs
| Aspect | Freelance | Full-Time |
|---|---|---|
| Salary or Payment | Paid per project or hourly | Fixed salary per month/year |
| Benefits | Typically no benefits are provided | Benefits such as healthcare, retirement plans, paid time off, etc. provided |
| Overhead Costs | Minimal | Included in company expenses |
| Equipment and Supplies | Self-provided | Provided by the employer |
| Taxes and Insurance | Self-managed | Employer handles deductions and provides insurance coverage |
| Work Schedule Flexibility | Typically more flexibility | Follows set work hours |
| Job Security | Less stable | More stable employment |
| Training and Development | Self-directed | An employer may provide training and development opportunities |
| Workload Management | Self-managed | Managed by employer/supervisor |
| Work Environment | Remote or self-selected | Predetermined office/workspace |
| Collaboration | Variable depending on the project | In-house collaboration |
Pros and Cons Freelance work for software development
Freelance software development comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. In this blog post, we’ll explore the pros and cons of freelance work in software development, helping you make an informed decision about whether it’s the right choice for you.
Pros of Freelance Software Development:
-
Flexibility:
One of the most appealing aspects of freelance work is the flexibility it offers. As a freelance software developer, you have the freedom to choose your hours, projects, and clients. This flexibility allows you to create a schedule that suits your lifestyle and work preferences, whether you prefer to work early in the morning or late at night.
-
Diverse Projects:
Freelance software developers have the opportunity to work on a wide range of projects across different industries. This variety not only keeps the work interesting and challenging but also allows developers to gain experience in various technologies and domains. Working on diverse projects can also help freelancers build a robust portfolio, which can attract more clients in the future.
-
Higher Earning Potential:
In many cases, freelance software developers have the potential to earn more than their counterparts in traditional employment. Freelancers can set their rates based on their skills, experience, and the complexity of the projects they undertake. Additionally, freelancers have the opportunity to take on multiple projects simultaneously, further increasing their earning potential.
-
Independence:
Freelance software developers enjoy a greater degree of independence compared to employees in traditional workplaces. They have the autonomy to choose the projects they want to work on, negotiate their terms and conditions with clients, and manage their workflow. This independence can be empowering and allows freelancers to take control of their careers.
-
Remote Work Opportunities:
With advancements in technology, remote work has become increasingly common in the software development industry. Freelancers have the flexibility to work from anywhere with an internet connection, whether it’s from the comfort of their own home, a co-working space, or a coffee shop. Remote work eliminates the need for commuting, saving time and money, and allows freelancers to enjoy a better work-life balance.
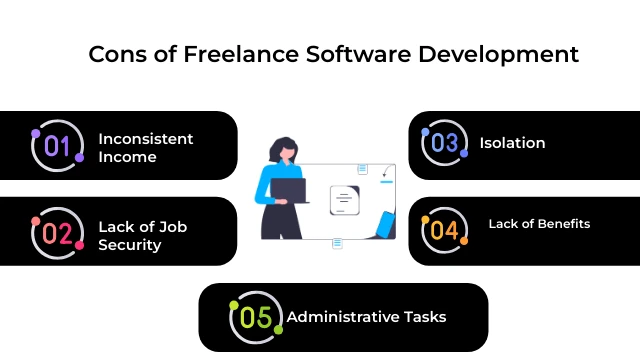
Cons of Freelance Software Development:
-
Inconsistent Income:
One of the biggest challenges of freelance work is the inconsistency of income. Freelancers may experience fluctuations in workload and earnings, depending on the availability of projects and clients. This inconsistency can make it difficult to budget and plan for expenses, especially during lean periods.
-
Lack of Job Security:
Unlike traditional employees who have the security of a steady paycheck and benefits, freelance software developers are responsible for finding and maintaining their client base. This lack of job security can be stressful, especially for those who are new to freelancing or have not yet established a solid reputation in the industry.
-
Administrative Tasks:
Freelance work often entails various administrative tasks that can be time-consuming and tedious. From marketing and client communication to invoicing and tax filing, freelancers are responsible for managing every aspect of their business. These administrative tasks can take away valuable time and energy from actual software development work.
-
Isolation:
While remote work offers flexibility and freedom, it can also lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness. Freelancers may miss out on the social interaction and camaraderie that comes with working in a traditional office environment. Additionally, freelancers may struggle to separate work from personal life when working from home, leading to burnout and fatigue.
-
Lack of Benefits:
Unlike employees who often receive benefits such as health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans, freelance software developers are responsible for sourcing their benefits. This can be costly and complicated, especially for those who are self-employed. Freelancers must consider the additional expenses of health insurance premiums, retirement savings, and other benefits when setting their rates and managing their finances.
Pros and Cons of Full-time Developers for Software Development Projects
While each approach has its merits, employing full-time developers for software projects warrants a closer examination of the associated pros and cons. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the advantages and drawbacks of hiring full-time developers and helping businesses make informed decisions about their software development needs.
Pros of Hiring Full-time Developers:

-
Dedication and Commitment:
Full-time developers are dedicated to their roles within the company, committing their time and expertise to the success of ongoing projects. Their alignment with the company’s goals and values fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, leading to increased productivity and quality of work.
-
Team Integration:
Full-time developers become integral members of the in-house team, fostering collaboration, knowledge sharing, and synergy. Their presence allows for seamless communication and coordination, facilitating faster decision-making and problem-solving processes. Team cohesion often leads to a more cohesive and efficient development environment.
-
Long-term Stability:
Hiring full-time developers provides a sense of stability and continuity to software development projects. Unlike freelancers or contractors who may come and go, full-time employees offer consistency and reliability, ensuring that projects can be completed on schedule and within budget. This long-term commitment enables businesses to build and maintain complex software systems effectively.
-
Cultural Fit:
Full-time developers have the opportunity to immerse themselves in the company’s culture, values, and mission. This alignment fosters a sense of belonging and camaraderie, enhancing employee satisfaction and retention. Developers who resonate with the company culture are more likely to stay motivated, engaged, and loyal to the organization.
-
Skill Development:
Employing full-time developers allows businesses to invest in the professional growth and development of their employees. Through training programs, mentorship, and opportunities for skill enhancement, companies can cultivate a highly skilled and adaptable workforce. Continuous learning and upskilling contribute to the overall competitiveness and innovation of the organization.
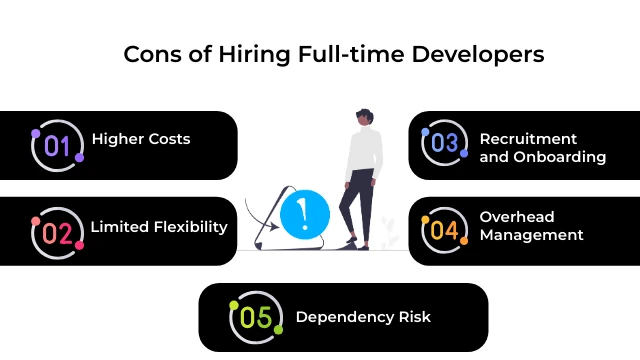
Cons of Hiring Full-time Developers:
-
Higher Costs:
Employing full-time developers entails significant financial commitments, including salaries, benefits, office space, equipment, and overhead expenses. These costs can add up quickly, especially for small and medium-sized businesses with limited budgets. Additionally, full-time employees may require ongoing training and support, further increasing the overall expenditure.
-
Limited Flexibility:
Full-time developers are bound by employment contracts and organizational policies, limiting their flexibility and autonomy. They may be constrained by fixed working hours, vacation policies, and bureaucratic processes, which can hinder agility and responsiveness in a rapidly changing market. Businesses may find it challenging to scale their development teams up or down based on fluctuating project requirements.
-
Recruitment and Onboarding:
Hiring full-time developers involves a time-consuming and resource-intensive recruitment and onboarding process. From sourcing candidates and conducting interviews to training new hires and integrating them into the team, businesses must invest considerable time and effort to find the right talent and ensure a smooth transition. Delays or mismatches in the hiring process can disrupt project timelines and deliverables.
-
Overhead Management:
Managing a team of full-time developers requires effective leadership, supervision, and performance management. Businesses must oversee day-to-day operations, track progress, address conflicts, and provide support to ensure optimal team performance. Without proper management and oversight, productivity may suffer, leading to project delays and cost overruns.
-
Dependency Risk:
Relying solely on full-time developers for software development projects can create a dependency risk for businesses. If key team members leave the company or are unable to work due to unforeseen circumstances, it may disrupt ongoing projects and jeopardize deadlines. Businesses must have contingency plans in place to mitigate the impact of employee turnover or absences.
Financial Aspects: Freelance vs full-time work
When comparing freelance and full-time work from a financial perspective, several factors come into play.
-
Income Potential
Freelancers have the potential to earn higher hourly rates or project fees compared to their full-time counterparts. With the ability to set their rates and negotiate contracts, freelancers can leverage their expertise and experience to command higher pay. However, freelancers must also factor in the time spent on non-billable tasks such as marketing, networking, and administrative work, which can impact their overall earnings.
-
Stability
Full-time employment offers a stable source of income, with regular paychecks and benefits such as health insurance and retirement contributions. In contrast, freelancers may experience fluctuations in income, depending on the availability of projects and clients. Building a steady client base and managing cash flow are essential for freelancers to weather lean periods and maintain financial stability.
-
Expenses
While freelancers enjoy certain tax benefits and deductible expenses such as home office costs and business supplies, they are also responsible for covering overhead expenses such as healthcare, retirement savings, and self-employment taxes. On the other hand, full-time employees receive benefits such as employer-sponsored health insurance and retirement contributions, reducing their out-of-pocket expenses.
Non-Financial Factors: Freelance vs full-time work
Beyond financial considerations, there are various non-monetary aspects to consider when evaluating freelance and full-time work.
-
Flexibility
Freelancing offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing individuals to choose when, where, and how they work. This flexibility is especially valuable for parents, caregivers, or those pursuing other interests outside of work. Full-time employees may have less control over their schedules and may be required to adhere to rigid work hours and policies set by their employers.
-
Work-Life Balance
Achieving a healthy work-life balance is often easier for freelancers, who can adjust their workload to accommodate personal commitments and prioritize self-care. In contrast, full-time employees may struggle to balance their professional and personal lives, especially if their job demands long hours or frequent overtime.
-
Career Growth
While full-time employment may offer structured career paths, training opportunities, and promotional prospects within a company, freelancers have the freedom to chart their career trajectory. Freelancers can pursue diverse projects, gain exposure to different industries, and develop a versatile skill set that may enhance their long-term employability.
Is freelancing more profitable than full-time work?
When comparing the profitability of freelancing versus full-time work, it’s essential to consider both financial and non-financial factors. While freelancers have the potential to earn higher hourly rates, they must contend with variable income, self-employment taxes, and the responsibility of managing their business affairs.
On the other hand, full-time employees enjoy the stability of a consistent paycheck and access to employer-sponsored benefits, albeit at the cost of autonomy and flexibility.
How can you transition from full-time work to freelancing?
Transitioning from full-time employment to freelancing can be an exhilarating yet daunting journey. It offers freedom, flexibility, and the opportunity to pursue your passions, but it also requires careful planning and adjustment. If you’re considering making this leap, you’re not alone.
Many professionals are choosing to embrace the freelance lifestyle for its myriad benefits. In this blog post, we’ll explore practical steps and strategies to help you navigate this transition successfully.
-
Self-Assessment:
Before embarking on your freelancing journey, take the time for honest self-assessment. Evaluate your skills, strengths, and areas for improvement. Consider what services or expertise you can offer as a freelancer and assess the demand for these skills in the market. Reflect on your motivations for transitioning to freelancing and set clear goals for yourself. Understanding your strengths and motivations will lay a solid foundation for your freelancing career.
-
Financial Planning:
Transitioning from full-time work to freelancing often involves a shift in income stability. Freelancers typically experience fluctuations in income, so it’s crucial to have a solid financial plan in place. Calculate your monthly expenses, including living costs, business expenses, and savings goals. Determine how much income you need to sustain yourself and your business during the transition phase and beyond. Consider building an emergency fund to cover unforeseen expenses and fluctuations in income.
-
Building Your Brand:
As a freelancer, your personal brand is your most valuable asset. Invest time and effort in building a strong online presence that showcases your skills, expertise, and unique value proposition. Create a professional website or portfolio to showcase your work and attract potential clients. Utilize social media platforms to network with industry professionals, share valuable content, and establish yourself as an authority in your field. Consistent branding and messaging will help you stand out in a competitive market.
-
Networking and Marketing:
Networking is essential for success in the freelancing world. Attend industry events, conferences, and networking meetups to connect with potential clients and collaborators. Join online communities and forums relevant to your niche to exchange ideas, seek advice, and build relationships with fellow freelancers. Invest in marketing strategies such as content creation, email marketing, and search engine optimization to attract clients and grow your business. Remember to prioritize building genuine relationships and providing value to your network.
-
Setting Boundaries:
One of the perks of freelancing is the flexibility to set your own schedule. However, this flexibility can also blur the boundaries between work and personal life. Establish clear boundaries to maintain a healthy work-life balance and prevent burnout. Define your working hours, set aside time for breaks and leisure activities, and create a dedicated workspace free from distractions. Communicate your boundaries to clients and colleagues to manage expectations and ensure mutual respect.
-
Continuous Learning and Development:
Freelancing requires adaptability and a willingness to learn and grow continuously. Stay updated on industry trends, technologies, and best practices relevant to your niche. Invest in professional development opportunities such as online courses, workshops, and certifications to expand your skill set and stay competitive in the market. Seek feedback from clients and peers to identify areas for improvement and refine your services accordingly. Embrace lifelong learning as a cornerstone of your freelancing career.
Challenges of Hiring Full-Time Developers for Your Software Project
While having an in-house team offers benefits like control, collaboration, and continuity, it also presents various hurdles that must be navigated effectively. Let’s explore some of the common challenges faced when hiring full-time developers for your software projects.
-
Talent Acquisition:
One of the primary challenges is finding skilled developers who not only possess the technical expertise but also align with your company culture and values. The demand for top-tier developers often exceeds the supply, making it a competitive landscape where attracting and retaining talent requires a comprehensive strategy.
-
High Costs:
Hiring full-time developers involves significant financial investment, including salaries, benefits, office space, equipment, and training. For startups and small businesses with limited budgets, this can be particularly daunting. Balancing the costs with the need for quality talent is a constant challenge.
-
Onboarding and Training:
Integrating new developers into your team and familiarizing them with your project, workflows, and technologies can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Without a structured onboarding process, there’s a risk of inefficiency, miscommunication, and slow productivity ramp-up.
-
Retention:
Once you’ve successfully hired talented developers, retaining them becomes a priority. In a competitive market, developers may be lured away by better offers or opportunities elsewhere. Creating a conducive work environment, providing growth opportunities, and offering competitive compensation and benefits are essential for retention.
-
Adapting to Change:
Software development is an ever-evolving field, with new technologies, frameworks, and methodologies emerging regularly. Full-time developers need to continually update their skills to stay relevant. Keeping up with these changes and ensuring your team remains proficient can be challenging, requiring ongoing training and professional development initiatives.
-
Scaling Up or Down:
The dynamics of software projects can change rapidly, requiring you to scale your development team accordingly. Hiring full-time developers means committing to their salaries and benefits, which can pose challenges during periods of expansion or contraction. Finding the right balance between flexibility and stability is crucial.
-
Managing Diverse Skill Sets:
A software development team typically comprises individuals with diverse skill sets and expertise. Managing this diversity effectively, ensuring everyone’s contributions are valued, and fostering a collaborative environment can be challenging, especially when dealing with conflicting opinions or approaches.
-
Ensuring Productivity and Accountability:
Monitoring the productivity and accountability of full-time developers can be challenging, especially in remote or distributed teams. Without proper tools, processes, and communication channels in place, there’s a risk of inefficiency, missed deadlines, and subpar outcomes.
-
Cultural Fit and Collaboration:
Building a cohesive team culture where developers collaborate effectively is essential for project success. However, achieving cultural fit and fostering collaboration among full-time developers, particularly in diverse or distributed teams, requires intentional effort and clear communication.
-
Balancing Workload and Burnout:
Software development projects often involve tight deadlines and high-pressure situations, leading to the risk of burnout among full-time developers. Balancing the workload, managing expectations, and promoting work-life balance are critical to preventing burnout and ensuring the well-being of your team.
Freelance vs Full-Time Costs: What Should You Choose?
To determine which option is more profitable for new software development projects, it’s essential to conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, For short-term projects with fluctuating requirements, freelancers may offer a cost-effective solution. Conversely, long-term projects with stable requirements might justify the investment in full-time employees. Complex projects requiring close collaboration and extensive coordination might benefit from a dedicated team of full-time employees. On the other hand, simpler projects with well-defined tasks could be efficiently handled by freelancers.
Each option comes with its own set of advantages and challenges, and the decision ultimately depends on factors such as project scope, duration, complexity, and budget constraints.
Considerations such as intellectual property protection, data security, and compliance may influence the decision between freelancers and full-time employees. Businesses must evaluate the risk factors associated with each option and implement appropriate measures.
Conclusion
In the perennial debate between freelance and full-time work, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Both options have their advantages and drawbacks, and the decision ultimately depends on individual preferences, priorities, and circumstances. While freelancing offers autonomy and flexibility, full-time employment provides stability and benefits. By carefully weighing the financial and non-financial factors discussed in this article, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their goals and aspirations.