In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, IoT (Internet of Things) is no longer just a trending buzzword; it has become a core technology driving modern digital transformation. From smart homes that respond to your voice to intelligent enterprises and data-driven cities, IoT is redefining how the physical and digital worlds connect.
At its core, the Internet of Things enables physical devices to sense, communicate, and act on data over the internet, without continuous human involvement. Whether it’s a smartwatch monitoring health vitals in real time or industrial systems predicting equipment failures before they occur, IoT is fundamentally changing how technology interacts with people, processes, and environments.
As we move into 2026, IoT is evolving beyond basic connectivity. It now works closely with AI, edge computing, automation, and real-time analytics, enabling smarter decisions, faster responses, and scalable innovation across industries.
In this comprehensive 2026 guide, you’ll learn:
-
What IoT is
-
How IoT works
-
Core components of IoT architecture
-
Real-world IoT applications across industries
-
Key benefits for businesses and users
-
Challenges, security, and compliance risks
What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of physical devices connected to the internet that can collect, share, and act on data using built-in sensors and software, often without requiring human intervention.
These connected devices, commonly known as smart devices, continuously capture real-world data such as location, temperature, movement, usage patterns, or system performance. The data is then transmitted over the internet to be processed, analyzed, and used to trigger actions or insights in real time.
Read More: Agentic AI vs. Generative AI: Key Differences CTOs Must Know in 2026
IoT devices exist across multiple environments, including:
-
Consumer electronics, such as smart TVs, wearables, and voice assistants
-
Vehicles and logistics systems, enabling real-time tracking and route optimization
-
Industrial machines and sensors, supporting automation and predictive maintenance
-
City infrastructure and utilities, including traffic systems, energy grids, and smart lighting
By connecting physical objects to digital systems, IoT enables organizations and individuals to monitor operations, automate processes, and make data-driven decisions at scale.
How Does IoT Work? (Step-by-Step)
IoT systems typically follow a four-layer operational flow, optimized for automation and intelligence.
1. Sensing and Data Collection
IoT devices use built-in sensors to capture real-world data, such as:
-
Temperature
-
Motion
-
Location
-
Light
-
Heart rate
-
Machine performance metrics
2. Connectivity and Data Transmission
Collected data is transmitted using communication technologies like:
-
Wi-Fi
-
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
-
LPWAN (LoRaWAN, NB-IoT)
-
Zigbee
-
5G (increasingly dominant in 2026)
3. Data Processing and Analysis
Data is processed using:
-
Edge computing
-
AI and machine learning models
This step transforms raw data into actionable insights.
4. Action, Automation, and Alerts
Based on analysis, IoT systems:
-
Trigger automated actions
-
Send alerts or notifications
-
Adjust systems in real time
Example: A smart thermostat automatically adjusts temperature based on occupancy and weather data.
Key Components of an IoT System
1. IoT Devices and Sensors
These are the physical components that collect data. Examples include:
-
Smart thermostats
-
Fitness trackers
-
Industrial sensors
-
Smart meters
Sensors detect changes in the environment, movement, pressure, or usage patterns.
2. Connectivity and Communication Networks
To function effectively, IoT devices rely on reliable communication protocols such as:
-
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth (consumer IoT)
-
LPWAN (long-range, low-power use cases)
-
5G (high-speed, low-latency enterprise IoT)
3. Cloud & Edge Computing Platforms
IoT generates massive volumes of data. Platforms like:
-
AWS IoT
-
Microsoft Azure IoT
-
Google Cloud IoT
store, process, and analyze this data.
By 2026, edge computing plays a bigger role by processing data closer to the device, reducing latency and cloud costs.
4. IoT Security and Data Protection
Security remains critical due to constant data exchange. Common measures include:
-
End-to-end encryption
-
Device authentication
-
Secure firmware updates
-
Blockchain-based identity management (emerging use)
Real-World Applications of IoT (2026)
IoT is used across several industries. It helps improve productivity and security and enhances user experience. Let’s look at some of the industries that have adopted IoT in their products.
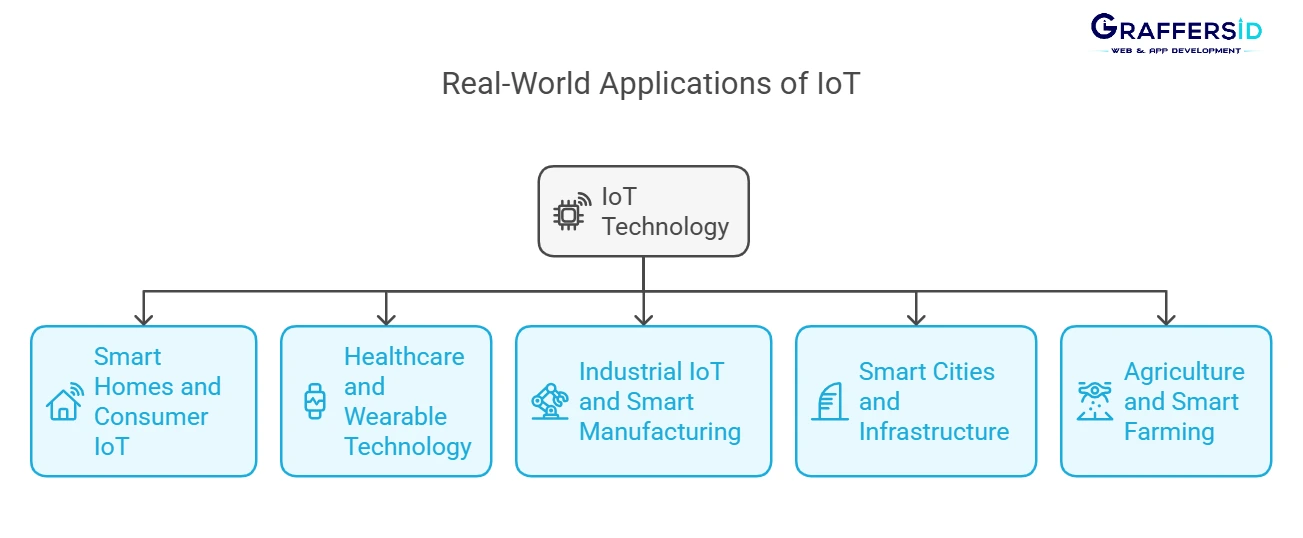
1. Smart Homes & Consumer IoT
Popular devices like Amazon Alexa, Google Nest, and smart security systems allow users to:
-
Control appliances remotely
-
Monitor home security
-
Optimize energy consumption
Smart homes now integrate AI-driven automation, not just basic connectivity.
2. Healthcare & Wearable Technology
IoT-enabled wearables track:
-
Heart rate
-
Oxygen levels
-
Sleep patterns
-
Physical activity
Hospitals use IoT for remote patient monitoring, enabling real-time health data sharing with doctors, improving outcomes, and reducing costs.
3. Industrial IoT (IIoT) & Smart Manufacturing
Factories use IoT sensors for:
-
Predictive maintenance
-
Equipment monitoring
-
Production line optimization
This reduces downtime and improves operational efficiency.
4. Smart Cities & Infrastructure
Governments worldwide use IoT to manage:
-
Traffic signals
-
Smart parking
-
Waste management
-
Air quality monitoring
Connected systems improve sustainability and citizen safety.
5. Agriculture & Smart Farming
IoT helps farmers monitor:
-
Soil moisture
-
Weather conditions
-
Crop health
-
Livestock movement
Smart irrigation and drone-based monitoring improve yield and reduce water waste.
Read More: AI Assistants vs. AI Agents (2026): Key Differences, Features, and Use Cases Explained
Key Benefits of IoT
1. Increased Efficiency Through Automation
IoT enables end-to-end automation of routine and complex processes, significantly reducing manual effort and operational errors. This is especially valuable in industries like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and utilities, where real-time responsiveness is critical.
2. Cost Reduction and Smarter Resource Use
By continuously monitoring assets, energy usage, and operations, IoT helps organizations reduce waste, prevent breakdowns, and optimize resource allocation, leading to measurable cost savings over time.
3. Better Decisions with Real-Time Data
IoT systems generate continuous data streams that, when combined with AI analytics, support accurate forecasting, predictive insights, and proactive decision-making aligned with business goals.
4. Improved User and Customer Experience
IoT-powered systems deliver faster, more personalized, and more convenient experiences through smart assistants, connected environments, and adaptive services that respond to user behavior in real time.
Challenges & Security Risks in IoT in 2026

1. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Risks
IoT devices are frequent targets for cyberattacks due to weak authentication, outdated firmware, or unsecured networks. Without strong security controls, sensitive personal and business data can be exposed or misused.
2. Managing Large Volumes of IoT Data
IoT systems generate massive amounts of real-time data that require scalable storage and fast processing. Without proper cloud or edge infrastructure, data handling can become costly and impact system performance.
3. High Setup and Implementation Costs
Implementing IoT solutions involves upfront investment in hardware, connectivity, platforms, and system integration. For small and mid-sized businesses, these initial costs can slow adoption without expert guidance.
4. Regulatory, Ethical, and Compliance Challenges
As IoT devices collect continuous user data, organizations must comply with strict regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Failure to manage data responsibly can lead to legal penalties and loss of user trust.
Conclusion: Why IoT Matters for Businesses in 2026
From smart homes and connected healthcare systems to intelligent factories and data-driven cities, the Internet of Things is becoming a core layer of digital transformation. IoT enables organizations to collect real-time data, automate decisions, and build smarter systems that continuously improve with usage.
As IoT adoption accelerates in 2026, its true value lies not just in connected devices but in how data is processed, secured, and turned into actionable intelligence. Businesses that succeed with IoT focus on building architectures that are secure, scalable, and flexible enough to evolve alongside emerging technologies like AI, edge computing, and automation platforms.
To unlock long-term value from IoT-driven ecosystems, organizations must prioritize:
-
Secure and compliant system design to protect data and user trust
-
Scalable digital architectures that grow with business and device volume
-
Seamless integration with existing applications, platforms, and workflows
-
A future-ready innovation strategy that supports AI-led decision-making
While IoT connects devices, intelligent software and AI automation turn data into real business outcomes, and that’s where GraffersID helps.
As a trusted offshore development partner, GraffersID specializes in custom AI-powered solutions and web and mobile app development.
Contact GraffersID today and start building intelligent, AI-driven solutions for 2026 and beyond.