In 2026, back-end development is no longer a purely technical choice; it is a business-critical decision. The back-end now determines how effectively your product integrates AI, automates workflows, scales globally, and maintains security under real-world load.
Modern applications are AI-first, real-time, and cloud-native by default. From AI agents and intelligent automation to event-driven systems and global SaaS platforms, the back-end programming language you choose directly impacts performance, time-to-market, hiring flexibility, and long-term product velocity.
For CTOs, CEOs, and product leaders, the wrong back-end stack can quietly become a scalability bottleneck or security risk, while the right one can accelerate innovation and future-proof the business.
This guide explores the best back-end programming languages in 2026, their strengths, limitations, and future readiness, with a clear decision framework for technology leaders.
Best 8 Back-End Programming Languages in 2026 (AI, Scale & Performance)
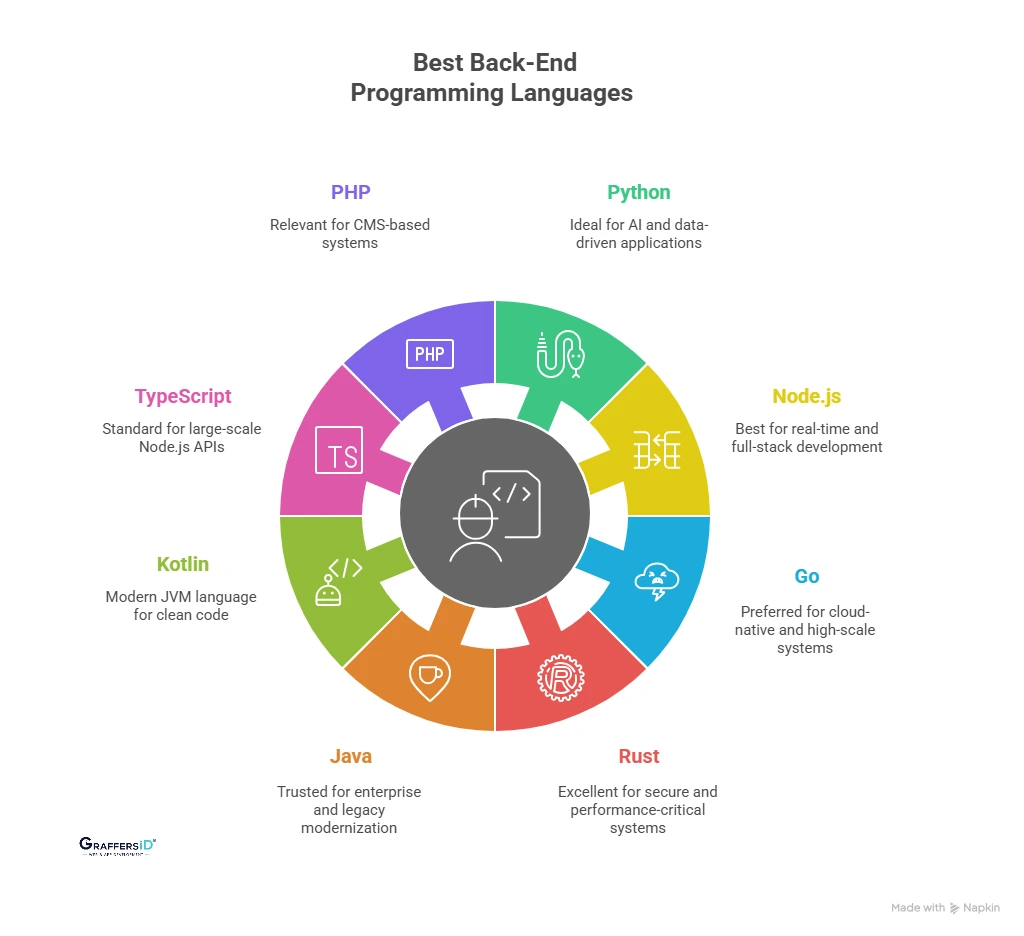
1. Python: Best Back-End Language for AI, Automation, and Intelligent Applications
Python continues to be one of the most widely used back-end programming languages in 2026, especially for products that rely on AI, automation, and data-driven decision-making.
Its dominance in AI and machine learning ecosystems, powered by tools like TensorFlow, PyTorch, LangChain, and OpenAI SDKs, makes Python the default choice for AI-first back-end systems. Frameworks such as FastAPI, Django, and Flask enable rapid development of secure, scalable APIs and microservices.
Best suited for:
-
AI-powered platforms and AI agents
-
SaaS products with automation workflows
-
Data-driven applications
-
Rapid MVPs and proof-of-concept builds
Why CTOs choose Python in 2026:
-
Fast time-to-market for AI-enabled products
-
Unmatched ecosystem for AI, ML, and automation
-
Strong developer availability globally
Pros of Python:
-
Clean, readable syntax
-
Massive open-source ecosystem
-
Strong support for AI, ML, and automation
-
Faster development cycles
Cons of Python:
-
Slower execution than compiled languages
-
Higher memory consumption
-
Limited true multithreading for CPU-bound tasks
2. JavaScript (Node.js): Best for Real-Time and Full-Stack Back-End Development
Node.js remains a top back-end choice in 2026 for applications requiring real-time performance, event-driven architecture, and fast iteration. Its non-blocking I/O model makes it ideal for applications that handle high concurrency.
Using JavaScript on both the front end and back end reduces development complexity and improves team velocity, one of the main reasons startups and scale-ups continue to adopt Node.js.
Best suited for:
-
Real-time applications (chat, streaming, dashboards)
-
APIs and microservices
-
Event-driven systems
Why CTOs choose Node.js:
-
Faster full-stack development
-
Strong ecosystem with npm
-
Excellent performance for I/O-heavy workloads
Pros of JavaScript:
-
Asynchronous, non-blocking architecture
-
Large package ecosystem
-
Ideal for real-time use cases
-
Strong community support
Cons of JavaScript:
-
Complex debugging in async-heavy codebases
-
Not ideal for CPU-intensive tasks
-
Requires disciplined architecture at scale
Read More: Most In-Demand Programming Languages in 2026 for Web, AI, and Scalable Apps
3. Go (Golang): Best Back-End Language for Cloud-Native and High-Scale Systems
Go has become a preferred back-end language for cloud-native architectures in 2026. Designed for simplicity and performance, Go excels in environments where high concurrency, low latency, and predictable performance are required.
It is widely used for microservices, distributed systems, and infrastructure-level backends.
Best suited for:
-
Microservices-based architectures
-
High-traffic APIs
-
Backend and DevOps tooling
Why CTOs choose Go:
-
High performance with low operational overhead
-
Built-in concurrency support
-
Easy deployment in containerized environments
Pros of Go:
-
Excellent concurrency handling
-
Fast execution and compilation
-
Low memory footprint
-
Simple and maintainable codebase
Cons of Go:
-
Smaller ecosystem than Python or Java
-
Limited abstraction for complex business logic
-
Less suitable for rapid UI-centric development
4. Rust: Best for Secure and Performance-Critical Back-End Systems
Rust is increasingly adopted in 2026 for back-end systems where security, reliability, and performance are mission-critical. Its memory-safe design prevents common vulnerabilities such as null pointer dereferencing and data races.
Rust is gaining traction in fintech, cybersecurity, blockchain, and high-performance back-end services.
Best suited for:
-
Security-critical applications
-
Blockchain and Fintech platforms
-
Performance-intensive systems
Why CTOs choose Rust:
-
Strong security guarantees by design
-
Near C/C++ level performance
-
Long-term system reliability
Pros of Rust:
-
Memory safety without garbage collection
-
High performance
-
Strong concurrency safety
-
Excellent tooling
Cons of Rust:
-
Steep learning curve
-
Slower initial development
-
Smaller web-focused ecosystem
Read More: 5 Best AI Frameworks and Libraries in 2026 Trusted by Leading Tech Companies
5. Java: Best Back-End Language for Enterprise and Legacy Modernization
Java remains a trusted enterprise back-end language in 2026, particularly for organizations operating at scale. With Spring Boot and cloud-native JVM frameworks, Java continues to support modern microservices architectures.
Best suited for:
-
Banking, insurance, and compliance-heavy systems
-
Long-term, mission-critical applications
Why CTOs choose Java:
-
Proven scalability and stability
-
Mature ecosystem
-
Strong backward compatibility
Pros of Java:
-
Enterprise-grade reliability
-
Excellent scalability
-
Strong multithreading support
-
JVM portability
Cons of Java:
-
Verbose syntax
-
Higher memory usage
-
Slower startup times compared to newer languages
6. Kotlin: Best Modern JVM Language for Clean and Maintainable Back Ends
Kotlin has firmly positioned itself as a modern, developer-friendly alternative to Java. In 2026, it is widely used for JVM-based back-end services that prioritize code quality and maintainability.
Best suited for:
-
JVM-based back-end services
-
Android and backend integration
-
Clean, maintainable APIs
Pros of Kotlin:
-
Concise syntax
-
Built-in null safety
-
Seamless Java interoperability
-
Growing ecosystem
Cons of Kotlin:
-
Smaller community than Java
-
Slower compilation in very large projects
Read More: Small vs. Large Language Models in 2026: Key Differences, Use Cases & Choosing the Right Model
7. TypeScript: Best for Large-Scale Node.js and Enterprise APIs
TypeScript has become the default standard for serious Node.js back-end development in 2026. Adding static typing to JavaScript significantly improves reliability and maintainability.
Frameworks like NestJS make TypeScript ideal for structured, enterprise-grade back-end systems.
Best suited for:
-
Large Node.js applications
-
Enterprise APIs
-
Teams prioritizing long-term maintainability
Pros of TypeScript:
-
Type safety reduces runtime errors
-
Better code structure
-
Excellent IDE and tooling support
Cons of TypeScript:
-
Additional compilation step
-
Learning curve for JavaScript-only teams
8. PHP: Best for CMS-Based and Content-Heavy Back-End Systems
Despite newer languages, PHP remains relevant in 2026 for content-driven and cost-efficient back-end systems. Frameworks like Laravel and Symfony have modernized PHP for scalable web applications.
Best suited for:
-
CMS platforms
-
Web portals
-
Budget-conscious projects
Pros of PHP:
-
Easy to learn
-
Large ecosystem
-
Strong CMS support (WordPress, Laravel)
Cons of PHP:
-
Lower performance compared to newer languages
-
Limited suitability for complex, non-web systems
Top Back-End Development Trends in 2026 Every CTO Must Know
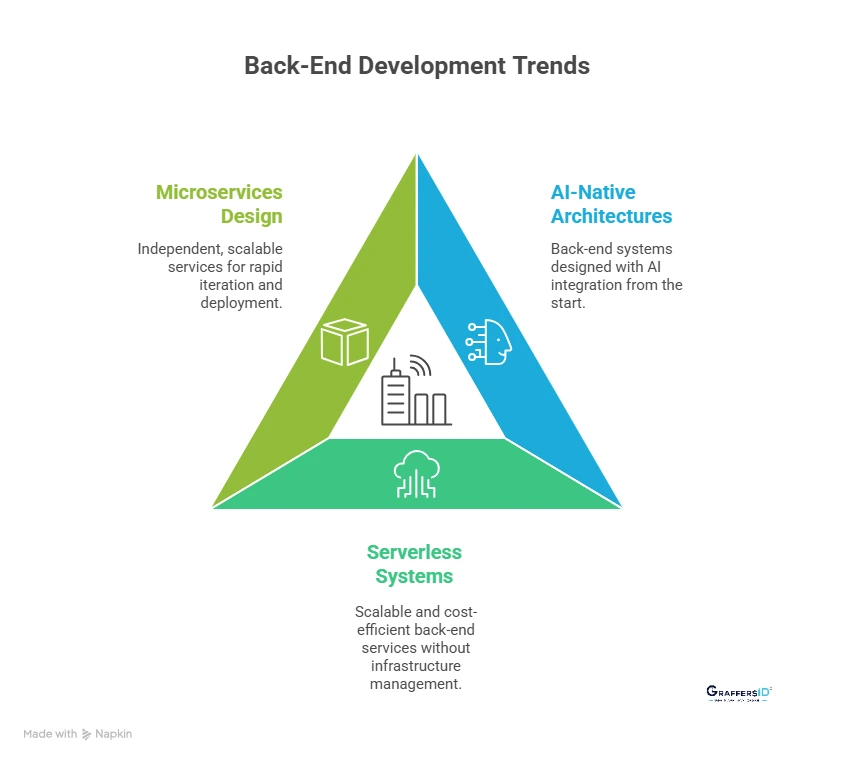
1. AI-Native Back-End Architectures
In 2026, back-end systems are increasingly designed around AI from day one, not added later as an enhancement. AI-native back ends integrate intelligence directly into APIs, workflows, and decision-making layers.
Modern applications embed AI agents within APIs to handle tasks such as customer support, recommendations, data enrichment, and autonomous actions. LLM-powered automation workflows now manage complex business logic, from document processing to intelligent routing and approvals.
AI-driven personalization engines are also becoming standard, enabling back ends to deliver real-time, context-aware experiences across products and platforms.
2. Serverless and Event-Driven Back-End Systems
Serverless and event-driven architectures continue to grow in adoption in 2026 due to their scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Back-end services now scale automatically based on demand, without requiring teams to manage infrastructure.
Read More: Advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) in 2026: Tools, Trends, and AI Applications
These architectures support faster scaling, reduce idle resource costs, and operate on pay-per-use models, making them ideal for unpredictable workloads and high-growth products.
Event-driven systems also enable faster response times by triggering back-end logic in real time based on user actions or system events.
3. Microservices and API-First Back-End Design
Microservices and API-first development remain core back-end strategies in 2026, especially for products that need independent scaling and rapid iteration.
By breaking applications into smaller, self-contained services, teams can deploy, update, and scale components independently. API-first design ensures that services are reusable, interoperable, and easy to integrate with front-end apps, mobile platforms, and third-party systems.
This approach significantly reduces deployment risk and accelerates feature delivery.
How to Choose the Best Back-End Programming Language in 2026?
Step 1: Define Your Product and Technical Requirements
- Real-Time vs. Batch Processing: Decide whether your application needs real-time responses (e.g., streaming, dashboards, AI agents) or batch-based processing, as this directly influences language performance and concurrency needs.
- AI and Automation Integration: Evaluate how deeply AI, machine learning, or automation will be embedded into your product. Languages with strong AI ecosystems simplify integration and future expansion.
- Scalability and Performance Expectations: Consider expected user growth, traffic spikes, and global usage. Your back-end language should support horizontal scaling, cloud-native deployment, and high availability.
Step 2: Evaluate Your Team’s Skills and Hiring Feasibility
- Existing Team Expertise: Choosing a language your team already knows reduces development time, lowers risk, and improves long-term code quality.
- Developer Availability and Hiring Market: Assess how easy it is to hire skilled developers for the language in your target geography, as talent availability impacts cost and scalability.
Step 3: Plan for Long-Term Maintainability and Growth
- Community and Ecosystem Support: Languages with active communities receive frequent updates, security patches, and long-term support, critical for production systems.
- Ecosystem Maturity and Framework Stability: A mature ecosystem offers reliable frameworks, libraries, and tooling that reduce development effort and technical debt.
- Cloud and Infrastructure Compatibility: Ensure the language works seamlessly with modern cloud platforms, containerization, and serverless architectures to future-proof your system.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Back-End Stack for Long-Term Success in 2026
There is no single “best” back-end programming language in 2026; there is only the right language for your product, scale, and AI strategy. Python continues to lead AI-driven and automation-heavy platforms, Go powers scalable cloud-native systems, Java remains the backbone of enterprise applications, and Rust sets the standard for secure, performance-critical back-end development.
What separates high-performing teams from struggling ones is not the language itself, but how well the technology aligns with business goals, scalability plans, security requirements, and long-term product vision. A future-ready back-end stack enables faster innovation, smoother scaling, and lower technical risk as AI, automation, and real-time systems become standard.
At GraffersID, we help startups and enterprises hire expert back-end developers, build AI-powered web and mobile applications using modern, future-ready technologies.
Hire AI developers, backend engineers, or build custom web and app solutions with GraffersID today.