In 2026, the difference between UI and UX matters more than ever, not just for designers, but for CEOs, CTOs, product leaders, and anyone building digital products. With AI reshaping how teams design, test, and ship interfaces, companies that understand UI vs. UX correctly build faster, reduce development waste, and deliver experiences users truly love.
Yet despite being closely connected, UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) solve different problems. Understanding these differences helps teams improve conversion rates, onboarding flows, retention, and overall product success.
This 2026 guide explains UI vs. UX in simple terms, shows how AI is transforming each field, and highlights why both are essential for building modern, high-performing digital products.
What is the Difference Between UI and UX Design?
Understanding the difference between UI and UX is essential for building AI-powered digital products. While they work closely together, each solves a different part of the user’s problem.
1. UI Design (User Interface): How the Product Looks & Interacts?
The graphical layout and appearance of a digital product are referred to as user interface design. It defines how a product looks and feels to the user. UI design focuses on the visual, interactive, and sensory layers of a digital product.
Key Elements of UI Design
-
Layouts
-
Color systems
-
Buttons & modular components
-
Icons & illustrations
-
Animations & motion
-
Typography & spacing
-
Microinteractions
UI in 2026: What’s New?
-
Adaptive Interfaces: Seamless experiences across foldables, wearables, AR/VR, voice surfaces, and automotive systems.
-
AI-Generated Design Systems: AI tools create tokens, palettes, spacing, themes, and component variations automatically.
-
Context-Aware UI: Interfaces adapt to user location, lighting, device posture, and behavioral patterns.
-
Emotion-Responsive Interfaces: UI adjusts to confusion or frustration by simplifying layouts or surfacing assistance.
Read More: Why Good UI UX Matter When Developing a Web App in 2026?
2. UX Design (User Experience): How the Product Works & Feels?
UX design is more comprehensive and focuses on the journey, structure, and overall satisfaction a user experiences from start to finish. Its main objectives are to maximize functionality, emotional resonance, and usability.
Core UX Responsibilities
-
User research
-
Persona development
-
Information architecture
-
User flows
-
Wireframing & prototyping
-
Usability testing
-
Accessibility
-
Continuous improvement
UX in 2026: What’s New?
-
Predictive User Journeys: AI anticipates drop-offs and friction before users experience them.
-
WCAG 3.0 Accessibility: AI checks structure, readability, motion guidelines, and contrast automatically.
-
Voice UX (VUX): Voice-first and multimodal journeys become standard across devices.
-
Emotion-Based Microinteractions: AI adjusts flows based on hesitation or confusion signals.
-
Behavior Modeling: AI tools detect intent, confusion patterns, and task success probability
Did You Know?
87% of users abandon an app if the onboarding UX is confusing, even if the UI looks good.
UI vs. UX: Key Differences
While both roles aim to increase user satisfaction and product usability, they differ greatly in terms of their objectives, deliverables, and scope.
| Aspect | UI Design | UX Design |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Visuals, layouts, interaction elements | End-to-end journey & usability |
| Starting Point | After UX defines the structure | Research & problem discovery |
| Goal | Make the interface attractive & intuitive | Make the experience smooth & valuable |
| Deliverables | Screens, mockups, prototypes, design systems | Personas, flows, IA, wireframes |
| AI Usage | Auto layouts, themes, component generation | Predictive flows, persona clustering |
| Metrics | Aesthetics, consistency, engagement | Retention, usability, drop-offs |
Remember: UI is what users see. UX is what users experience. UI attracts users. UX retains them.
Why Understanding UI and UX is Important for Digital Success in 2026?
In 2026, users expect far more than simply a functioning app; they expect experiences that are personalized, smooth, fast, and visually appealing across every device. This shift makes mastering UI and UX design essential for business growth, product adoption, and long-term user retention.
1. Design = Brand Identity in 0.05 Seconds
Users form a visual opinion instantly. Strong UI builds trust, while a strong UX keeps users engaged and reduces friction. Together, UI and UX shape how customers perceive your product and your brand.
2. AI Accelerates the Entire Design Lifecycle
Modern tools such as Galileo AI, Uizard, Figma AI, and Framer AI now automate layout generation, prototyping, journey mapping, personalization, and accessibility checks.
This means teams can design faster, test more accurately, and launch higher-quality versions in less time.
3. UX is Now a Core Business Strategy
UX is no longer just a design phase; it’s a data-driven revenue lever. Businesses now rely on UX insights to optimize conversion rates, onboarding flows, customer journeys, feature adoption, and product roadmaps.
A well-designed UX directly reduces churn and improves customer lifetime value (LTV).
Modern UI/UX Design Process in 2026
In 2026, high-performing product teams follow a streamlined, AI-accelerated UI/UX workflow that reduces research time, speeds up prototyping, and improves user experience accuracy.
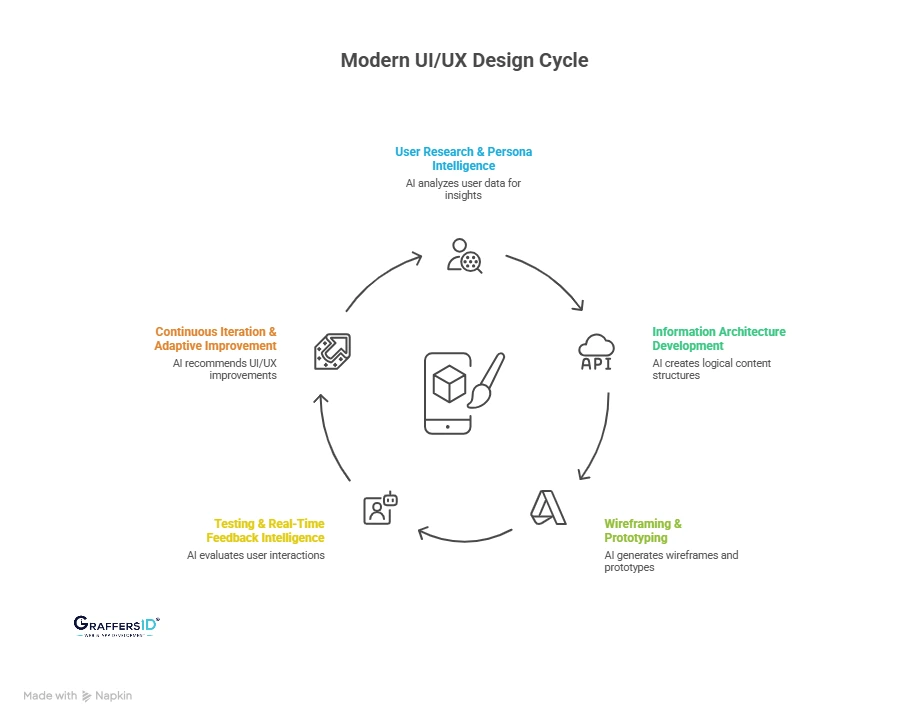
1. User Research & Persona Intelligence
Tools: Dovetail AI, UXtweak AI, Hotjar AI
What This Stage Achieves: AI analyzes user interviews, session recordings, and feedback to reveal deeper behavioral insights.
Outputs:
-
AI-clustered personas
-
Sentiment & emotion analysis
-
Behavioral pattern recognition
-
Use-case & motivation maps
2. Information Architecture (IA) Development
Tools: FlowMapp AI, Octopus.do
What This Stage Achieves: AI creates logical content structures and predicts how users will navigate the product based on past behavior and intent.
Outputs:
-
AI-generated content hierarchy
-
Predictive journey maps
-
Goal-based navigation flows
3. Wireframing & Prototyping
Tools: Uizard, Visily, Figma AI
What This Stage Achieves: Designers use AI to convert prompts into wireframes, reduce iterations, and produce prototype variations faster.
Outputs:
-
Low/high fidelity wireframes
-
Auto-generated prototypes from text or sketches
-
Multiple layout alternatives
-
Seamless design-to-dev handoff structures
4. Testing & Real-Time Feedback Intelligence
Tools: Maze AI, Hotjar AI, Amplitude AI
What This Stage Achieves: AI evaluates user interactions, identifies friction, and predicts drop-off points before release.
Outputs:
-
Heatmaps & scrollmaps
-
Usability scores & task completion rates
-
A/B/n variant performance reports
-
Funnel breakage predictions
5. Continuous Iteration & Adaptive Improvement
Tools: Figma AI, Amplitude AI, Mixpanel AI
What This Stage Achieves: AI continuously monitors user behavior and recommends UI/UX improvements that enhance engagement and retention.
Outputs:
-
Updated user flows
-
Adaptive UI variants based on behavior
-
Real-time personalization adjustments
AI’s Impact on UX and UI Design in 2026
Artificial intelligence is reshaping both UX and UI at every stage, from research to testing to interface generation. AI does not replace designers; it amplifies their capabilities, accelerates workflows, and delivers highly personalized, user-centric digital experiences.
A: AI in UX Design: How AI Is Transforming User Experience in 2026
AI is transforming how UX professionals understand, design, and optimize user journeys.
1. Automated User Research: AI tools analyze raw data from interviews, session recordings, and feedback to generate actionable insights, create personas, identify behavioral patterns, and highlight friction points in minutes rather than weeks.
2. Predictive UX & Intelligent Flow Simulation: AI anticipates user issues before they occur, simulating drop-offs, retention risks, and task failures, allowing designers to proactively refine flows and optimize the overall experience.
3. Automated Wireframing & Prototype Generation: Designers can provide sketches, prompts, or flow descriptions, and AI instantly converts them into wireframes, mockups, and clickable prototypes, dramatically reducing the design cycle from weeks to hours.
4. AI-Driven A/B & Usability Testing: AI performs multivariate testing and real-time usability analysis, automatically suggesting layout changes, optimizing funnels, and adapting onboarding to improve retention and engagement at scale.
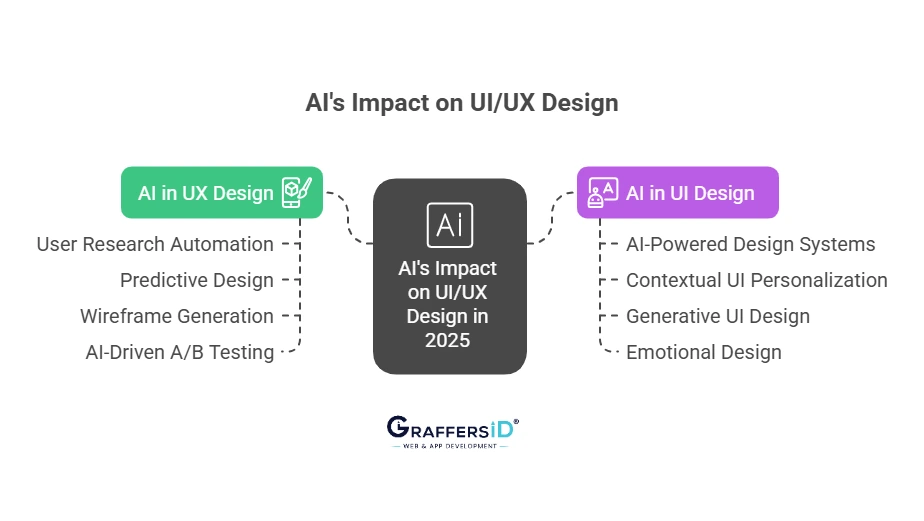
B: AI in UI Design: How AI Is Transforming User Interface Design in 2026
UI designers benefit enormously from AI’s ability to automate visual decision-making, enforce consistency, and generate creative options at scale.
1. AI-Powered Design Systems & Component Generation: AI tools automatically generate layouts, color palettes, spacing rules, component variants, and accessible themes, ensuring consistent, brand-aligned interfaces without manual oversight.
2. Contextual & Adaptive UI Personalization: AI tailors interfaces for individual users based on behavior, device, environment, and even mood signals, creating more intuitive, context-aware experiences that reduce cognitive load.
3. Generative UI Design & Visual Exploration: Designers can use AI prompts to instantly generate multiple UI variants, themes, and interaction states, providing creative baselines that speed up ideation and exploration.
4. Emotion-Driven UI Personalization: AI detects user emotions through permitted signals such as facial expressions or gestures and adjusts colors, animations, microinteractions, and pacing to create interfaces that feel human and responsive.
Read More: 10 Essential Web Design Features for a High-Impact Website in 2026
UI and UX Collaboration in 2026: How AI is Merging Both Roles Into a Unified Workflow
In 2026, the line between UI and UX designers is thinner than ever. Instead of asking “UI or UX?”, product leaders now operate as collaborative design systems, where UI, UX, and AI tools work together to deliver seamless digital experiences.
- UX as Strategy & Structure: UX designers lead the foundational work, mapping end-to-end user journeys, defining information architecture, validating usability, and identifying friction points with AI-driven research.
- UI as Visual Identity & Emotion: UI designers build the emotional layer, crafting visually consistent interfaces, shaping brand identity through colors, typography, and motion, refining microinteractions, and ensuring accessibility through adaptive UI elements.
- AI Integration: AI-powered design tools connect both roles by enabling faster prototyping and layout generation, predictive journey mapping, automated accessibility checks, personalization based on behavioral insights, and adaptive design systems that update components in real time.
Conclusion: Why UI + UX + AI is the New Product Advantage in 2026
In 2026, UI and UX are no longer independent creative tasks; they are core business growth levers. When combined with AI, they directly influence retention, conversions, product adoption, user satisfaction, and long-term scalability. Modern digital products must deliver:
-
Clarity: Intuitive layouts and predictable interactions.
-
Usability: Fast, frictionless task completion.
-
Emotion: Interfaces that match user intent and mood.
-
Speed: AI-powered design cycles and real-time optimization.
-
Accessibility: WCAG-compliant experiences for every user.
-
Personalization: Adaptive interfaces shaped by behavior and context.
Companies that integrate UI + UX + AI outperform traditional design teams in efficiency, innovation speed, and customer experience. This unified approach is now the foundation for creating apps and platforms that stand out in competitive markets.
GraffersID creates intelligent, data-driven digital experiences, not just interfaces.
Hire remote AI developers and UI/UX designers to build future-ready, high-performing digital products.





