In 2026, every business wants speed, scalability, and intelligence in its digital products. From AI-powered SaaS platforms to real-time marketplaces and data-intensive dashboards, the demand for performance-driven backend solutions has never been higher.
Node.js continues to dominate as the go-to backend runtime for modern web applications. Its unique blend of asynchronous event handling, lightweight architecture, and a massive open-source ecosystem makes it the preferred choice for enterprises that prioritize performance and efficiency.
Trusted by global leaders like Netflix, PayPal, and Uber, Node.js has proven its ability to handle millions of concurrent users, support microservice architectures, and power AI-integrated applications at scale.
But what truly sets Node.js apart in 2026, and what challenges should tech leaders be aware of before adopting it? Let’s break down the key advantages and disadvantages of Node.js that every CTO, developer, and decision-maker should know.
What is Node.js? A 2026 Overview

Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment built on Google Chrome’s V8 engine. It enables developers to execute JavaScript code outside the browser, making it possible to build end-to-end (full-stack) applications using a single programming language.
Unlike traditional server-side technologies, Node.js is event-driven, non-blocking, and operates on a single-threaded architecture, allowing it to handle multiple concurrent requests efficiently, making it ideal for real-time and high-performance applications.
Key 2026 Node.js Updates
Node.js continues to evolve rapidly, with new features enhancing performance, scalability, and AI integration:
-
Native support for ES Modules and top-level
awaitfor cleaner, modern syntax. -
Improved multithreading with the Worker Threads API, enabling better utilization of CPU resources.
-
Enhanced AI and data-processing capabilities through libraries like TensorFlow.js, LangChain.js, and OpenAI SDKs.
Quick Fact: Node.js isn’t a framework, it’s a runtime environment built in C++ with JavaScript bindings around the powerful V8 engine, enabling lightning-fast code execution and cross-platform efficiency.
Advantages of Node.js in 2026
Here are the advantages of using NodeJS for server-side programming:
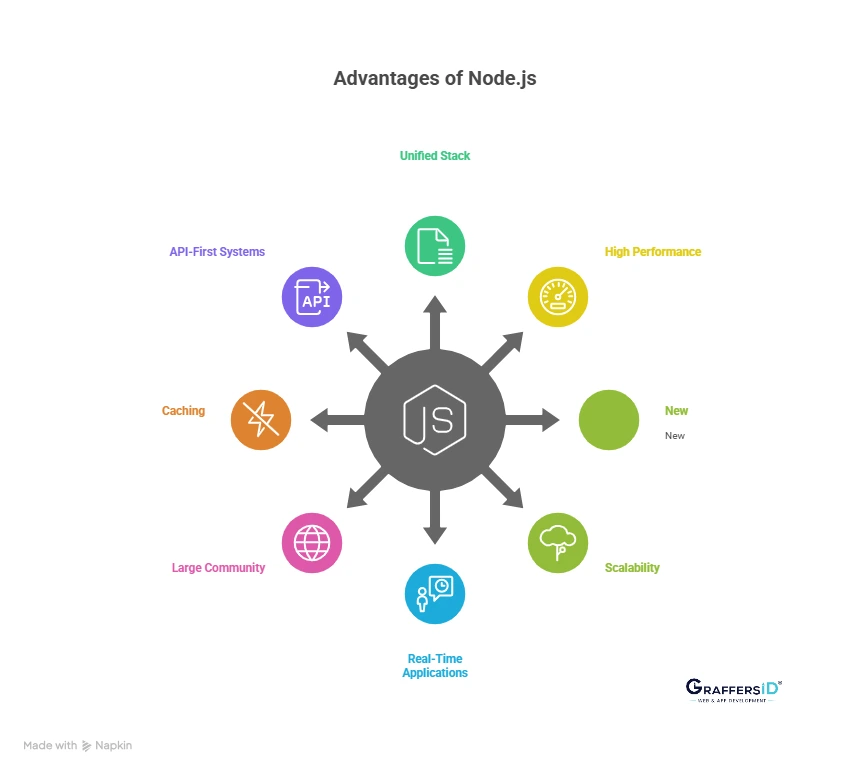
1. Unified JavaScript Stack for Frontend and Backend
With Node.js, teams can use one language (JavaScript/TypeScript) across the stack. This reduces development time, improves collaboration, and makes it easier to share code between client and server.
In 2026, this full-stack consistency is even more valuable for AI-enhanced applications, where developers integrate APIs, AI models, and real-time data pipelines seamlessly using JS-based tools like Next.js, Express, and LangChain.js.
2. High Performance with the V8 Engine
Node.js compiles JavaScript into machine code using Google’s V8 engine, ensuring rapid execution. The latest V8 versions have enhanced garbage collection and WebAssembly support, making Node.js extremely efficient for CPU-light but I/O-heavy workloads such as APIs, chat apps, and streaming platforms.
Example: Netflix reduced startup time by 70% after migrating to Node.js, enabling faster user experiences and lower latency.
3. Scalability Across Modern Architectures
Node.js supports both vertical and horizontal scaling:
- Vertical scaling: Add more power (CPU, RAM) to a single instance.
- Horizontal scaling: Add multiple Node instances using clustering or Docker orchestration.
In 2026, with cloud-native deployments on AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Run, and Kubernetes, Node.js easily scales microservices and event-driven architectures that serve millions of requests per second.
Read More: What is Generative AI and How It’s Transforming Software Development in 2026?
4. Excellent Support for Real-Time and Event-Driven Applications
The non-blocking, asynchronous I/O model enables real-time communication, ideal for:
- Live chat and collaborative tools (e.g., Slack clones)
- Multiplayer games
- IoT dashboards and monitoring systems
- Stock market or logistics tracking dashboards
Modern frameworks like Socket.IO v5 make real-time integrations even smoother, while WebSocket and EventSource APIs support live synchronization with minimal latency.
5. Large Developer Community and NPM Ecosystem
With over 2.5 million packages on npm in 2026, Node.js continues to offer unmatched ecosystem support. Developers can quickly integrate libraries for AI processing, authentication, cloud services, and data visualization.
The active global community ensures rapid updates, abundant learning resources, and long-term stability for enterprise adoption.
6. Built-in Caching and Faster Load Handling
Node.js allows caching of single modules, reducing recompilation times and improving response speed. This is particularly beneficial in microservices or serverless environments, where every millisecond counts in delivering real-time data or model outputs.
7. Ideal for API-First and AI-Integrated Systems
In 2026, enterprises are building API-first architectures and integrating AI inference layers using Node.js. It works smoothly with:
- OpenAI, Anthropic, and Hugging Face APIs
- Edge deployments with Cloudflare Workers
- Lightweight AI tools like AnythingLLM and LangChain.js
This makes Node.js an excellent fit for AI agents, recommendation engines, and automation pipelines that need both real-time response and scalability.
Disadvantages of Node.js in 2026
Despite its advantages, Node.js isn’t the best fit for every project. Let’s explore the major limitations to consider.
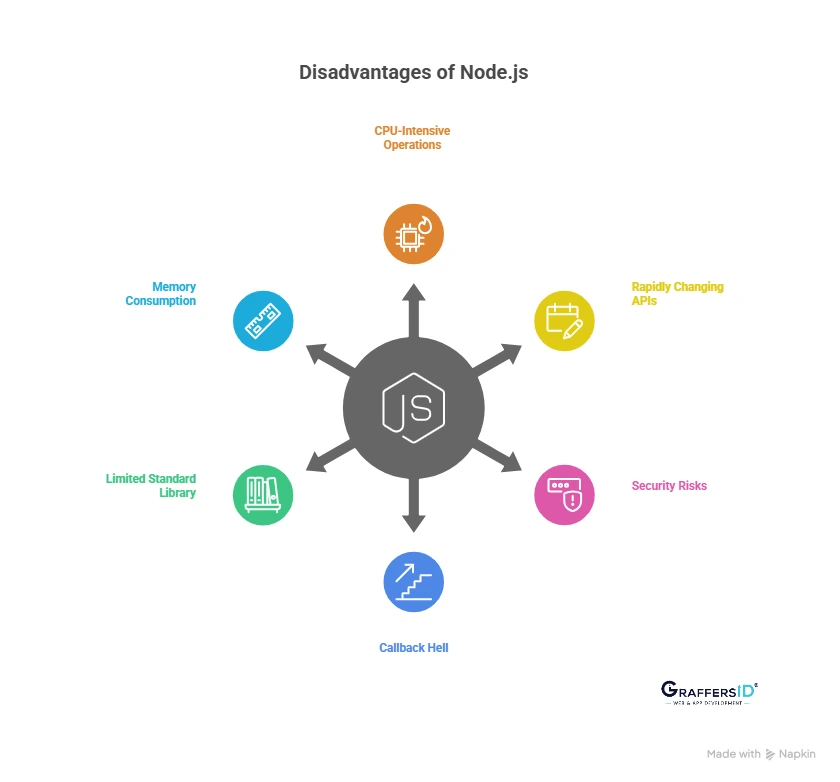
1. CPU-Intensive Operations Remain a Weak Spot
While Node.js excels at I/O-bound tasks, CPU-heavy operations (like video processing or AI model training) can block the event loop. Although the Worker Threads API helps offload tasks, Node.js still lags behind multi-threaded environments like Java or Go for computationally intensive workloads.
2. Rapidly Changing APIs
Node.js frequently updates its APIs, introducing breaking changes between versions. In enterprise setups with large legacy systems, maintaining compatibility can demand additional effort and testing cycles.
3. Security Risks from Third-Party Dependencies
The npm ecosystem, though massive, can introduce vulnerabilities from unmaintained or malicious packages. Developers must regularly audit dependencies using tools like:
npm auditSnyk- GitHub Dependabot
Read More: How to Secure Offshore Node.js development? Top Node.js Security Best Practices in 2026
4. Callback Hell and Asynchronous Complexity
Although modern syntax like Promises, async/await, and RxJS has simplified async code, older projects may still struggle with deeply nested callbacks. This can make debugging and maintaining legacy codebases more complex.
5. Limited Standard Library
Node.js relies heavily on external packages for advanced functionalities like image processing or AI integration. Compared to languages like Python, which include extensive native libraries, Node.js requires more dependency management to achieve similar capabilities.
6. Memory Consumption and Multi-Core Scaling Challenges
Each Node.js instance consumes more memory than lighter runtimes like Bun.js or Deno. Moreover, while Node supports clustering, true multi-core utilization still requires additional orchestration. This can complicate scaling in high-performance computing (HPC) scenarios.
When Should You Use Node.js?
Node.js remains a top choice for building fast, scalable, and modern applications, especially those requiring real-time performance or handling heavy data loads. Here’s when Node.js truly excels:
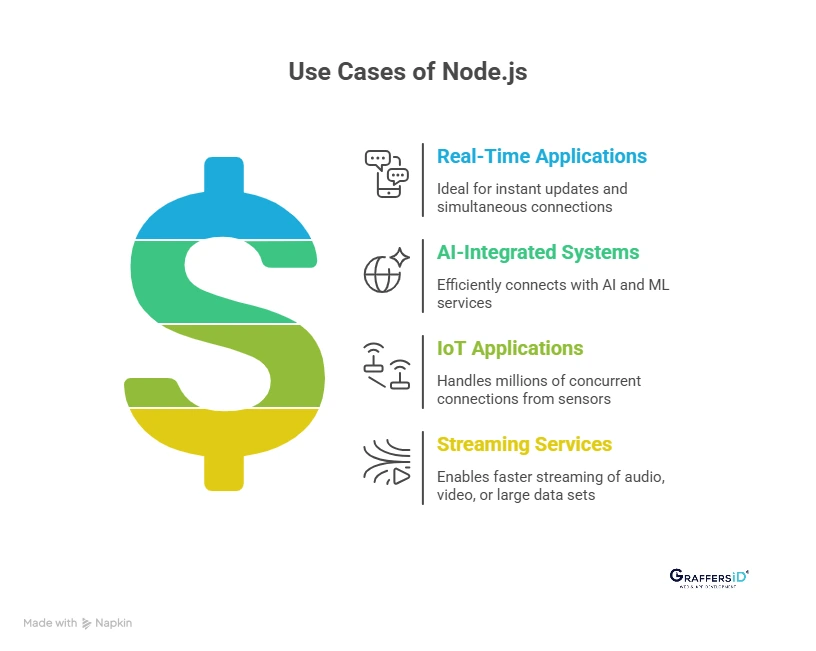
1. Real-Time Applications
Node.js’s event-driven, non-blocking I/O model allows it to manage thousands of simultaneous connections with minimal latency, making it perfect for apps that require instant updates, like messaging platforms, live dashboards, and real-time location tracking.
2. AI-integrated systems
With smooth API integration capabilities, Node.js efficiently connects with AI and ML services for intelligent automation, recommendations, and natural language features. Its lightweight nature ensures faster request handling and data processing for AI-driven workflows.
3. IoT Applications
Node.js handles millions of lightweight, concurrent connections from sensors and devices, making it a powerful choice for IoT ecosystems. Its event-based architecture ensures smooth real-time data transmission between devices and servers.
4. Streaming services
Node.js enables data to be processed in chunks instead of waiting for the complete file to load through its stream and buffer modules. This results in faster streaming of audio, video, or large data sets, ideal for platforms like OTT apps or live streaming solutions.
Future Trends of Node.js: 2026 & Beyond
In 2026, Node.js is evolving rapidly to stay at the forefront of modern software development.
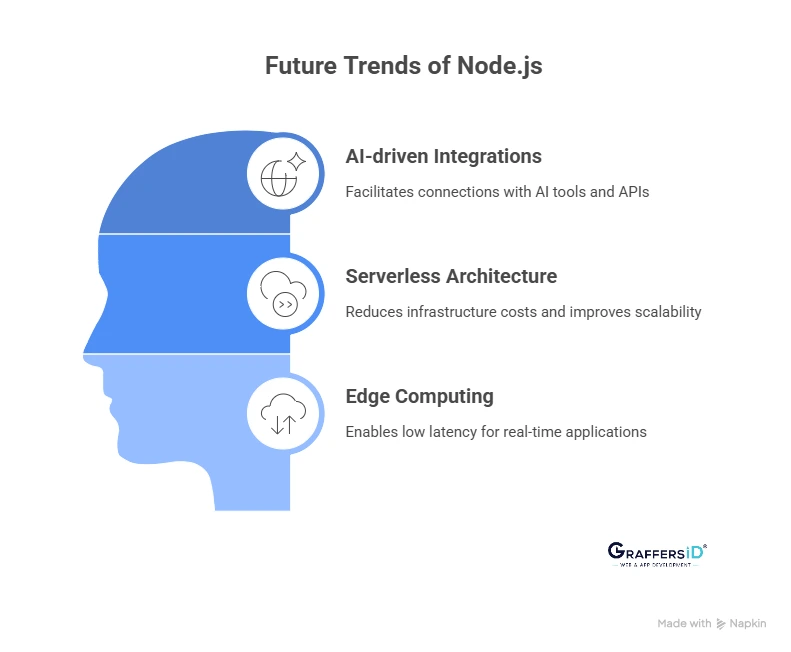
-
AI-driven integrations: Node.js makes it easy to connect with large language models (LLMs), AI APIs, and automation tools through ready-to-use SDKs and lightweight frameworks.
-
Serverless architecture: With smooth integration into platforms like AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Vercel, Node.js helps reduce infrastructure costs while improving scalability and deployment speed.
-
Edge computing: Modern Node.js runtimes support execution at the network edge, enabling ultra-low latency for real-time applications and global users.
With these advancements, Node.js continues to be a future-proof technology for building fast, intelligent, and scalable digital solutions across industries.
Conclusion
Node.js continues to be one of the most reliable, future-ready backend technologies for modern applications. Its non-blocking architecture, lightning-fast performance, and full-stack flexibility make it a perfect fit for real-time systems, AI-driven platforms, and API-heavy applications.
In 2026, as businesses shift toward automation, microservices, and AI-powered ecosystems, Node.js stands out for its speed, scalability, and cost efficiency, making it a top choice for startups and enterprises alike.
At GraffersID, we help global enterprises hire top Node.js developers from India, experts in creating real-time, high-performance applications powered by cutting-edge AI integrations.
Build faster, scale smarter, and innovate confidently with GraffersID. Hire Node.js Developers Today!