Are you a tech enthusiast exploring the development world or a business professional aiming to build a robust digital product? Either way, your journey starts with one crucial decision—choosing the right technology stack.
In software and online development, the term “stack” refers to a set of technologies used to design and run an application. With countless options available, two of the most prominent contenders in full-stack development are the Java full-stack and the MERN Stack.
However, how can you choose the best option for your project? In this full guide, we will help you make an informed selection by looking thoroughly into both stacks.
Front-End vs Back-End vs Full Stack
- Front-End: Focuses on UI/UX, using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Angular.
- Back-End: Manages server, database, and application logic using technologies like Java, Node.js, Python, etc.
- Full Stack: Combines front-end and back-end technologies to enable end-to-end development.
Popular Web Development Stacks
The top stacks for front-end, back-end, and full-stack web development are as follows:

1. Front-End Development Stacks
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript (Core front-end trio)
- React Stack (React, Redux, Webpack)
- Vue Stack (Vue.js, Vuex, Vite/Webpack)
- Angular Stack (Angular, RxJS, TypeScript)
2. Back-End Development Stacks
- Node.js Stack (Node.js, Express, MongoDB/MySQL)
- Java Stack (Spring Boot, Hibernate, MySQL/PostgreSQL)
- PHP Stack (Laravel, MySQL, Apache/Nginx)
3. Full Stack Development Stacks
- MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js)
- MEAN (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js)
- LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP)
- LEMP (Linux, Nginx, MySQL, PHP/Python)
- Java Full Stack (Java, Spring Boot, Hibernate, with Angular/React)
Where Do MERN and Java Full Stack Fit?
Two of the most widely used stacks nowadays are MERN and Java full-stack. MERN is often chosen for speed and flexibility in front-end development, while Java full-stack is favored for enterprise-grade applications that require strong backend capabilities and security.
What is the MERN Stack?
The MERN stack is a popular web development framework made up of four robust open-source technologies: MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js. It is a complete JavaScript solution that helps developers create scalable, reliable, and maintainable web apps quickly.
Components of MERN Stack
Let us examine each component of the MERN stack and its function:
1. MongoDB
MongoDB is a NoSQL, document-oriented database that stores data in JSON-like format using key-value pairs. It allows flexible schema design, making it easy to build and scale applications quickly. Developers can interact with the database through the Mongo Shell, using JavaScript to query, update, or remove data.
2. Express.js
Express is a simple and adaptable framework for Node.js web applications. It simplifies backend development by eliminating the need to write repetitive code and manually handle server configurations. With built-in middleware and a powerful routing system, Express makes it easy to build APIs and web services efficiently.
3. React.js
React is a JavaScript package that creates flexible and adaptable user interfaces. It allows developers to design reusable user interface (UI) components and is particularly well-suited for single-page applications (SPAs). React’s component-based architecture and virtual DOM ensure fast development and excellent performance.
4. Node.js
Node.js is a cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment that runs code outside of a web browser. It is ideal for developing scalable and fast network apps as it is built on Chrome’s V8 engine. Using many different modules in the npm (Node Package Manager) can speed up development.
Read More: MEAN Stack vs MERN Stack: Which is Better Technology Stack
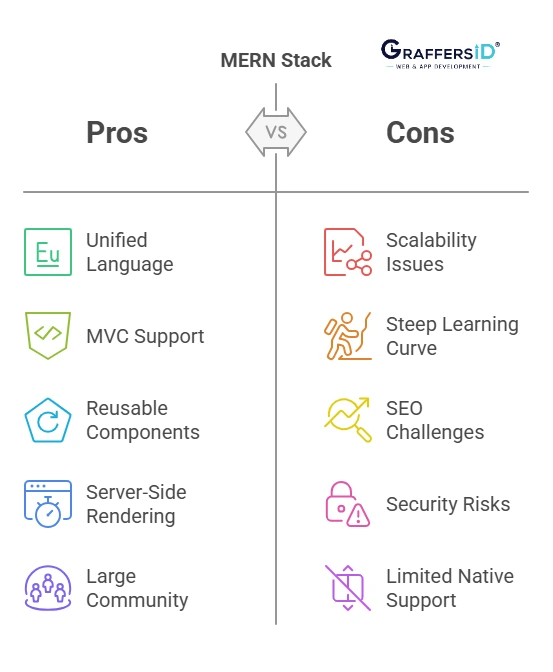
Advantages of MERN Stack Development
The MERN stack is widely known for its flexibility, scalability, and developer-friendly ecosystem. The following are the main advantages of using MERN for your next project:
-
Unified Language: Entire development (front-end and back-end) is done using JavaScript and JSON, reducing complexity and improving productivity.
-
MVC Architecture Support: Makes sure all concerns are clearly separated, which simplifies the development cycle.
-
Reusable Components: React’s component-based architecture enables modular code, improved organization, and reuse.
-
Server-Side Rendering: React allows you to render pages on the server, which improves performance and SEO.
-
Large Ecosystem & Community: Supported by strong communities and extensive documentation.
-
Built-in Testing Tools: MERN offers integrated testing frameworks and tools for streamlined debugging.
-
Open-Source Technologies: All components are free and continuously improved by the developer community.
-
Full Development Cycle Coverage: From UI development to database management, everything is covered under one stack.
-
Cross-Platform Development: Allows the creation of web, mobile, and desktop applications using JavaScript.
Do you want to scale your project more quickly? Hire remote MERN developers!
Limitations of MERN Stack
While the MERN stack offers several advantages, it also comes with a few limitations:
-
Scalability Challenges for Large Enterprises: While scalable, it may not be the best fit for highly complex, enterprise-grade back-end systems. Monolithic architectures like Java/Spring may offer better long-term stability and performance.
-
Learning Curve: Learning the MERN stack can be challenging for newcomers, especially if they are new to JavaScript or web development. The stack involves multiple technologies that need to be learned and integrated.
-
SEO Challenges: Even though JavaScript-based information can now be better indexed by search engines, MERN apps may still encounter certain difficulties with SEO.
-
Security Concerns: JavaScript frameworks can sometimes be at risk of security issues because of the large number of third-party packages and dependencies they use. Keeping up of security fixes is important.
-
Limited Native Support: For specific features like file handling, background tasks, or advanced server-side functionalities, additional libraries or custom development may be needed.
What is the Java Full Stack?
Java full-stack development refers to developing both the frontend (client-side) and backend (server-side) parts of a web application using Java and its supporting technologies.
Unlike the MERN Stack, which is JavaScript-based across all layers, Java full-stack utilizes a combination of Java-based back-end tools and independent front-end technologies to build scalable, secure, and enterprise-grade applications.
Components of Java Full Stack
To understand how Java fits into full-stack development, let’s break down the three major layers it touches:
Front-End Development (Client Side)
Although Java is primarily a backend language, Java full-stack development involves frontend technologies for building intuitive user interfaces. Some commonly used frontend tools include:
-
HTML, CSS, JavaScript: The building blocks of modern UI
-
Angular or React: Popular JavaScript frameworks for creating dynamic front-end interfaces
These are integrated with the backend to provide a seamless user experience.
Back-End Development (Server Side)
This is where Java shines. Usually, the server-side part of the program is created with:
-
Core Java: For the application’s base logic
-
Spring Framework / Spring Boot: To build scalable, secure, and easily testable REST APIs
-
Hibernate: For Object-Relational Mapping (ORM), handling interactions with relational databases
-
JPA (Java Persistence API): For abstracted database persistence tasks
Database Layer
Java full-stack usually pairs with relational databases, though it is flexible enough to support NoSQL as well. Common databases used:
-
MySQL
-
PostgreSQL
-
Oracle DB
Full Stack Integration Tools
For DevOps, CI/CD, and full-stack integration, Java developers often use:
-
Jenkins: For continuous integration and deployment pipelines
-
Docker & Kubernetes: For containerization and orchestration
-
RESTful APIs: For communication between the frontend and the backend
This integrated toolchain supports robust application development with scalability and maintainability.
Advantages of Java Full Stack Development
Java full-stack remains a popular choice for large-scale enterprise projects. Here’s why:
-
Strong Ecosystem & Libraries: Java offers a vast ecosystem with mature libraries, frameworks, and community support.
-
Platform Independence: Java’s “write once, run anywhere” concept makes it a dependable solution for various platforms.
-
High Performance: Java applications are known for their speed, multi-threading capabilities, and memory management.
-
Enterprise-Grade Security: Java has built-in security features and frameworks like Spring Security to handle authentication and authorization.
-
Scalable Architecture: Especially with Spring Boot and microservices architecture, scaling a Java-based application becomes easier.
-
Flexible Frontend Options: Java full-stack allows developers to pair backend logic with any frontend of their choice (Angular, React).
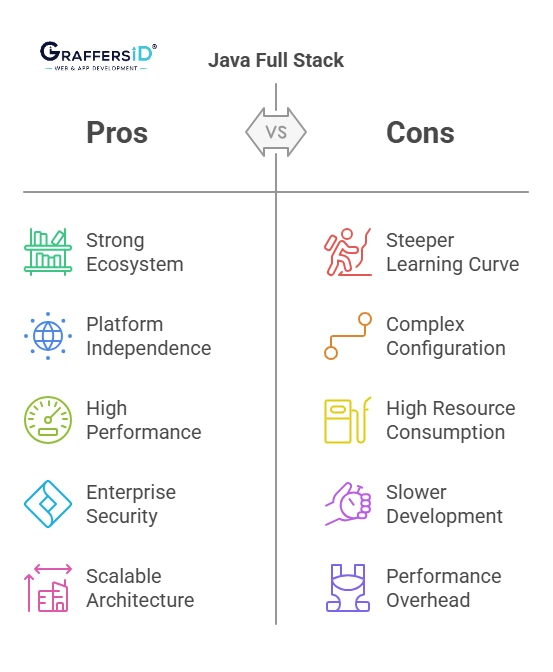
Limitations of Java Full Stack
Despite its advantages, Java full-stack comes with a few drawbacks:
-
Steeper Learning Curve: Java is more verbose than other modern languages like JavaScript or Python, which can slow down new developers.
-
Complex Configuration: Compared to frameworks like MERN, setting up Java full-stack can be more time-consuming and requires handling multiple XML/annotation-based configurations.
-
Higher Resource Consumption: Java applications generally require more memory and CPU, making them heavier to run than lighter stacks like Node.js.
-
Slower Development Speed: Especially for small or medium-sized projects, Java full-stack may feel over-engineered.
- Performance Overhead: Java programs may have higher overhead than those written in lighter languages, which in some cases may affect performance.
- Scalability: Java’s scalability is a strength, but its architecture and configuration can sometimes be complicated, requiring a solid understanding of distributed systems and related topics.
- Deployment Complexity: Java programs usually require the installation of a Java Runtime Environment (JRE) on the host machine, which can complicate deployment.
MERN Stack vs Java Full Stack: Detailed Comparison
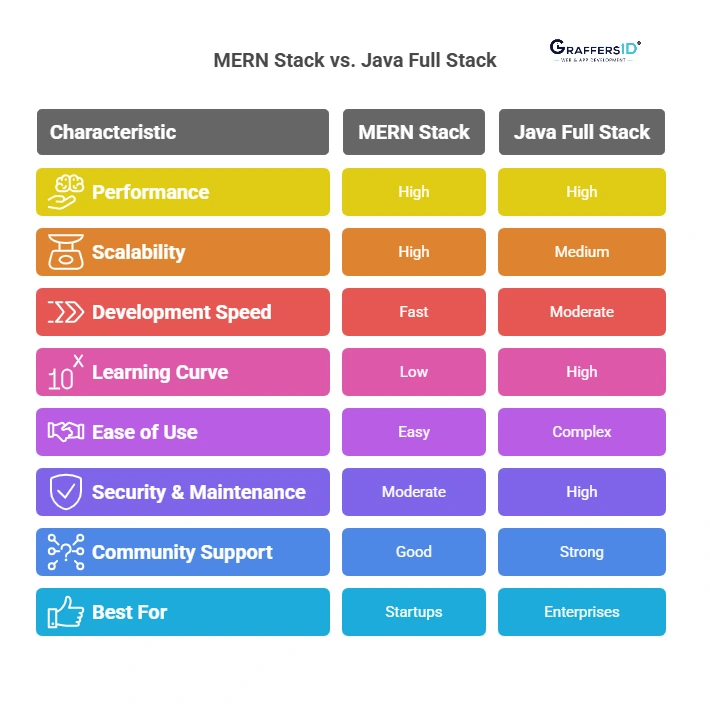
1. Performance
MERN Stack: Uses Node.js, which is event-driven and asynchronous. This is ideal for apps needing to handle many requests at the same time (e.g., chat apps, live collaboration tools). Since JavaScript runs on both client and server, the data flow is smooth and fast for I/O-heavy tasks.
Java Full Stack: Java’s strong multi-threading capabilities and robust JVM (Java Virtual Machine) make it better for CPU-intensive applications like complex enterprise systems, big data processing, or banking platforms.
2. Scalability
MERN Stack: Designed for horizontal scaling, meaning you can add more servers to handle growth. Good for cloud-native apps, microservices, and modern web apps.
Best for: SaaS startups, SPAs, real-time dashboards.
Java Full Stack: More suited to vertical scaling (upgrading server capacity), which fits large enterprise ecosystems with stable architecture and lots of interdependencies.
Best for: ERP systems, banking platforms, or government databases.
3. Development Speed
MERN: Uses JavaScript across the stack, which simplifies development and shortens the learning curve. React allows quick front-end development with reusable components. Faster prototyping and MVP launches.
Java Full Stack: Involves multiple tools (Spring Boot, Hibernate, JSP/Thymeleaf, etc.) and configurations. Takes longer, but offers solid structure and maintainability. Ideal for stable, large, and secure platforms.
4. Learning Curve & Ease of Use
MERN Stack: Simpler for new developers who know JavaScript or front-end. Numerous online resources are available, including YouTube tutorials and open-source support.
Java Full Stack: Steep learning curve due to the object-oriented nature of Java, configuration-heavy frameworks like Spring, and XML/annotation usage. Better suited for developers with a Computer Science background.
5. Security & Maintenance
MERN: Needs manual implementation of security features (e.g., JWT, input validation, CORS). Open-source tools may have issues if not updated. Requires extra attention to secure coding practices.
Java Full Stack: Known for strong built-in security, backed by Java EE and Spring Security. Preferred for handling sensitive data, compliance needs, and user authentication.
6. Community Support & Ecosystem
MERN: Supported by Facebook (React) and Node.js Foundation. A robust, rapidly evolving ecosystem of modules, plugins, and community assistance.
Java Full Stack: Java is mature with decades of enterprise trust, a huge community, and vast documentation. Strong support from Oracle, Spring community, and enterprise architects.
Factors to Consider While Choosing Between MERN vs. Java Full Stack
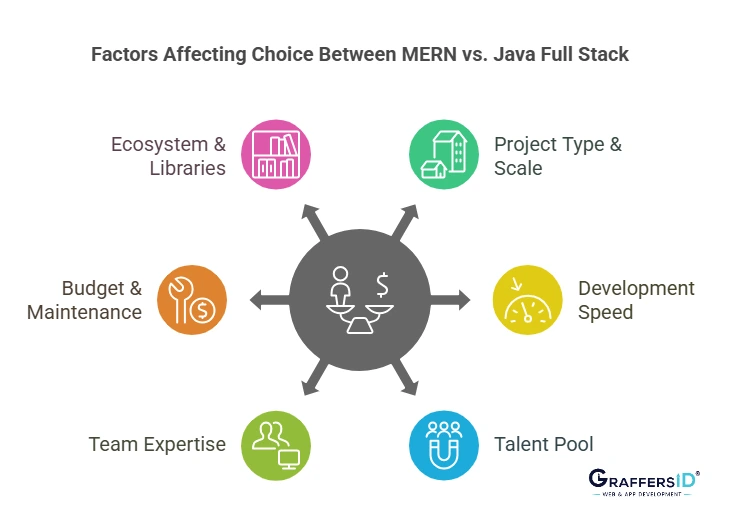
When picking between the MERN stack and the Java full-stack, various factors are important to consider. Each project has its own set of requirements, and understanding these affecting factors allows you to make an informed choice.
1. Type and Scale of the Project
- Use MERN for flexible, quick-to-deploy applications.
- Use Java full-stack for mission-critical, enterprise-level apps.
2. Development Speed & Time-to-Market
- MERN provides faster prototyping and deployment.
- Java is better when thorough testing and stability are priorities.
3. Available Talent Pool
- JavaScript/MERN developers are abundant and cost-effective.
- Java developers tend to have more experience and are common in enterprise settings.
4. Team Expertise & Stack Familiarity
- Choose the stack your team is already experienced in.
- Consider training time and onboarding costs.
5. Project Budget and Long-Term Maintenance
- MERN is cost-effective for short-term, quick-to-market solutions.
- Java full-stack offers long-term reliability and maintenance ease for critical systems.
6. Ecosystem and Third-Party Libraries
- The MERN stack uses JavaScript’s large ecosystem, which includes many third-party libraries and tools.
- Java full-stack contains a wide range of well-established libraries and frameworks that cater to various needs.
Which Stack is Better for Your Web Application?

- Go for MERN if you’re looking for speed, flexibility, and a strong front-end experience.
- Choose Java full-stack if you’re building something complex, secure, and enterprise-ready.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tech stack for your web development project is a critical decision that impacts the performance, scalability, and long-term success of your application. Both the MERN stack and Java full-stack have their distinct advantages, catering to different project needs.
Ultimately, your decision should align with your business goals, the complexity of your project, and the expertise of your development team. Understanding the strengths of each stack will help you make an informed choice.
At GraffersID, we specialize in providing top-tier developers for both MERN and Java full-stack technologies. Contact us today to hire expert developers who can bring your project to life.
FAQs
Q1. Which is better, Java or MERN?
For large-scale enterprise applications with complex business logic and stringent performance requirements, Java full-stack may be the preferred choice. Conversely, for startups, small to medium-sized projects, or applications demanding rapid development and real-time features, MERN Stack offers a compelling solution.
Q2. Which is better, Full Stack Developer or Java developer?
Full Stack Developers handle both front-end and back-end, making them ideal for startups. Java Developers focus on strong, scalable backend systems, best for enterprise apps. The better choice depends on your project needs.
Q3. How much does it cost to hire a full-stack developer?
Hiring a full-stack developer remotely from India typically costs approximately $1,800–$4,200/month, depending on experience and tech stack. In the US, the cost can range between $8,000–$12,000/month, with senior developers charging even more.
Q4. Which full-stack is in demand?
MERN and Java full-stack are most in demand—MERN for startups and speed, Java Stack for security and enterprise-grade apps.